Heating » Types and systems
Published May 24, 2015 at 2:08 am
Among the existing variety of heat supply schemes, alternative options are of particular interest, which can be an excellent addition to the traditional system or completely replace it. And one of them can be called ceiling heating.
Today the most popular and widely used methods are:
- air heating, in which the heat generated by various sources (boilers, furnaces, air conditioners, etc.) is distributed throughout the premises through a system of air ducts;
Figure 1 – Example of air heating of a small room
- heating using infrared emitters of various types, powered by electricity (heaters, lamps, film structures) or gas (burners).
Figure 2 – Example of heating an office space using a ceiling-mounted IR heater
But there is another option for ceiling heating - a panel water radiant heating system - which has already gained popularity in Western countries and is still developing the Russian market, which will be discussed below.
Design features of water radiant panels
First of all, it must be said that the ceiling system in question combines two types of heating: traditional water and infrared. Therefore, the design of the panels, the main elements of the circuit, is quite complex, massive and dimensional.
The main elements of such products are:
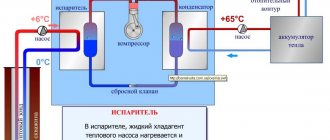
- pipeline system - as a rule, metal pipes with a diameter of 18-28 mm are used; coolant (water) flows through them, supplied from a conventional heating network or heated by autonomous heat sources (electric, solid fuel or gas boilers, heat pump);
- case-based infrared emitter made of profiled galvanized metal 0.5 mm thick (heating elements are mounted in technological recesses); to enhance the emissivity, the surface facing the room is coated with powder paint;
- protective screen (the upper part of the panel located near the ceiling), which is a structure made of an insulating foil layer of mineral wool about 40 mm thick and a profiled metal sheet;
- mounting accessories – suspension elements (chains, cables), fasteners (carabiners, rods).
Figure 3 – General view of the water beam panel
As a rule, panels are manufactured in modular dimensions (usually a multiple of 1000 mm), but depending on the project, non-standard sizes are also possible. In this case, if the length of the products is sufficiently long, steel stiffeners are mounted on the inside of the emitter to strengthen the structure.
It should be borne in mind that the dimensions indicated by manufacturers correspond to the length of the pipes, taking into account the necessary technological projections (60 mm) for connection to the manifold, supply pipeline or other panels. For example, in a product with a length of 3000 mm, the same size of the emitter will be 2880 mm.
It should be noted that the panels are produced with maximum assembly, i.e. completely ready for connection to the manifold using press fittings.
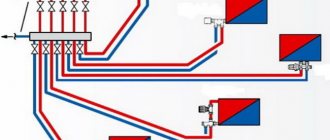
If it is necessary to create a system of several products, the latter are placed in parallel at a distance of 35 mm. They can be secured with common fasteners and connected via a common manifold.
Figure 4 – Scheme for creating a ceiling system from several panels
Figure 5 – Possible schemes for tying water radial panels
Today, the most famous brands of hydronic radiant panels for ceiling heating are:
- "Teplopanel" (Russia);
- "Zehnder" (Germany);
- "MARK" (Netherlands);
- Fraccaro Waterstrip (Italy);
- "Duck Strip" (Italy).
Radiant home heating: types and operational features
Features and applications of radiant heating systems
Heating systems are improving. Designers create much better, economical, attractive and good devices. Radiant heating is one of the most modern developments. Radiant heating systems have appeared on the market not so long ago, but have already proven themselves to be excellent. The working principle is based on heating objects with radiant energy, and the objects, for their part, transfer heat to the air in the room. The source of infrared energy can be powered from an electrical network or run on gas; TENS are placed in panels or multilayer film.
Types of radiant heating systems
There are film radiant electric heaters (PLEN) and panel ones. The former operate only on electricity, while the latter, depending on the type, will usually operate on both electricity and gas. In private apartments and houses, in most cases, electrical systems are installed, because... they are no longer dangerous. Gas radiant heating (GLO for short) is perfect as a heating system for industrial premises, warehouses, hangars, and large workshops.
PLEN consists of two layers of polymer material, between which there are resistors, which, when heated, transfer heat energy to aluminum foil. Radiation from the foil coating heats objects. In most cases, the width of the film heater does not exceed 30 cm, thickness – 1 mm. Heating temperature – up to 450 degrees. Certain parameters depend on the technical specifications, according to which the desired power of heating systems is formed.
Radiant heating can be water or electric. The heat sources in this case are surfaces in the middle of which there are pipes with hot water, or iron panels with infrared heaters. Traditional underfloor heating is very common and is known as underfloor heating systems. Installation of this type of heating system is very complicated, so most consumers are looking for an alternative and selecting electric thermal panels.
Working diagram of a panel heating system
Film radiant heating systems
Film heaters are quite compact, convenient and functional. The systems are equipped with external water thermostats or GSM controllers. It takes no more than an hour to warm up the room, but local thermal comfort zones are created almost immediately after turning on the appliances, because they warm objects and people first. In temperature maintenance mode, the heaters turn on every hour for approximately ten minutes. This ensures low electrical energy consumption.
Electric heating systems themselves are expensive, but with rational operation, costs can be significantly reduced. If the room is non-residential and does not need to systematically maintain a high temperature, then operating the system in a low temperature mode would be an excellent solution.
Film heater design
Where is PLEN installed?
The area of use of film systems is quite extensive. Heaters are installed in rooms for a variety of purposes:
- apartments, houses, houses outside the city;
- heated balconies, loggias;
- buildings for production;
- warehouse type premises;
- offices;
- shops, trade pavilions;
- restaurants, cafes;
- hotels;
- medical, treatment and preventive institutions.
For residential premises and those in which people are regularly present, film heat supply is used not only as the main heating system, but also as an additional heating system. Moreover, PLEN is not used for its intended purpose. For example, in rooms for painting car bodies, heaters are installed to speed up the drying of painted parts.
How the PLEN system does not stop working
Positive qualities of film systems and limitations in their use
Heaters can be installed in new and reconstructed buildings. Their advantages:
- compactness, light weight;
- relative ease of installation;
- stylistic neutrality;
- durability;
- eco-, fire safety.
Despite all these advantages, PLEN systems also have great limitations in application. Installation in an apartment in the city is often impractical, because... the owner unwittingly heats not so much his own living space as the adjacent apartments. The device heats all surfaces - floor, ceiling, walls, and part of the energy is used to supply heat to neighboring rooms. The problem can be partly solved with the help of insulation. Another important disadvantage is the high price of electric heating. Traditional water convectors are much cheaper.
Electric panel radiant heating
Panel radiant heating systems are installed in residential premises, offices, and points of sale. Heating devices do not dry out the air, are comfortable and compact.
Types of heating electric panels
The following types of panels are distinguished:
These are “hybrid” devices that work as radiators and convector heaters at the same time. The outer surface is a glass-ceramic panel, and the outer surface is a heat-accumulating component that provides natural convection. The heater consumes a relatively small amount of electrical energy for operation, while the heat transfer rate is high.
These are metal structures 2 cm thick, in the middle of which there is a nichrome wire. The device is equipped with a reflective insulating layer. Wall panels are classified as energy-efficient heating systems. They are not dangerous and can be installed in premises for a variety of purposes as the main, backup or additional heat supply. They are not recommended to be installed in buildings with a ceiling height of more than three meters.
- Wall, floor, ceiling panels "EINT"
Energy-saving radiators are reliable and not dangerous. Long-wave infrared radiation has a beneficial effect on human health, making heating devices of this type suitable for children's rooms. There are “vandal-proof” models that are installed in crowded places. Heating is carried out only by radiation; there are no convective components, as a result of which dust spreads less.
Heating panels at the point of sale
Do-it-yourself installation of electrical panels
Ease of installation and convenient operation are important advantages of the heating system. Installing wall panels is so simple that anyone can handle this work, even if they have no experience in repair and construction work. In addition to the device, the kit includes fastening elements and instructions for the installation process. As a rule, there is no need to purchase anything additional.
- Choose a place to hang the structure. Very often, heating devices are located near the coolest areas (under windows, next to doors) and those areas that require a special thermal regime (for example, near a crib for children, a work table, etc.).
- Drill holes in the wall for fasteners.
- Fasten the fasteners and hang the heating device on them.
- Connect the device to the network.
- Make sure it functions and is securely fastened.
Film and panel heaters are mainly used for residential premises. Gas radiant heating is better suited for installation in large industrial premises with high ceilings and excellent ventilation, because Gaseous, liquid and solid substances are usually released into the air. In most cases, gas systems are installed in showrooms of car dealerships, warehouses, and workshops. Each of the systems has its advantages. When selecting, you must be guided by the needs of the owner of a particular premises.
Panel radiant heating Roth Original-Tacker® System
Water panel radiant heating system "TEPLOPANEL" from
Features of the functioning of water radiant heating panels
The main principle of operation of such a heating system is the transfer of heat to surrounding structures and objects (not air) by radiation.
As noted above, heating of the panels, namely the radiating element, is carried out using the energy of a hot coolant, the temperature of which can vary in the range of + 40°C...+ 120°C, supplied from the main heat source to the pipes of the products. Once the underside of the ceiling panel heats up, it begins to emit infrared waves. In this case, the heat goes completely downwards due to the effective thermal insulation of the upper part of the panel structure.
Figure 6 – Functional diagram of ceiling heating panels
Subsequently, the process of heating the room is no different from the principle of using conventional IR devices: the heated objects located below, walls and floors, begin to emit heat again and heat the air through convection.
It should be noted that ceiling heating using water radiant panels allows you to achieve a comfortable and even microclimate in the room, saving up to 40% of energy at similar temperature conditions of traditional heating using radiators.
Figure 7 - Comparative parameters of the temperature regime of various heating schemes a) traditional radiator heating; b) heating with ceiling panels
It must be said that the use of such products allows not only to heat the house during the cold season, but also to cool it in the summer. Of course, the efficiency of this process is not so significant, but, nevertheless, the costs of maintenance and operation of air conditioning system equipment are noticeably reduced.