We select the volume of the tank.
Understanding the main functions it performs will help you choose an expansion tank.
The main task of the expansion tank (as it is also called from the English “expanse” - to expand) is to absorb the excess volume of coolant that is formed as a result of thermal expansion.
How much does the volume of water, as the main coolant, increase when heated?
When water is heated from 10 o C to 80 o C, its volume increases by approximately 4%. We must also not forget that a closed expansion tank consists of two parts, one of which receives an excess of expanding coolant, and the other is pumped with gas or air under pressure.
Taking into account the design of the expansion tank, it is recommended to select its volume as 10 - 12% of the volume of all water in the heating system of the house:
- in pipes;
- in heating devices;
- in the boiler heat exchanger;
- a small initial volume of water, which with an initial temperature under pressure enters the tank itself (static pressure in the system is usually higher than the air pressure in the expansion chamber).
Purpose, design and operational features
An expansion valve is a device designed to compensate for the expansion of the coolant when heated. In other words: if this reservoir is not provided, the liquid that has expanded under the influence of temperature will have nowhere to go and it will rupture the pipes, radiators, and heat exchanger of the boiler unit, creating a danger of explosion.
In addition, no matter how sealed the CO is, the coolant still evaporates from it. Its quantity in the circuit decreases, which significantly reduces the efficiency of heating the home. A membrane expansion tank for heating allows you to replenish the volume of liquid while maintaining the necessary tightness in the system.
The design of this device consists of a steel, corrosion-resistant tank, in which there is an elastic diaphragm in the middle. This tank contains a spool valve for pumping the required pressure, a safety valve and a pipe connecting the device to the CO.
We configure the tank to work in the heating system.
To set up the expansion machine, we will use the recommendations of the well-known German manufacturer of similar equipment, Reflex.
Detailed instructions can be downloaded by right-clicking on the link: “Installation and maintenance instructions for Reflex membrane expansion tanks.”
Here we will give the basic principles for setting up the tank.
When setting up a tank, we are dealing with different types of pressures that need to be coordinated with each other:
Pst – static pressure of the system (equal to the height of the water column, determined, in turn, by the height of the heating system from the tank connection point to the top of the last uppermost element);
P – air pressure in the air chamber of the tank;
Pinit – initial recharge pressure;
Pexp – pressure created in the system as a result of water expanding in volume;
Pkon is the pressure that is created as a result of additional replenishment when the heating system is brought to the upper operating temperature mode. (When expansion pressure is involved in the system);
Pkl – safety valve pressure (for private houses 3 bar);
Pmax is the maximum operating pressure for which the most sensitive element of the system (usually the boiler heat exchanger) is designed.
Design and functions of the expansion membrane tank of the heating system
The basic membrane heating tank has a rather complex design. If the owner can make a regular open-type expansion tank himself using a welding machine, an angle grinder and sheet metal, then an expansion membrane tank for heating is often purchased ready-made in a store. This can be an expansion tank for heating Reflex, characterized by decent consumer characteristics, or an expansion tank from another trusted manufacturer, the operating parameters of which satisfy the requirements of the circuit. You can read about choosing a heating circuit and installing heating in a private house here.
Traditionally, the membrane expansion tank of the heating system, the price of which is about one hundred dollars for a model with a capacity of 80 liters, has the following design:
- steel body;
- a membrane dividing the expanzomate into two parts;
- fitting (used for pumping air under pressure);
- flange (used to connect the coolant supply line to the hydrophore body).
With the proper level of operation and correct selection, the heating expansion tank will serve in the system for quite a long period of time. However, in the event of a breakdown, membrane expansion tanks for heating systems can only be repaired if they are equipped with a replaceable membrane. Thus, in terms of maintainability, they are superior to an open expansion tank for heating, because in the event of a leak, it can be quickly sealed and restored.
However, in terms of functionality, an expansion tank for open-type heating, which you can buy in a specialized store, is inferior to a membrane expansion tank. In the circuit, a membrane heating tank, the operating principle of which is to compensate for the thermal expansion of water, performs the following functions:
- protection of the circuit from water hammer;
- preventing leaks of radiators, pipelines and connections as a result of pressure surges;
- ensuring the durability of heating devices;
- regulation of coolant pressure in the system;
- air release;
- promoting uninterrupted and reliable operation of the boiler.
What to do before setting up the tank
All listed pressures must be expressed in bars (1 bar = 10 m). Let's take as a basis a two-story house with a heating system height of 4 m.
The tank must be disconnected from the heating system or shut off with a tap. The pressure in the water chamber must be released. When pumping air, the system pressure should not exert its influence, otherwise the tank will not be able to be adjusted.
The same must be done when, before the start of the heating season, you check the pressure in the tank, or when you suspect that the tank has stopped working - the rubber bulb has leaked.
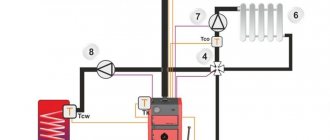
On the left we offer a diagram of connecting the tank to the heating system.
Does it make a difference how to install the tank: with the water pipe up or down? From the point of view of its operation and the dynamics of pressure changes in the heating system, there is no difference. But from the point of view of its operation: in the event of a membrane malfunction (when it is leaky), there is a difference.
If the tank is connected to the heating system with the water pipe facing up, then if the membrane fails, the tank will not be able to release water to the system, although it will be filled with water.
And if you connect it the other way around (with the water pipe down), then even if it is faulty, the expansion tank will still be able to release coolant.
Tank setup.
We start with Pst = 4 / 10 = 0.4 bar;
Next we need to create pressure P (pump air into the corresponding chamber of the expansion tank).
What pressure P should be pumped? Let's use the formula from Reflex:
P = Pst + 0.2 bar, or P = 0.4 + 0.2 = 0.6 bar.
According to Reflex P recommendations > or = 1 bar.
Since the height of our house is small and the sum of Pst and P is less than 1 bar, we take the value P = 1 bar.
We install the tank into the system or open the shut-off valve.
Then we open the make-up valve and create an initial pressure in the system Pinit.
To what extent? The following recommendations will help us with this:
Pstart > or = P + 0.3 bar or Pstart = 1 + 0.3 = 1.3 bar.
Purpose of closed tanks
All of them, regardless of volume and performance, are designed to level out the expansion of the coolant (special liquids, water), which occurs when its temperature increases.
This is done in order to avoid destructive water hammer, damage to fittings, fittings, rupture of heating system pipes, and extrusion of gaskets.
Example: the coolant (water) expands by four percent as the temperature rises to 95 °C. Which is quite enough for the engineering system to fail.
Expanzomat design and components
Any such modern product consists of the following structural elements:
- housings;
- coolant chambers;
- a gas chamber into which ordinary air or inert gas is pumped;
- membranes.
The option of filling the gas chamber with inert gas is more preferable, because it provides the container with greater durability. But regular air is more accessible.
The membrane is made of elastic materials, therefore it is able to change its position as the temperature of the coolant increases or decreases. This structural element can be of the diaphragm or balloon type, and their operating principle is similar.
The tanks are connected to the heating system using a special pipe. A valve is provided for pumping gas. Closed-type containers are manufactured in a horizontal or vertical layout, which makes it easier to complete the heating system.
Tasks, functions and operating principles
To understand the need to install such units, it is necessary to consider the functions that these expansion machines perform. An increase in the temperature inside the boiler for every 10 degrees Celsius leads to an increase in the volume of heated liquid by approximately 0.3%.
The simplest mathematical calculations make it clear that bringing the coolant fluid to the boiling point (100 degrees) will lead to an increase in the total volume of water by approximately 3%. This is a fairly significant volume that can seriously affect the functioning of the entire system as a whole. Therefore, a special device is used to compensate for the thermal expansion of the liquid.
Design and principle of operation of the expansion machine.
Thus, the expansion tank for heating performs several important functions at once:
- removal of excess volumes of water into the drain when a certain fill level is reached;
- replenishment of water volumes when it leaks or when the temperature drops;
- maintaining the required level of hydrostatic pressure by adding or removing appropriate volumes of coolant;
- collection of air and water vapor that is released in the boiler when the temperature of the liquid increases.
In any heating system that uses ordinary water as a coolant fluid, a certain percentage of air is constantly present. According to experts, 1 liter of tap water contains 40 mg of air, which is in a dissolved state.
However, with increasing temperature, its solubility deteriorates somewhat, which leads to the release of about 90% in the form of air bubbles. Open type tanks allow excess air to be released into the atmosphere.
Flaws
Despite all the variety of functions it performs, the expansion tank for heating has some negative qualities:
- large sizes, which may make it difficult to place them indoors;
- reducing the resistance of various devices, pipes and radiators to corrosion;
- the walls of this heating equipment consume heat in certain quantities.
Depending on the design features, expansion tanks are divided into two main groups: open and closed. Let's look further at how to choose the one that suits you.
Recommendations for choosing a container
The most important feature that you should pay attention to when choosing an expansion tank model is the volume of its tank. For closed systems with a small circuit, the volume of coolant in which does not exceed 150 liters, the capacity is easy to calculate.
So, it should be:
- when using water as a coolant - 10% of the volume of the entire heating system (for example, if this figure is 100 liters, then the expansion tank must hold at least 10 liters);
- when using glycol liquid as a coolant - 15% of the volume of the heating system.
In the latter case, the capacity should be larger due to the greater expansion coefficient of the specified antifreeze.
The volume of the tank for larger systems, the circuit of which circulates more than 150 liters, is most conveniently calculated using the parameter of the total volume of the system and a table for selecting a tank.
To calculate the total volume of the system, you can use the following methods:
- Measure the volume of coolant circulating in all individual elements of the system (boiler, radiators, pipelines) and then sum up the results obtained. This method is highly labor intensive, but at the same time it is the most accurate.
- Multiply each kilowatt of boiler power by 15, assuming that on average there are about 15 liters of coolant per 1 kW. This method is simple, but you should remember that you can trust the result only when you are confident in the correct selection of the heating element for the system.
- Drain all water from the system and refill it, calculating the required displacement.
You can also use formulas or an online calculator to calculate the required tank volume. Why is it necessary to know the volume of coolant, its temperature and pressure in the system.
The method with formulas is more complex and the volume obtained as a result of calculations will not differ significantly from the rough calculation given above. Moreover, the found value must be rounded up.
The most practical solution when choosing will be an expansion tank designed for closed-type heating systems, equipped with a safety valve.
The reason is that when the pressure rises to critical standards, the device will start working and bleed it. That is, this valve can significantly increase the safety of the entire heating system.
When purchasing a container, you should take into account that red paint is most often used to mark expansion tanks used for heating.
This feature will help to distinguish the desired product from other similar ones, for example, water supply tanks of similar size and shape - hydraulic accumulators, which are mainly covered with blue enamel.
But if necessary, you can find tanks of various colors, which will help you place the one you need in any room without compromising its aesthetic qualities.
When choosing, you should also pay attention to the quality of the materials used in the production of the container body and membrane. And the presence of a guarantee for the purchased equipment and instructions for installing and connecting it to the system.
How to install?
There are no significant restrictions affecting the installation location of the expansion tank in the system. Nevertheless, it is advisable to carry out the installation at any convenient point in the return line of the existing heating system.
The reason is that the coolant there is cooler. And this allows you to significantly extend the life of the expansion tank and its membrane.
In addition, if you install the tank near a solid fuel boiler, then in certain situations steam may enter the coolant chamber. As a result, the container will lose the ability to compensate for the expansion of the coolant.
Installation of the tank can be done in two ways. These include installation:
But it should be understood that the first option is intended only for cases where the expansion tank has a moderate volume.
You should not skimp on connecting the tank to the heating system.
So this procedure should be performed using:
- a shut-off valve with a so-called “American” - this design element will allow you to quickly remove the tank from service and, if necessary, replace it, without waiting for the coolant to cool down;
- a tee with a drain tap, which will allow you to quickly empty it before replacing the tank;
- pressure gauge for measuring pressure;
- safety valve or nipple to regulate the pressure inside the equipment.
Connecting the expansion tank
The location for installing such a tank is chosen where the intake of excess coolant will be as efficient as possible.
When figuring out how to properly install an expansion tank in an open heating system, you need to pay attention to three important points:
- select the highest point of the contour;
- place the tank directly above the heating boiler so that they can be connected by a vertical pipe;
- provide overflow in case of an accident.
The requirements are explained by the peculiarities of the functioning of gravity heating systems. The hot coolant moves from the boiler through the pipes and reaches the expansion tank, losing a significant part of the thermal energy.
The cooled water naturally flows through the pipes into the heat exchanger for new heating. The location of the tank at the highest point allows air bubbles trapped in the system to be removed from the coolant.
Calculating the tank capacity for an open system is easy. The total volume of coolant in the circuit is measured, 10% of this indicator will be the required figure. Most often, the expansion tank is installed in the attic.
This is especially convenient if you need a large capacity, because a significant amount of coolant may be required for normal operation of a gravity system. A small expansion tank can even be placed in the kitchen under the ceiling, if this allows it to be connected correctly to the heating boiler.
If the device had to be placed in the attic, you need to take care of its insulation. This is especially important if the attic is not heated. Although the coolant enters the tank already cooled, you should not neglect the opportunity to save some of the thermal energy. In the future, heating will require less time and fuel, which will significantly reduce heating costs.
To connect the expansion tank and overflow, you need to run two pipes into the boiler room. The overflow is usually connected to the sewer, but sometimes home owners decide to simply take the pipe outside, and an emergency discharge is made outside.
After the location for installing the expansion tank has been selected and its volume has been calculated, you need to find and install a suitable container. Small tanks are mounted on the wall using brackets or clamps.
Large containers must be placed on the floor. There is no need to seal this tank hermetically, but you will still need a lid. It is necessary to protect the coolant from debris.
Some of the water from an open system evaporates, the lost volume must be replenished. The coolant is usually added to the open circuit through the expansion tank.
This point must be taken into account when choosing a place to install the device. It is not always convenient to carry water into the attic with a bucket. It is easier to provide in advance for the installation of a supply pipe that leads to the expansion tank.
Operational Maintenance
It must be remembered that during breaks in use, the tanks, like other components of the heating system, should be emptied and then dried. This point should not be ignored, as failure to comply will lead to corrosion and reduced service life.
When using any closed tank, owners should regularly perform a number of simple operations.
Which include:
- periodic inspections to detect corrosion and mechanical damage - this procedure should be carried out twice a year;
- checking the pressure in the system, which is performed every six months;
- periodic inspections of the integrity of the membrane - such operations are carried out according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
And in addition, throughout the entire operation, users will have to comply with the requirements regarding permissible temperature and pressure standards.
To repair tanks, you should use only original components, as this will ensure not only the required performance, but also safety of use.
The following article will introduce you to the rules and features of selecting an expansion tank for open-type heating systems, which owners of houses with open heating circuits should read.
How to choose a membrane tank
Membrane tanks come in oval shapes and flat ones with a diaphragm. The second option is more compact; it can be installed between the wall and the interior decoration. This way you will save space in your home. The main parameters of such a tank are the required volume of liquid. It is pre-calculated.
The service life of the tank depends on the quality and parameters of the membrane.
Main characteristics of the membrane:
- The material from which the membrane is made.
- Operating temperatures and pressure.
- Diffusion stability.
Tanks that are used for heating are painted red, and those that are used for the water supply system are painted blue.