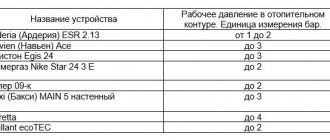
Standard pressure indicators
Before looking for the cause of the drop in pressure, you need to know the norms. The main parameters are specified in the technical data sheet of the devices. There are also average operating pressure values for autonomous lines. On average, the pressure is 1.5–2 atm. An indicator of 3 bar for an autonomous network is the peak limit; measures must be taken to reduce the level.
To prevent normal levels from rising and falling, it is recommended:
- equip the system with Mayevsky cranes;
- check the cleanliness of the air valves;
- carry out preventive inspections of pipelines and areas where they meet radiators;
- use high-quality coolant;
- install pipes of the design cross-section.
After the heating network with the heating boiler is put into operation, the pressure will drop for several days. This is normal and indicates that excess air is escaping. To restore volume, you must frequently add water to the circuit. The pressure also drops after the coolant cools down.
How to check the pressure in the boiler and network
Modern thermal power equipment is equipped with indicating devices: spring and electric contact pressure gauges, as well as primary pressure sensors. Spring pressure gauges use an arrow to indicate the pressure that corresponds to the state of the medium in the circuit.
An electric contact pressure gauge and a primary sensor measure pressure; if the pressure is low, they generate a corresponding electrical signal and send it to the automation and instrumentation system to make a decision on process control while simultaneously recording the readings on the operating display of water heating boilers.
Pressure devices are located at the coolant outlet from the boiler on flexible hoses, on the safety group, after the electric pump and on the heat supply circuit. The process of pressure formation in the circuit:
- The circuit is energized and the air plug is released until the pressure equalizes to 1.2 bar.
- Start the electric pump and achieve stable operation in the heating circuit
- The unit is started and heating of the coolant begins according to the specified temperature schedule.
- Along with the rise in temperature, the pressure in the Ariston boiler increases; when it reaches the operating load, it cannot be higher than those set by the manufacturer.
- During the heat transfer process, the state of the medium in the circuit is monitored using the boiler pressure gauge and its indicator on the boiler screen.
- When the hydraulic pressure drops, the arrow on the device on the boiler unit will drop, and an error code caused by low pressure of the medium will appear on the display.
If measures are not taken and it continues to decrease, the boiler will automatically shut down.
Why does the pressure in the heating system drop, how to increase it
The most common and commonplace reason for a drop in pressure is a power outage.
In case of frequent outages, this can be solved by additionally installing an alternative source of electricity.
If turning off the light occurs rarely and only in emergency situations, then the trouble that has arisen will be solved on its own after turning it on.
In case of a power outage, it is recommended to check the pressure shown by the sensor. Its normal value is considered to be 2 atm; at a higher value, there is a risk of depressurization of the heating structure. When water is supplied and power is turned on, this value should be 1.5 atm.
Attention! A prolonged power outage can cause the radiators to defrost. This situation is dangerous due to costly repairs and replacement of a large amount of equipment.
Leak in the heating system
An equally common problem is the appearance of a leak. It can manifest itself both in open and in hard-to-reach places. You can find it by the characteristic whistle that is created by escaping air, as well as by coating joints and other problem areas with soapy water. The presence of a microcrack will be indicated by the appearance of soapy air bubbles.
Photo 1. Leak in the heating system pipe. The formation of a leak can cause a decrease in pressure.
A leak can occur inside a heated floor when the integrity of one of the branches is accidentally broken. This reason for the drop in pressure can be easily detected by the formation of a wet spot on the floor covering or the appearance of a small fountain of water. To fix this problem, you will need to disassemble part of the floor and install a special coupling at the site of the breakdown. Such repair work requires special skills and experience, which is why they are recommended to be performed only by professionals.
Air coming out of the expansion tank, but no leaks
A few months after starting the heating system, the pressure may begin to decrease and the reason for this is the release of air from the expansion tank. At the top of this structure there is a nipple through which air is gradually released. Its complete release occurs only when the tank capacity is completely filled with coolant.
To normalize the indicators, measures are taken to reduce air ingress. To do this you will need:
Competent creation of a heating scheme and putting the heating system into operation according to it
The work must be carried out by a professional, paying attention to all connections and elements of the heating structure. Mistakes made at this stage require large financial costs and time.
Organization of testing of the system before its launch. To do this, a compressor is used to supply pressure 25% more than the optimal one. If within half an hour there is a sharp jump, this indicates the presence of a leak or a large amount of air entering. Filling the system with coolant should occur slowly and using cold water. Before this stage, you should open the taps intended for draining water. If possible, their radiators are also bleed.
Photo 2. Pressure standards for different degrees of filling of the expansion tank in the heating system.
Common reasons
- Water leakage in places where pipelines intersect.
- Pipe damage from rust.
- Acceptable errors during installation and startup of the heating system.
- Deformation of the expansion tank membrane.
- The appearance of microcracks on the heat exchanger.
- Violation of the automated operation of the boiler.
Preventing the formation of air jams
Preventative measures against the occurrence of air locks are as follows:
- Pay attention to the correct installation of pipes and connections of heating devices. Many problems are caused precisely by mistakes made at this initial stage.
- To prevent air locks, proper commissioning of the equipment is necessary, before which it is important to first check all components and connections.
- Before putting devices into operation, check them for functionality. Using a compressor, you need to apply a pressure level that is ¼ higher than its normal operating value. If it does not weaken within 30 minutes, then everything is in order and the system is ready for operation. If the pressure drops sharply, then leaks are possible, which should be promptly identified and repaired before starting operation.
We recommend: Pellet stove: automatic pellet stove, pellet boiler with water circuit, long-burning heating stove
The pressure in the boiler drops or increases, what are the reasons?
One of the common malfunctions is that the pressure in the heating system slowly drops and when it drops below normal, the boiler turns off.
There are two reasons
Leak in the heating system
First reason
—
in general, it’s not related to the boiler; it’s more a problem with the heating system itself.
Namely, an elementary leak of coolant from pipes or a radiator, and most often what is used as a coolant? That's right water! Believe me! Such a leak can sometimes be difficult to detect, but the fact is that you will not see a puddle on the floor, well, of course, unless it is a serious leak, but most often it is just droplets flowing, for example, from under a radiator cap, or a poor-quality connection or soldering, and You won’t see these droplets, because during the heating season they immediately evaporate from heated pipes. As a result, the pressure slowly but surely drops, you add water over and over again and this continues to kill radiators and pipes.
It is not uncommon for modern radiators, aluminum or bimetallic, to also become unusable, sometimes in inconspicuous places, between the ribs or from below, they begin to dig in due to metal corrosion. Not rust, of course, but various chemical processes also render them unusable. They must be carefully inspected when searching for a leak.
It will be easier to detect various types of leaks if you turn off the heating for a while, let the radiators cool and add pressure to about 2.5 Bar. Carefully inspect the radiators themselves, pipe connection points, and soldering points.
The second
reason
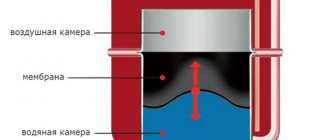
for the pressure drop in the heating system and, accordingly, in the boiler is associated with the expansion tank. The expansion tank is designed to compensate for the pressure created during the expansion of the heated coolant; it is a container divided by a membrane, one half of the tank is filled with inert gas or just air, the other is filled with coolant (read water). When heated, water expands and fills the tank; when cooled, it is again pushed into the heating system.
A) In an extremely rare case, there may be a malfunction of the tank itself. For example, the tank body has lost its tightness. Or there may be a rupture of the membrane inside the tank, but it is not so delicate, so you need to try to break it. But if this happens, then the coolant enters from the heating system into that part of the tank that should be filled with air. This is not difficult to determine; in the upper part of the tank there is a spool through which air is pumped (as in a car, bicycle), if pressing the spool the water is thrown out of the tank, the tank needs to be replaced.
B) In the second case, the reason is that the air has escaped from the part of the expansion tank in which it should be or does not have sufficient pressure.
It can manifest itself like this: FIRST STAGE
...The pressure in the boiler drops slowly, about once a week you have to top up the boiler, and there are no leaks in the heating system itself.
SECOND STAGE
...
On the boiler pressure gauge, the pressure constantly “walks” in heating mode and rises until the relief valve is activated, in hot water mode it drops to values less than 1 bar and then the boiler begins to turn off, the protection is activated. THIRD STAGE
...
If there is no air left in the tank, then the pressure on the pressure gauge drops to zero in a very short time, sometimes in a minute
.
Solution: You need to create pressure in the expansion tank of your boiler.
Reasons for increasing pressure in the system
Sometimes, when checking the pressure in a closed heating system, the home owner may notice an increase in the indicators.
The reasons for the increase in pressure are:
- the coolant temperature in the circuit is too high, which has led to its excessive expansion;
- For some reason the water stopped moving along the contour;
- a valve is closed on one of the pipeline sections;
- an air lock or mechanical blockage has formed;
- the tap is not closed tightly, as a result of which water is constantly added to the boiler;
- the cross-section of the pipe entering and exiting the boiler does not meet the requirements;
- the pump power is higher than necessary, or it is not working correctly; problems with the pump can lead to water hammer inside the circuit.
Thus, it is important to find out what exactly caused the increase in pressure and solve the problem. Sometimes, in an efficiently operating system, a sharp surge in pressure occurs with the pressure gauge needle moving into the emergency zone. The reason for this is most likely that the water in the boiler has boiled. In this case, the fuel supply should be minimized as quickly as possible.
Most modern boilers for heating private houses have an expansion tank. This is a special sealed block, divided inside in two by a rubber partition. One compartment contains air, and the second contains hot water. If the water temperature is too high, the pressure increases and moves the baffle in the expansion tank to increase the size of the water reservoir and compensate for the difference.
In addition, boilers are equipped with safety relief valves, which are activated when the coolant boils or a critical pressure surge. They can be located either in the expansion tank or on the pipe leaving the boiler. When the maximum pressure in the heating system is reached, excess coolant is poured out through the valve, preventing damage to the circuit.
With proper design, bypass valves can be provided in the heating system. They allow you to redirect the coolant to a small circuit when a gap or air lock forms in the main circuit. This measure allows you to avoid overheating and breakdown of the heating system.
The performance of the components of the heating system must be periodically checked, since coolant leaks and violation of normal pressure levels in the expansion tank can lead to significant fluctuations in pressure in the circuit.
We recommend: Warm water floor
How to prevent air from entering the heating system?
It is very difficult to completely avoid air getting into the system, but you can minimize the problem and learn how to easily and quickly remove traffic jams:
- It is necessary to monitor the serviceability and tightness of all joints, shut-off valves, etc.
- Before starting the system, air is pumped into it using a compressor at a pressure 20% greater than the working one. Measurements from the pressure gauge are taken at the beginning of the test and after 20 minutes. If the indicator has not changed, there are no leaks, the system is sealed. A leak will be indicated by the pressure gauge needle, as well as a characteristic whistle. To finally make sure that the leak has been found, lubricate it with a thick soap solution.
- The system must be filled with cold water and smoothly. After filling, the air is released several times using air vents and Mayevsky taps. Each time after draining, water is added to the system.
- It is recommended to use stainless or bimetallic heating radiators.
- It is also advised not to change the coolant too often. A fresh portion of water always contains oxygen impurities.
- To bleed air, install air vents in all problem areas and use them regularly. Or equip radiators with automatic devices and monitor their serviceability.
The adaptation period of the system, during which it is necessary to bleed air and add water again and again, is several days.
External leaks
First, let's look at external leaks, that is, leaks through pipes. Mostly, cheap types of pipes are used in heating systems, such as metal-plastic and plastic pipes. Copper pipes are very rarely used. All of them can cause leaks.
First of all, you need to check the entire system for leaks. To do this, the boiler is turned on to the maximum (for example, 80 degrees), the entire system is completely heated, and after warming up the entire system, we bring the pressure in the system to the maximum, which will be approximately 2-2.5 Bar. On some boilers this value can be around 3 Bar. That is, the pressure is brought to the maximum possible value, above which the explosion valve will operate.
After pumping up the pressure, you should wait until the system begins to cool. While the system is cooling, take regular napkins, toilet paper, newspapers or any other material on which water leakage will be visible. Using this material, all tubes, all shut-off valves and other elements are crimped, passing through all points.
Particular attention should be paid to those places where there are oxides. They usually form around the places where the fittings enter the battery
Such oxides can accumulate in large quantities. Why is it necessary to heat the heating system?
When the heating system heats up (read about choosing and comparing heating systems here), the water expands to its maximum, and if there is a leak somewhere, the crack will expand, and water will begin to flow out from there. When the heating system is heated to 80 degrees, the leak cannot be detected. The leak can only be determined when the heating system cools down to 20-30 degrees. At high temperatures, the water will simply evaporate, and the leak will not be noticeable.
If a section of the heating system is walled up in the walls or floor, then it will be almost impossible to determine a leak in this place. For example, if the heated floor is made of low-quality pipes, then in this case it will not be possible to find a leak.
Norm and control
The heating system is adversely affected by both excessively high and low pressure, measured in atmospheres. In this case, the normal level is 1.5-2 atmospheres.
Healthy! In multi-storey buildings with central heating, this standard is slightly higher, since here the pipes must also withstand water hammer.
Types of pressure in the system
In double-circuit heating systems, pressure is divided into the following types:
- static - formed under the influence of gravitational forces on the coolant; increases by 0.1 bar with an increase in height by one meter;
- dynamic - created through forced operation of the pumping unit or an increase in temperature when the working medium moves;
- working - static + dynamic;
- excess - the difference between atmospheric and measured;
- absolute - excess + atmospheric;
- nominal - indicated by the manufacturer in the technical documents for the gas boiler;
- maximum - the maximum permissible, threshold value that the device can withstand;
- limit (pressure testing) - the value at which the device is tested; can exceed the operating level by one and a half times.
Control devices
Gas boilers contain various components responsible for regulating the parameters of the equipment and maintaining it in working condition. This system requires constant monitoring of the functioning of the system. Pressure gauges and thermomanometers are used to control fluid pressure.
Interesting! Thermomanometers allow you to additionally control the temperature level.
Some systems use electronic sensors instead of conventional dial gauges. The sensors transmit the received information to an electronic unit, which processes it and displays it on the screen.
Water pressure control is provided by a sensor installed in the system - a pressure gauge.
If the heating unit does not have a pressure gauge, then it is provided with a safety group, which consists of the following components:
- The pressure gauge itself or the thermomanometer.
- Air bleeder to prevent airing of the circuit.
- Safety valve for relieving coolant pressure when it increases greatly.
Optimal value for a private house or cottage
The pressure in the heating system of a private house should not exceed the stability limit of one of the weakest components - the heat exchanger built into the boiler. The most durable devices can withstand pressure up to three atmospheres. The designation should not be confused with megapascal, since 1 unit of atmospheric pressure equals 0.1 MPa.
Elements located outside the boiler, for example, the radiator circuit, have a higher degree of strength and can withstand up to 6 atmospheres.
The solution to the problem of what pressure in the heating system of a private house is considered correct depends on the type of device.
Composition of a closed heating system
The standard type of device is an installation with conventional, or rather natural circulation of heating fluid, which is called a thermosiphon or gravity installation. In this case, the pressure is generated due to the magnitude of the run-up in the heights of the nodes, the lowest and the highest.
If the gap is 10.34 m, a pressure of 1 atm is formed in the lower node. It turns out that with a maximum endurance level of 3 atm, the heating device will break down only if the unit is 31.02 m higher than it (multiply the gap by 3 atm).
It should be taken into account that the maximum level is formed in the lowest plane; with each meter of elevation, the static designation decreases.
The excess pressure level in the highest plane of the installation is zero; an expansion tank mounted on the circuit can look like a regular open tank. However, if the device is equipped with a circulation pump unit that pumps water, the system should be of a closed type.
Pressure in a closed heating system
The circulation pump unit generates high pressure in the area of the pipeline located behind the device. This method has a number of advantages:
- The circuit with normal coolant circulation must be no more than thirty meters long; with a closed installation, the dimensions of the element are not limited.
- It becomes possible to use pipes with small diameters.
- Radiator elements can be connected in series.
- When installing radiators in parallel, two-pipe type, the circular pump is able to evenly distribute heat along the circuits.
- The device, equipped with a circulation pump unit, is suitable for operation at low temperatures. This factor allows you to heat the room between seasons. For comparison, a gravity-type device, due to low pressure, is not capable of forcing water to circulate through radiator sectors and pipelines at low temperatures.
VIDEO: Pressure dynamics in a closed loop
reference Information
The pressure in the heating system in a private house, which develops thanks to the circulation pump, is often called dynamic. It should also be remembered that its level cannot be unlimited and must meet several basic requirements:
- The pressure value cannot exceed the maximum level specified in the operating instructions for heating equipment and other additional elements.
- The power of the pressure developed must be set in such a way that it is able to withstand hydraulic resistance, which completely depends on their size, length, configuration, radius, and the value of the speed of water movement.
From the user's perspective, the calculation taking into account all of the above factors may seem complicated, but they are not required. It is enough just to correctly adjust the power of the pumping unit so that the temperature range at the inlet and outlet does not have a big difference; 20°C is often considered the standard indicator.
Indicators of expansion of water as a result of heating
An easy way to calculate the problem of what pressure is in the heating system of a private house with a circular pump installed is to add the standard type of pressure and the statistical type. The result should be at least 1.5 atm, no more than 2.5. However, it should be taken into account that as the length of the pipeline increases, the pumping dynamic pressure decreases due to the hydraulic resistance in the circuit. In this situation, an open-type expansion tank requires an increase in the installation height of the equipment by more than 10 m/1 atm from the bottom of the pipeline, otherwise the coolant will splash out. That is why in such cases a membrane device with a built-in air cushion is used - closed-type heating.
Reasons why blood pressure drops
The operating pressure in the heating system tends to decrease its level. This problem is due to the following reasons:
Let's look at the most common causes of coolant leaks:
- Through the gaps of the membrane expansion tank. It is difficult to determine a leak, since the coolant still remains in the tank. To confirm or exclude an aspect, you should cover the spool pumping air with your hand. If liquid leaks from it, the membrane shell is damaged.
- A leak can occur due to boiling water passing through the heat exchanger, causing the coolant to flow out of the safety valve.
- Damage to rust, poor tightness of connecting elements or other pipeline malfunctions.
For the system to operate correctly, all elements must be assembled in the exact sequence
- The water released air, which was then removed using an air vent
After the user has studied why the pressure in the system is needed, the heating installation should be correctly filled with coolant - in frequent cases, it is incorrect filling that can cause a drop in the pressure level.
To solve the problem, the coolant must be deaerated before filling the circuit, reducing the volume of dissolved oxygen by thirty times. Please note that the entire process takes place in slow motion, starting from the bottom of the system, using only cold water.
- Combined heating device with aluminum radiators
Why does the pressure rise in the heating boiler?
Filling the heating circuit is carried out subject to the exact sequence of actions; deviation from the rules leads to malfunctions of the system. When starting the system seasonally, it is necessary to adjust the adjustable auxiliary elements and fix the position of the valves in the correct position.
Air lock in the system
Thermal imager shows a plug
If the heating system malfunctions, expressed in an arbitrary increase in pressure, the temperature of the coolant sometimes drops and the boiler blocks. As a consequence, in such situations, an imbalance occurs in the functioning of the system, leading to the failure of expensive elements.
Airing of the circuit can lead to similar consequences, and the resulting plugs are recognized as a common reason why the pressure in the boiler increases.
Air locks can occur for a number of reasons:
- equipment malfunction;
- the system was launched with violations;
- automation failure;
- formation of cracks in the heat exchanger housing.
The above consequences are the result of neglecting the established rules for operating the heating system.
The following actions can lead to these breakdowns:
- the DHW circuit is filled from the top point;
- upon startup, the system is rapidly filled with water;
- before launch, the check required for the air vents, as well as each Mayevsky valve, was not carried out;
- air was not bled from the radiators after repair;
- The vibrating impeller with which the circulation pump is equipped slowly pumps air, causing a circulation problem.
Such problems are eliminated by relieving pressure from the heating circuit. Next, the circuit is filled with water, carried out from the bottom point
It is important to consider that while filling the system, it is necessary to keep the air bleed valves open. Filling is carried out gradually without undue haste, and the end of the process is signaled by the appearance of water at the top point of the system
Expansion tank malfunctions
The expansion tank can look like a separate wall element or as part of the boiler. It is designed to collect excess coolant from the heating circuit. When water in the system is heated, its volume can increase by up to 4%, and the expansion tank is designed to compensate for this difference.
Incorrect calculation of the system volume may lead to the installation of a tank with a smaller capacity than necessary for compensation. In this case, all the excess water cannot leave the system and this becomes the explanation why the pressure increases. The dimensions of the tank are also affected by the power of the installed boiler.
A hidden breakdown is considered to be a rupture of the membrane in the expansion tank. Such damage may not be noticed immediately, but in the meantime, unfixed coolant can fill the entire internal cavity. The pressure in the circuit will decrease, but if, in this situation, the system is recharged, this will lead to an arbitrary increase in pressure.
Other causes of high blood pressure
Other malfunctions also come into view, which may explain why the pressure in the heating system increases. If you do not regularly check the pressure readings in the system, then inconspicuous problems can cause expensive repairs.
- If the fittings are blocked, then at the time of intake the pressure will increase, and the control sensors will block the equipment. To avoid consequences caused by this reason, during startup it is necessary to inspect the valves and taps to ensure that the valves are in good condition.
- Dirt and rust that gradually accumulate in the system can clog the mesh filter. Therefore, you should either clean this element regularly, and if washing the filters does not help, then you should install a washable or magnetic filter. With the correct design of such elements, the pressure does not rise above the permissible level.
- A controller or thermostat can fail, and problems with automation lead to negative consequences. The cause may be either premature wear or a manufacturing defect. In addition, a malfunction of these elements can be caused by an incorrect connection.
Such problems can be identified in a timely manner only if the readings of control devices are systematically monitored. They are not capable of dramatically disrupting the operation of the system, but are capable of gradually changing the indicators, leading to the critical point at which the boiler operates under load.
Adviсe. Video
Competent expert advice on what to do if the pressure in the system drops is presented in this video.
Thus, a decrease in pressure is caused either by leaks in the heating pipes, or by incorrect operation of the boiler, or by incorrect calculation of the volume of the expansion tank. When the pressure decreases, all these factors should be checked and eliminated if detected.
You should not try to fix the problem yourself unless you have professional plumbing skills. Only an experienced specialist will quickly determine the location of the problem and be able to take measures to eliminate it.
Causes of pressure drop and solutions
A drop in pressure can adversely affect the normal operation of the heating system. In this situation, water stops flowing into the unit and it automatically turns off
Therefore, it is important to provide timely maintenance, inspection and repair
The reasons for a drop in pressure can be different, let's look at the most common ones.
The pressure in the system drops when hot water is turned on
This problem is quite common. This phenomenon is explained by the special design of boiler units.
According to experts, in reality it is just a pressure gauge that reflects an incorrect value. The pressure drop may be caused by air leaks into the circuit or improper operation of the three-way valve.
For information! If, when you open a hot water tap, normal operation of the system is not restored over time, it means that the pressure is decreasing, and the problem really exists.
Pressure drops due to leaks
To eliminate this type of problem, the owner needs to diagnose and inspect the entire heating system, since liquid can escape through any component.
The cause of the leak may be a loose connection, worn-out heat exchangers, cracks in pipes and batteries. Most often, the level of tightness is checked when the circuit is put into operation, however, the tightness can be compromised during operation itself.
Nodes that need to be inspected and checked first:
- connecting fittings;
- radiators;
- expansion tanks;
- double-circuit boilers.
Detected problems must be corrected, after which the system will be recharged with liquid until the normal pressure level is restored.
Air jams
The formation of cracks and depressurization of the heat supply system leads not only to leaks, but also to the opposite effect - the suction of air masses into the circuit. The result of this is the formation of air bubbles.
Low blood pressure may occur due to air pockets
Bubbles also form when the circuit is not filled correctly, which is why air pockets appear in it, causing a significant drop in pressure.
Recommendation! This problem is solved by simply de-aerating the system, thanks to the installation of bleeders.
Problem with expansion tank
There are cases of problems with expansion tanks. A gap forms here or the nipple may leak air. The inside of the tank consists of two compartments separated by a membrane. One compartment contains air, and the other is filled with coolant. When the liquid working medium is heated, it expands and presses on the membrane with greater force. The membrane, in turn, affects the compression of the gas mixture.
When the equipment operates for a long time, the nipple wears out and begins to leak air, which leads to a decrease in pressure.
A problem with the expansion tank may cause pressure changes
The only solution to this problem is to completely replace the tank, however, before doing this, you should make sure that the problem lies precisely in this, and not in leaking pipes, radiators and airing of the system.
Measuring equipment malfunction
Sometimes diagnosing a system for the integrity of its components may not yield results. If you have not been able to find a visible cause, then you should think about checking the proper operation of the boiler automation and control equipment. This equipment may break down and give incorrect readings.
It is quite difficult to determine this type of malfunction on your own, so it is better to seek help from specialists. The problem is solved by replacing control and measuring instruments.
Cracks in the heat exchanger in the boiler
Over time, microcracks can form on the walls of heat exchangers, allowing water to pass through from the heating system. Since the water in the boiler evaporates quickly, it is by no means easy to identify this breakdown yourself in the same way as in the previous situation. In addition, cracks can occur during washing, which is carried out for prevention or due to manufacturing defects. This problem is eliminated by sealing the detected area with a crack.
Over time, microcracks may appear in the walls of the heat exchanger
The coolant drain valve is not closed tightly
Sometimes the reason may lie in a completely simple issue, such as a faucet that is not clamped tightly enough, due to which the pressure level in the unit decreases. The problem can be fixed easily and quickly by tightening the tap.
Related Posts
- How to treat pressure drops in a heating system; norms for operating deviations
- Subtleties of crimping a heating system
- Reducer or water pressure regulator in the water supply system for home and apartment
- Safety relief valve: operating principle, applications and installation
- What to do if the bottom of the battery is cold and the top is hot?
- Hydraulic accumulator selection and principle of operation
- GOST 25136-82 connection of pipelines. leak test methods
- Why the water station does not gain pressure: the main reasons
- Categories and groups of classification of water supply systems
- How to set up a water pressure sensor in a water supply system
- A supply of hot water that is always at hand: how does an electric water heater for heating work?
- How to choose and install an air valve for heating
- Water pressure in the apartment's water supply
- The principle of operation of a hydraulic accumulator and why it is needed in a water supply system
- How to make steam heating
- At what temperature of the coolant is the heating system turned off and turned on in an apartment building according to GOST
- Major heating repairs in an apartment building
- Hydroarrow: principle of operation, purpose and calculations
- Dry running sensor for pump
- Installation and connection of the expansion tank
- Leningrad heating system for a private house
- Why does the air conditioner gurgle when not working when there is wind?
- How to choose the right pumping station for a private home
- Pumping station for increasing water pressure: features of selection and installation in an apartment and house
- Features of analyzing water from a well: when is it necessary and what is the cost?
Read with this
- How to treat pressure drops in a heating system; norms for operating deviations
- Subtleties of crimping a heating system
- Reducer or water pressure regulator in the water supply system for home and apartment
- Safety relief valve: operating principle, applications and installation
- What to do if the bottom of the battery is cold and the top is hot?
- Hydraulic accumulator selection and principle of operation
- GOST 25136-82 connection of pipelines. leak test methods
- Why the water station does not gain pressure: the main reasons
- Categories and groups of classification of water supply systems
- How to set up a water pressure sensor in a water supply system
Why does the fall occur - reasons
Sometimes it happens that the pressure constantly drops. Of course, you can ignore it and just feed the system occasionally. But these are short-term measures. It is better to determine the cause, since the consequences of low pressure can be disastrous.
Important! It is not necessary to contact specialists. Most of the reasons are easy to identify and eliminate on your own.
A leak
A leak is an unplanned decrease in the volume of coolant. This usually happens because the joints are not tight enough or welded incorrectly.
Sometimes a leak can be detected visually. It is enough to look at all the connections in the heating. If everything looks normal, you will have to turn off the heating and check differently.
To do this you will need:
- Turn off the boiler.
- Wait until the system cools down completely.
- Turn off the taps on the radiators.
- Raise the pressure to 1.5 bar.
- Turn on the boiler.
If there are two heating wings, check one first, then the other. Now all that remains is to monitor the pressure. If it falls, the cause is the boiler or pipes.
If the pressure remains within normal limits, you need to open the taps at each radiator one by one. The reason is one of them.
Attention! Sometimes leakage occurs due to corrosion of the metal when it comes into contact with air. Therefore, it is not recommended to drain water from heating in summer.
Water may leak through threaded connections. Then they need to be tightened or the gasket replaced. Sometimes the taps leak.
In this case, you will have to install new ones. If water escapes through welding joints, you can use cold welding. If it is a polypropylene seam, you will have to desolder and resolder the fitting.
Cracks
Nowadays, in most cases, pipes made of polypropylene or cross-linked polyethylene are used for heating.
Metal and metal-plastic pipes are also installed, but much less frequently. Cracks almost never occur on them. But the radiators and heat exchanger in the boiler may crack.
Identifying a crack in a radiator is easy. Water will leak out of it.
Even if there is no puddle underneath, smudges will still appear. If the radiator is sectional, this will not cause any special costs.
Of course, you will have to remove it and unscrew it, but only the broken sections will need to be replaced. If the radiator is a panel one, you will have to replace it completely. Or try brewing it.
Reference! To see the crack in the heat exchanger, you will have to disassemble the boiler. To do this you will need a screwdriver or torx. It all depends on the model.
First you need to remove the front cover. In non-turbocharged boilers, the combustion chamber is open, so it is easier to get to the heat exchanger. But a closed chamber does not cause any particular difficulties.
We recommend: Coaxial pipe for a gas boiler: types, features and installation diagrams
Now you need to inspect the heat exchanger. Usually, in the place where the crack is located, the metal oxidizes and acquires a greenish tint.
If there is one, then the heat exchanger needs to be changed . Sometimes it is possible to weld a crack using a gas torch , but most models cannot be repaired.
Expansion tank and its bleeding
In a closed-type system, the cause of a drop in pressure in the circuit may be the failure of the expansion tank.
Symptoms:
- Frequent recharge of the system. If there is a need to additionally introduce coolant into the system at least once a week, without visible leaks, then the problem lies in the incorrect operation of the expansion tank;
- Dispersion of pressure gauge readings for different operating modes of the system. A sharp drop in coolant pressure in the system when using hot water supply also indicates a malfunction in the RB.
Pressure inside the expansion tank
To check its functionality, it is necessary to bleed the tank and check that the pressure in it corresponds to the pressure in the heating system.
Sequence of pumping actions:
- Close the shut-off valves (direct and return water supply);
- Open the fitting, drain the water until the pressure in the boiler becomes zero;
- Take readings on the expansion tank in the “open” position. The presence of condensation on the RB should not be observed;
- Pump air into the RB until liquid stops flowing from the fitting. Allow the water to drain completely from the tank;
- Release the air;
- Repeat the procedure, keeping the pressure in the RB at 1.1...1.3 bar;
- Open the shut-off valve;
- Connect the coolant to the network. Set the pressure level to 1…1.1 bar.
Air injection
If there is no special pump for RB, you can use a regular bicycle one.
Attention! Most manufacturers indicate the pressure value in the air compartment in the equipment passport. This greatly simplifies the procedure for selecting an expansion tank for the boiler.
Open tap
To fill water into the heating, use a make-up tap. It connects the water supply and the boiler. Users often forget to close it, and this is precisely why the pressure may decrease.
Important! If the boiler is double-circuit, it works both for heating and for heating hot water. In this case, the effect of communicating vessels occurs.
When hot water is not used, the pressure is normal. As soon as the mixer is opened, the pressure drops sharply. This happens because water from the heating goes into the water supply.
By the way, this can be understood by the smell that comes from the water supply. Typically, heating water does not smell very pleasant. If the make-up valve is working properly, just close it. If it is broken, you will have to change it.
Proper installation of boilers involves installing ball valves at all outlets and inlets. Therefore, you can simply turn off the water taps when not in use. But this is a short-term solution.
Air in the system
When the system is filled with water, some air may remain in the pipes.
This problem is solved by automatic drains, which are installed at the highest heating points.
Unfortunately, the air is not always removed completely. Much depends on the design of the system. For example, aluminum radiators emit hydrogen. It also comes out through the drains, but it is precisely because of this that the pressure in the system drops.
Over time, this process may slow down or disappear altogether. But at first you will have to put up with the problem. Or replace the radiators with others.
There are other reasons for the appearance of air in the system:
- Incorrect installation.
- Long downtime of heating.
- Water itself releases oxygen.
- Various chemical reactions.
Attention! Practice shows that it is impossible to achieve complete sealing of the system by any means. Air gets into the heating anyway.
Air jams
Cracks and lack of sealing in the heating system lead not only to leaks, but also to the opposite phenomenon - air being sucked into the circuit. As a result, air bubbles form in it. Some of them are eliminated by air bleeders, but they are not present in all systems. If the pressure in the system drops, there is probably a strong airing of the heating.
Air bubbles can also form as a result of improper filling of the circuit - air pockets form in it, due to which the pressure in the heating system drops. Airing causes many other phenomena:
- Gurgling and murmurs traveling through pipes are sound effects caused by air bubbles;
- Cold batteries and pipe sections - not only the pressure drops, but also the heating efficiency;
- Metal corrosion – the presence of air in the heating system leads to the thinning of metal components.
Thus, banal deaeration of the system will help to increase the pressure in the boiler.
Relief valve malfunction
The operating principle of a spring safety valve designed for an individual heating system.
The relief (safety) valve is part of the safety group or installed separately; it is necessary to relieve excessive pressure in the heating system. The principle of its operation is as follows: the spring presses on the valve, which blocks the flow of coolant, but as soon as the pressure exceeds the permissible limits, the spring compresses, opening the valve and releasing excess air or coolant.
After 7-10 cycles, spring relief valves fail due to wear of the spring, which no longer holds the same pressure: it jumps or decreases. In this case, there is a constant leak.
It is strongly not recommended to disassemble and repair the relief valve yourself; it is better to simply replace the mechanism. The issue price is only 500-900 rubles.
Faulty pressure gauge
If the system is working normally, but the pressure readings are still below normal, the cause may be a broken pressure gauge. Usually his arrow just stays in one place. Although it also happens that she continues to move. It can be difficult to understand this visually, so the pressure gauge needs to be removed.
Reference! You cannot unscrew the pressure gauge while holding it by the body. For these purposes, use a fitting and a regular wrench.
If the pressure gauge is unscrewed and it continues to show pressure, then it is faulty. They usually have a very thin entrance that can simply become clogged. In some cases it is enough to clean it, but sometimes it is easier to replace it.
Use of aluminum radiators
Aluminum radiator
One of the serious disadvantages of an aluminum radiator is increased gas formation when interacting with a water flow. Water, entering into a chemical reaction with aluminum, causes its oxidation, which results in the release of hydrogen. This process is actively occurring in the new device. After a certain period of time, the oxidation reaction subsides and gas evolution stops.