Home / Boiler automation
Back
Published: 05/24/2019
Reading time: 3 min
1
2691
Modern scientists, together with engineers, are searching for increased efficiency of heating systems in order to reduce the negative consequences affecting our environment. One way to solve this problem is weather-dependent automation that can control heating systems.
This group of devices is capable of monitoring fuel consumption in a running unit, taking into account current weather changes. In this case, it is possible to predict excessive cooling or excess temperature in a heated room in order to immediately compensate for possible deviations.
It is important to understand that the work carried out by weather-compensated automation is aimed at maintaining the optimal balance between a comfortable microclimate and an economical heating mode.
- 1 Weather-compensating automation device
- 2 Operating principle
- 3 Advantages and disadvantages
- 4 When weather-compensated automation comes in handy
Design and principle of operation of weather-compensated automation
The mechanical part of the heating automation is a pump with an adjustment valve. The equipment is controlled by a computer based on data from 4 temperature sensors that respond to indoor and outdoor temperatures. The smart regulation program for weather-dependent boiler control is built into the controller. The circuit is adjusted according to operating conditions and type of room.
Existing regulatory schemes are based on three principles:
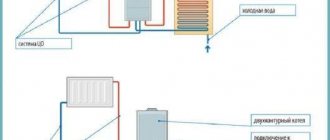
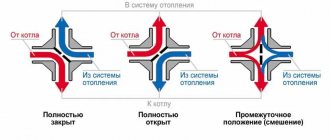
- The hydraulic elevator uses return water, mixing it with the water heated in the boiler. The device is controlled by a weather-dependent heating regulator, sending a command to move the cone valve according to sensor readings.
- A circuit with a circulation pump and a three-position valve limits the heated flow and returns waste coolant to the system. The three-way valve is controlled by a processor according to a given program.
- The shut-off valve on the return pipeline is closed by a valve. The device is controlled by a weather-dependent heating system controller based on data from temperature sensors.
Weather-dependent automation sensors for heating systems of an apartment building (ABC) are installed in the living room.
The individual heating point (IHP) is located in the basement, where it is easier to maintain the equipment.
Features of equipment setup
In order for performance indicators to be correctly calculated automatically, adjusted for street weather conditions, it is necessary to set the correct mode for assessing the thermal regime at the stage of setting up the controller. The user is required to establish a calculated dependence factor between the initial temperature readings on remote sensors and the required microclimate values in the room.
For example, setting up weather-dependent automation can record two values - the step of the relationship between the temperature outside the window and the correlation between the water temperature and the thermal regime in the house. A simple setting scheme in this case may look like this: at a temperature of -20 °C outside, the room temperature should be 20 °C. As for the coolant, the average temperature in this configuration will be about 60 °C. At the same time, conditional violations in direct configuration schemes cannot be excluded, when the equipment self-adaptation function can be activated. For example, if the weather conditions outside remain the same, but heat comes out indoors due to open windows. Accordingly, completely different powers are required. Based on the readings of sensors located indoors, the automation will take into account such nuances, making appropriate adjustments in work.
Types of automatic control systems
Apartment owners who use individual heating often encounter problems with temperature control. The manual adjustment method is inaccurate and consumes fuel excessively. The use of automatic weather-compensated control of the heating system saves resources and frees up personal time.
Types of automation:
- a thermostat connected by a wire to a dependent mechanism;
- wireless control of the heat preservation system depending on the weather.
Functions of control devices:
- The thermostat keeps the room temperature at a given level;
- programmatic setting of the heating level by time of day for up to one week.
Types of devices:
- mechanical thermostat – turns on the electrical network when the ambient temperature changes;
- electronic device – precisely regulates heating based on sensor signals;
- electromechanical device - a temperature relay controls the valve drive.
Thermostats that control heating can be connected to a pump, boiler or mechanical shut-off actuator.
Boiler control using a room thermostat
Another popular and more modern way to regulate the operation of a heating boiler and exclude human participation from this process is to use a relay room thermostat in the heating system.
A thermostat is a device that measures the temperature in a living room and, depending on the environment and the set temperature value, controls the turning on and off of the boiler’s gas burner. However, the inertia of the thermal system causes large delays in responding to commands from the room thermostat. And often the temperature in a living room differs significantly from the set one (up or down), which is displayed on the green graph of room temperature in the form of the appearance of red (overheating) and blue (underheating) segments.
It should be noted that for faster heating, the boiler is set to a higher coolant temperature (in our case, 80°C). Hence the certain “crescent” shape of the orange graph - we see rapid heating to 80°C, and then turning off the burner and gradual cooling until the room thermostat again commands the burner to turn on. If the outside temperature drops, the thermostat will turn on the burner more often, and the lower limit of the coolant temperature (red “ON” dot on the orange graph) will increase, which compensates for the decrease in outside temperature. Thus, with the help of a thermostat, it has become possible to stabilize the room temperature without human intervention, although short-term cyclic “overheating” and “underheating” are possible.
When using a relay thermostat, the automatic ignition operates much less frequently than with manual control, but due to the high threshold value of the coolant temperature, excessive consumption of gas fuel occurs.
This disadvantage can be compensated for by improving room thermostats. Thus, modern programmable models of these devices allow you to set various daily and weekly operating modes. For example, the temperature in rooms can be lowered at night and raised during the day. Likewise on weekdays and weekends. A flexible schedule of the required temperature allows you to achieve significant gas savings. Advantages:
- Elimination of human participation from the process of adjusting the operation of the boiler;
- Reducing the number of boiler on/off cycles, which has a beneficial effect on the service life of the automatic ignition system;
- Saves electricity by automatically turning off the pump when the burner is off.
Flaws:
- Costs for purchasing and installing a thermostat;
- There may be noticeable fluctuations in air temperature in the room.
Rules for operating weather-compensated heating
Heating control systems have a self-diagnosis function. Error messages appear on the display, and the owner can choose how to eliminate them.
If the temperature controller is not working, you need to check the electricity first.
Frequent problems:
- crackling noise during operation – poor contact with the power supply;
- weak heating of the room at a high set level - possible extraneous thermal influence on the sensor;
- the device connected according to the rules does not turn on - the reason is in the design, replacement will be required;
- LED blinking – temperature sensor is broken;
- The thermostat does not provide the specified mode - the device is faulty.
For long-term operation without failures, it is enough to comply with the operating requirements established by the manufacturer. Installation and configuration of the system are carried out according to the instructions.
Using automatic heating control
Heating control systems differ in function and price. Simple models are controlled by a remote control or touch screen. Complex systems have their own software with remote control access. Weather-compensated automation is available in different types of heating boilers:
- wall-mounted, located in one of the rooms;
- floor-mounted, installed in the boiler room;
- electric boiler
In the controller program setting, the initial value is set when the inside and outside temperatures coincide. Then calibration is performed, coolant parameters are selected for each type of weather. The manufacturer programs its own options by default, one of which can be selected for operation.
To configure the system, you need to install temperature sensors outside and in the room so that the data is transmitted without distortion.
The advantages of control are the presence of autonomous operation and resource saving. Disadvantages of weather-compensated automation - maintenance and repairs can be expensive due to the replacement of faulty electronics.
Weather-compensated Vaillant automatic
Vaillant's Multimatic VRC 700 controls underfloor heating and up to 10 mixed heating circuits.
Characteristics of Vaillant VRC 700 Multimatic:
- setting parameters using the rotary knob;
- work with solar heating of coolant and forced ventilation;
- preset Vaillant heating curves - night, guest, day and ventilation;
- recording an individual control program;
- remote diagnostics of the system by the service department.
Control circuits for weather-compensated automation VRC 700:
- One direct heating circuit and recirculation pump with additional module.
- Two lines with mixing coolant, expansion VR 70, boiler pump.
- Direct coolant flow control.
- Circuits - direct and with mixing, two VR 70 modules, recirculation pump.
- Control of two lines with mixing of coolant with expansion VR 70, module VR 91 regulates the process.
- Regulation of two mixing circuits using the VR 70 extension and the boiler via the condensing boiler board.
- Three mixing lines with VR 71 module and recirculation pump.
- Control of more than 3 circuits, one of which is direct. The circuit includes extensions VR 60, VR 32, VR 90.
The Vaillant VRC 700/6 weather-compensated automation version can connect several boilers, and with the VR 900 unit, control the cascade remotely in a special application.
Baxi boilers with weather-dependent control
Gas boilers, even in normal mode, consume fuel, since the burner continues to operate when there are no people in the house. If the house is well insulated, turning off the heating reduces the temperature by 2°C in 6 hours, and turning on the heating gives an increase of 2°C in one hour. Boilers of the Baxi Luna 3 Comfort model have remote control via a mobile application. You can link an automatic heating control script to the calendar.
The Baxi Slim series boilers have the following functions:
- remote temperature request in the apartment and outside;
- remote control of water temperature in forward and return circuits;
- gas meter reading;
- pressure control in the system;
- notification of errors and emergency stop of the boiler;
- remote activation of the boiler.
Advantages of wall-mounted boilers:
- separate heating and water heating circuit;
- constant coolant temperature;
- silent operation;
- electronic flame modulation;
- boiler operation at reduced gas pressure in the system;
- Possibility of connecting underfloor heating.
Baxi boilers from an Italian manufacturer are unpretentious.
OpenTherm protocol, modulating burners and weather-compensated automation
Nowadays, the most modern and high-tech heating control systems are equipment that supports the OpenTherm protocol. There are three main features that distinguish devices with OpenTherm from the examples above.
Flame modulation control
Flame modulation – regulation of heating power. The creation of new gas boilers with burners that control flame modulation contributed to the emergence of new opportunities for organizing more efficient and economical operation of heating systems. If the power is too high, the boiler switches on and off frequently (clocking), and if the power is low, achieving the set temperature becomes impossible. Therefore, the best flame modulation is considered to be the combustion level at which the boiler does not turn off, but the set temperature value is reached. None of the boiler control methods described above can control flame modulation. To work with the new burners, the OpenTherm protocol was invented, which makes it possible to effectively establish a connection between the capabilities of the new burners and modern weather-sensitive automation and electronics.
Working with automation
We can say that OpenTherm is a bridge built between boiler manufacturers and manufacturers of other automation and electronics. A single protocol standardly describes all the main commands for working with modulating burners. This allows you to connect a wide variety of equipment to it: from a thermostat to programmable temperature controllers, to which up to 10 temperature sensors can be connected. Modern thermal controllers are programmable devices that process the readings of temperature sensors located both in various zones of a heated facility and on the street. The heat controller maintains the set temperature and can change it depending on user commands, time of day or day of the week. Analyzing the received temperature data outside and inside the room, the controller sets a weather-dependent operating mode for the modulating burner of the boiler and pumps. On the graph we can see that the burner practically does not turn off, but only changes the intensity of its combustion. At the same time, regardless of external conditions, the target temperature graph practically does not change and lies within the hysteresis limits of the heating system. Also, the advantages of this control system are a noticeable increase in the service life of the burner and significant savings in gas fuel.
Access to automation settings and fixing errors
Among other things, the OpenTherm protocol provides the opportunity to gain full access to the boiler automation settings and change them from any control device (smartphone, tablet or desktop computer).
The protocol also provides the owner of the heating equipment, as well as maintenance personnel, with all the information about errors that occurred during the operation of the heating equipment. Advantages:
- Minimum fuel consumption compared to other control methods;
- Minimal fluctuations in air temperature in the house, regardless of the temperature outside, which ensures maximum comfort;
- The temperature is adjusted by changing the modulation of the burner flame, which minimizes the number of on/off cycles;
- Possibility of remote monitoring of the boiler condition and changing its settings.
Flaws:
- Higher price compared to other equipment, which is compensated by gas savings.
Automatic control of Protherm boilers
Boilers without regulation turn on heating depending on the parameters of the coolant. Weather-dependent Protherm equipment controls heating based on data from street and room sensors. Thermostats save up to 30% fuel, reducing the frequency of boiler switching on.
Room regulators that are used with the Proterm Skat electric boiler:
- Instat Plus with a wired connection, maintains temperatures from 5 to 30°C, and has a night heating reduction mode.
- Termolink B – room air heating controller in the range from 8 to 30°C, programmable operating mode for 24 hours, frost protection function.
Electric heating is a safe source of heat in the home without emissions. No ventilation system is required for installation. The equipment of a Protherm electric boiler is simpler than that of a gas boiler.
Temperature regulators on the eBus are used with Protherm Medved floor-standing cast iron boilers:
- Termolink P - there is a modulation mode, adjustment of air and hot water heating, a heating control curve depending on temperature sensors.
- Termolink S – can change the boiler operating mode according to the time of day, programmed for a week. Vacation mode and frost protection are preset.
Boilers of the Bear series change the water temperature using an injection burner. The heating element is made of cast iron. The display on the panel informs about the parameters of the coolant.
Weather-compensated automatic Meibes
The weather-dependent thermostat HZR-M Meibes controls the coolant mixing circuit independently in combination with other controllers. Characteristics of the Maybes device:
- interface with icons;
- built-in heating mode programs;
- integration with other controllers on the eBUS bus;
- Autonomous battery power supply;
- display backlight;
- connector for connecting a computer.
Weather-compensated automation for heating systems of a private home - devices with remote access Meibes LE HZ made in Germany.
The thermostat controls two circuits or a cascade of 2 boilers and recirculation pumps. Features of Meibes LE HZ:
- connecting controllers remotely;
- expansion of control to 8 circuits via eBUS;
- character menu;
Advantages: easy installation on the wall.
Automation of heating systems
If you need more modern automation of heating systems, today manufacturers offer quite unique devices that will meet all the requirements of modern times. This includes a room temperature regulator. Basically, such devices are installed directly in the room. It is mounted to the wall and allows you to control the air temperature in the room. The uniqueness of such a device lies in the fact that it performs a whole range of different tasks. It can turn on or off the fuel supply, if we are talking about gas or electric boilers, and also turn on and off the sediment for coolant circulation, if we are talking about solid fuel boilers.
Thermostat ZONT
Weather-compensated heating regulator ZONT H-1 is an intelligent system, remotely controlled via GSM or the Internet. The device is connected via a mobile application, personal account on the manufacturer’s website or via SMS commands. Thermostat capabilities:
- 2G SIM card management;
- transmission of temperature sensor readings and boiler operating mode;
- selection of heating control curve;
- programming room heating for a week;
- notification of errors and emergencies;
- message about a power outage in the house;
- transaction history for 3 months;
- software update via the Internet.
The thermostat is connected in 2 ways - through the terminals on the boiler or with an adapter to the digital bus. Heating control can be performed in relay mode, with periodic switching on of the gas burner. Digital control is possible via an adapter - electronic flame modulation.
Technical characteristics of ZONT H-1:
- operating voltage 10-28 V;
- analog and digital inputs;
- connection of 10 wired and radio sensors;
- operating range from –30 to +55°C;
- exit to mode – 50 seconds;
- plastic case, universal surface mounting.
Boiler operation with heated floors
For comfort in the house, a heated floor system is used, where the coolant is water or a liquid with a low freezing point. The circulation pump is regulated by weather-compensated automation.
Composition of the heated floor scheme:
- weather-compensated control controller;
- outdoor temperature sensor installed in the shade;
- mixing unit servo drive;
- circulating water temperature sensor;
- underfloor heating pipeline;
- thermostat in the heated room.
The Russian-made TRC-03 controller maintains the temperature according to the heating control curve.
Warm floors are used with other types of room heating. Four types of weather-compensating controllers are designed to work together:
- Main – controls 8 types of hydraulic circuits, 6 of which include the boiler.
- Expansion for 2 hydraulic systems in addition to the main regulator.
- Independent loop control with mixing, can independently regulate one system.
- Heating control device with buffer tank and timer.
Heated floors have significant inertia, so the room thermostat reacts more accurately to the weather.
Weather-compensated automation for greenhouses
Growing crops year-round in a northern climate is a difficult task. To ensure the growing season of plants, weather-dependent heating is used. The best option is a piped soil heating system, which stimulates root development and reduces energy consumption.
The temperature in the greenhouse is different at night and during the day, and the soil should be 2-3°C warmer. Aries TRM-32 automation or Aries PLC 100 controllers integrated into a system with a control center can cope with this task.
Characteristics of the Aries TRM-32 control system:
- control of coolant heating based on the signal from four external sensors;
- connection to a computer via an adapter;
- control range from –50 to +200°C;
- wired communication length – 1200 m;
- temperature in the greenhouse from +1 to +50°C;
- push-button control, information display;
- programming a heating schedule based on a given temperature value;
- switching from day to night operating mode.
Remote control of the microclimate of greenhouses is carried out by ventilation and changing the speed of the pumps.
Automation for pump
Regulates the operation of the system, controlling many functions, such as, for example, pressure, water distribution.
For normal operation, the following components are required: a manifold that provides water supply, a relay that controls the pump, a pressure gauge that measures pressure, a dry-running sensor that prevents the device from overheating if the water runs out.
All automation responsible for the pump is divided into several models, based on the time of creation:
First generation automation;
The first simplest water supply design. Used to solve simple problems when it is necessary to provide a room with a source of water. It consists of three components: a dry running sensor, a hydraulic accumulator that performs the task of accumulating water and contains a membrane, and a relay that controls water pressure. It usually does not cause any difficulties during installation, since the system completely eliminates complex electrical circuits. The mechanism is also extremely easy: the order is cyclical—when the water is completely filled, the pump turns off, then the cycle repeats.
Third generation automation
It is a more worthy version of its predecessors, and costs more accordingly. The unit stands out for its greatest reliability, efficiency, improved safety program, and most importantly, maximum accuracy of the device.
To maintain the device in automatic mode, a relay is installed. The mechanism is simple: when the water pressure decreases, the relay starts the system, and similarly, when the pressure increases, it stops.
Thermostat to turn the pump on or off
The most common type of automation for a pump in home heating. Mechanism: first, information is collected from the sensor, then the indicators are compared, the operation of the pump depends on this. For example, if the owner sets the mode to +60 and the hysteresis to +5, then the water must be +65 for the system to start, and for it to stop, the temperature must be +55.
Do-it-yourself automatic regulation
Weather regulation is used to maintain comfort and economy. They install weather-compensated heating in small private houses and dachas with their own hands. For stable operation of the system, factory-assembled devices are suitable. Homemade devices will not work stably; they are unsafe.
The Ochag universal boiler, which runs on solid fuel, is suitable for a country house. The control circuit has three temperature sensors - coolant in the boiler, waste gases and water in the boiler. The actuators are an air flow gate and a damper on the pipeline. Automatic control is organized using the Arduino Nano controller.
Weather-compensated heating control
At first glance, everything is logical, but I had a question about the advisability of constantly adjusting the temperature of the coolant in the heating system. There is an opinion that a one-time adjustment of the heating system over a period of time is sufficient in the event of a sudden change in outside air temperature. In this case, adjustment can be made manually using various remote control systems, while avoiding unnecessary “bells and whistles” in engineering systems and thereby simplifying their operation. In order to understand this, let's look at the second function that requires weather-dependent heating control - saving energy resources. I am sure that you don’t have to be an academic to answer the question of what type of coolant supply control will be the most energy efficient. Naturally, it's automatic. But the question immediately arises: by how much are the costs of generating thermal energy reduced if you use weather-dependent heating control, and how reasonable are the costs for it?
How necessary is a weather-compensated heating system?
Automation of heat management is not always necessary. Regulation occurs with a deviation of 2°C from the norm in the room with the sensor; in other rooms the variation is greater. The cost of installing automation installed separately reaches 2 thousand euros.
If the equipment is supplied with a heating boiler, the use of weather-dependent automation is justified. In other cases, the costs will not cover the possible savings.
Thermostatic radiator heads are sufficient for heating regulation.
Weather-dependent control of heating systems, its essence
Automation allows you to keep the boiler in the optimal temperature range, set in the comfortable temperature range. Thus, the owner can save on fuel consumption by reducing the amount of heat and technological heat losses. Without installing weather-dependent automation, the boiler maintains a fairly high temperature due to the fact that the gases that escape are an order of magnitude hotter than the air in the room.
When weather-compensated automatic heating systems are installed, the coolant keeps the permissible temperature at the lowest level required to ensure comfort in the room. This indicates that much less heat generated from fuel combustion enters the atmosphere.
Agree, an automated heating system control unit really makes it possible to save significant money on heating, since heat loss is minimized.
The specificity of a condensing boiler is its ability to operate in low temperature conditions, using the condensation energy of water vapor released during gas combustion. It is necessary that the mark of +55 degrees Celsius be captured in order to increase efficiency.
In the event that there is no weather-dependent automation of heating systems, for condensing-type heating devices it is necessary to select batteries designed for a low-temperature schedule, i.e. 2-3 times more. This, in turn, leads to an increase in the cost of radiator heating by a third; moreover, such radiators are quite bulky.
What conclusions can be drawn from this? With the help of such a controller, you can safely combine the condensation mode in the heating system with optimal dimensions and cost of batteries.
Advantages of automatic heating control
Due to its high cost, weather-dependent control is more often used in apartment buildings and industrial buildings, where it is economically justified. Advantages of automation:
- constant temperature;
- reduction of fuel consumption during temperature changes;
- automatic environmental control by sensors;
- maintaining a low temperature;
- lack of human factor.
Boilers of new models are equipped with automatic adjustment. The functions of these systems are sufficient for comfort in the home without unnecessary investments.