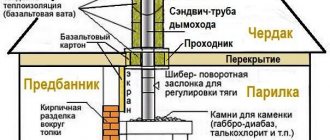
Types of chimney pipes for baths
The chimney for a bathhouse is selected depending on the material of the stove - steel and sandwich structures are installed with metal heaters, sometimes old asbestos-cement ones are found. A sauna heater is usually small; neither brick nor ceramic chimneys are used in conjunction with steel stoves. An exception is if an old house with a brick chimney in the center is converted into a bathhouse.
It is allowed to install chimneys of any type on brick stoves: brick, sandwich, ceramic, steel, asbestos-cement. Brick structures are more bulky; brick or ceramic pipes are more often used for them. But you can also install insulated steel pipes or sandwich structures on them. A rather serious drawback of brick and ceramic pipes is that they require a stationary foundation.
For a bathhouse, it is practical to install steel heaters - they heat up faster, transfer heat faster to the stones, the water in the heating tank, and the bathhouse itself. The sauna is used infrequently and not for a very long time, so it is metal structures that optimally satisfy the requirement of quickly heating the heater and the sauna room.
Metal pipes in a bathhouse are easier to bring up through the ceiling and roof, and they can also be used for additional heating. A bathhouse usually does not require long-term heating; there is no need to install modern long-burning stoves. After the bath procedures, the bathhouse needs to be dried - the bathhouse is heated for some time with hot stones (they have a very high heat capacity) and a hot tank of water.
So, the types of chimneys for a bathhouse:
- Indigenous with their own separate foundation, usually brick or ceramic.
- Mounted. The chimney is mounted vertically onto the outlet pipe. Above structures are usually hung on the wall.
- Built into load-bearing walls. A typical example is the installation of a chimney in the wall of old small houses and summer kitchens with stove heating.
- Hanging. Lightweight sandwich pipes are usually hung from the walls of the house.
- Now they have begun to use coaxial chimneys - “schidel”, or “pipe in pipe”. The exhaust gases heat the air entering the fireplace or boiler. A typical example is horizontal pipes for gas boilers. Vertical coaxial structures are used for large heating units; they are usually not used in bathhouses. In most cases, they try to transfer the heat from the exhaust gases to water in a heating tank or to stones in a heater.
Chimneys for baths are made of the following materials (the materials determine their design):
- Brick. They are rarely used; sometimes they use ready-made built-in chimneys from dismantled stoves. The brick box requires installation of a stainless steel box. Old brick hogs in the attic and above the roof surface need to be insulated.
- Ceramic. A foundation is needed; they are rarely used for heaters in bathhouses.
- Asbestos-cement. Installing new asbestos-cement pipes is undesirable, but sometimes old chimneys made of asbestos-cement pipes are found. If possible, they should be replaced with a modern sandwich.
- Steel. Sometimes they install single-layer pipes with homemade insulation, but this is already the last century. It is better to overpay and install high-quality three-layer sandwich chimneys.
Applications of kaolin
Such materials are produced using advanced scientific developments. Inorganic binding additives are added to the mullite-silica base in a vacuum and subsequent drying of the material. To increase strength, a clay binder is added to them.
Kaolin fibers have a number of advantages:
- safe for human health. They do not contain asbestos and do not emit harmful substances when heated; high level of safety from fires; thermal energy losses are reduced; the material is guaranteed not to be destroyed even after starting or stopping the furnace. Can be used in a country house with periodic use of the stove; the slabs are easy to process and install; low density with high thermal insulation values affects the size of the slabs and makes it possible to reduce the thickness while maintaining performance characteristics.
Types of ceiling penetrations
The chimney through the ceiling and roof of the bathhouse passes through protected openings. One of the main conditions for the safety of people in a heated building is heating the roof, ceiling and walls structures near the pipe to a temperature not exceeding 50 °C. Fire safety requirements for the installation of chimneys are set out in SP 7.13130.2013. Heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Fire safety requirements.
To pass the pipe from the bathhouse through the ceiling or roof structure, a through-ceiling assembly is installed - a prefabricated box with flanges. Insulation is placed between the flanges. The box insulates the surrounding structures from the heated surface of the pipe. You can make it yourself, it's not very difficult.
For the speed and convenience of passing pipes through the roof and ceiling, the industry produces ready-made passage units. They are round and square. As a rule, these units are made of stainless steel with a heat insulator, sometimes mineralite - cement boards with fiber fiber (mineral, cellulose). Previously, asbestos-cement slabs (flat slate) were used, but asbestos is carcinogenic, and their use indoors is prohibited by sanitary standards. This is still not a roof or a fence, the asbestos dust from which is washed off by rain and carried away by the wind. Sometimes there are pass-through units made of galvanized steel, but in humid bath air they will quickly rust, so they are used only as a last resort.
Mineral wool is mainly used as insulation (thermal insulator), but expanded clay, clay, and a mixture of clay and expanded clay are allowed. Mineral wool has a very significant drawback - when wet, it becomes thermally conductive (due to water), and after drying it does not completely restore its thermal insulation properties.
If the flange or body of the passage unit is made of steel, and the ceiling structures include flammable elements (wood, foam), then a layer of mineral wool must be laid between the structures and the steel elements. Otherwise, the structures may char or even burn.
Positive factors of an insulated chimney
Before answering the question - how to insulate a pipe, it is necessary to highlight the advantages of an insulated chimney. An insulated gas outlet protects the heating system from the influence of the external environment and combustion products. Of course, thermal insulation cannot completely protect the structure from destruction, but it will extend its service life. This occurs due to the following factors:
- Pipe insulation allows you to maintain a thermal balance in the middle of the structure, eliminating the possibility of aggressive acids and condensate falling onto the walls. Combustion products completely evaporate along with the smoke stream.
- Chimney insulation minimizes the possibility of temperature differences between the cooled smoke duct and the hot steam.
- Energy-saving properties are increased, contributing to fuel economy.
- The strength of the steam exhaust structure increases due to the reinforcing frame.
Properly selected chimney insulation increases the frost-resistant properties of the system, ensures long-term preservation of appearance and increases service life, which is very important.
Rules for installing a chimney pipe
The health and life of your family and friends depend on the fire safety of chimneys and the complete removal of flue gases - carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, toxic substances, smoke, soot. Therefore, when installing chimneys, you must strictly follow the rules for their installation. These rules are defined by regulatory documentation - SP 7.13130.2013.
The main rules when installing chimneys for a bathhouse:
- Maintain distances to the nearest structures - walls, ceiling structures, roof.
- Sufficient but not excessively high chimney height.
- To determine the cross-section of the internal chimney channel and its height, calculations are necessary.
- Durable fastening to the walls and ceilings of the bathhouse.
- Reliable sealing, good insulation during installation.
- Protecting hot structures from possible contact and burns: this is especially important for a bathhouse with its small size.
- Assembly of modules for condensate. Sandwich pipe elements are appearing, designed for simultaneous assembly of smoke and condensate.
The distance from pipes to combustible structures - wooden rafters, lathing, bitumen materials - must be at least 130 mm, from uninsulated ceramic pipes - 250 mm. The passage unit must be at least 70 mm greater than the thickness of the ceiling structure. The steel structures of the passage unit must be separated from the ceiling structures by non-combustible materials - slabs of mineral wool, mineralite.
Standards for clearances from pipes to walls
SP 7.13130.2013 determines the minimum size of setbacks - the distances between the outer surface of the chimney and the walls. If structures are made of flammable materials, then the offset should be from 260 to 500 mm. If non-combustible or combustible materials are covered with plaster, reinforced with metal mesh, heat-insulating non-combustible materials - from 200 to 380 mm.
The amount of indentation depends on the thermal insulation of the chimney (thickness of the brick wall or insulating layer). Before installing a stove with a pipe for a bath, you need a drawing indicating the exact dimensions of the pipe and the distances to the structures.
Best answers
Alexander Kudryavtsev OLD. OTVET:
At such temperatures Asbestos needs... the best. Wrap the pipe with corded asbestos, and then you can use basalt wool on top... but it will be easier. The temperature will no longer be the same
Oksana Shmuchkova:
The air gap is effective, since expanded clay outside the screed absorbs a lot of moisture and becomes a heat conductor. It is a FILLER, not an independent heat insulator.
I love Spitz!:
pour it out, there are no other options
Antonio M:
I wrapped the pipe with non-flammable paper, then 10 cm of heat-resistant mineral wool, then a galvanized iron box. Still, you can’t touch it with your hand during a good fire. Try expanded clay but at least 15 cm. The pipe will still be very hot
nik:
Expanded clay is not suitable for this purpose; it can only be used in fireproof ceiling cutting (around a heat-insulated pipe). Rockwool wired matt and its analogues are best suited as a heat insulator for pipes; the denser the heat insulator, the lower the temperature of the outer casing, but at the same time the temperature of the internal circuit increases
Leonid Shingarov:
I did this around the pipe. The wooden box inside was lined with glass-magnesium sheet; it can withstand temperatures of 1100 degrees, and the space was filled with expanded clay.
Oleg A:
vermiculite, what kind of expanded clay. Just so that it is definitely vermiculite. A slab made of heat-resistant cement GC 40 is better. In the case of using a slab or brick when fluffed, the distance from the inner wall of the pipe to the protected wood should be 380 mm, to the unprotected one - 500. 380 mm is one and a half bricks, and 50 mm fire butts rockwall, stuffed on a tree.
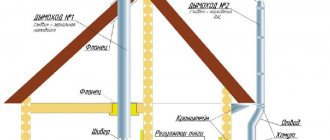
How to make a pipe passage through the ceiling and roof: a step-by-step guide from the master
The most common type of chimney for a bathhouse is made from sandwich pipes. It is his installation that I will consider. The sandwich is very easy to install; elements for pipes of any configuration are available for sale. Stainless steel chimneys last for several decades; the calculated thickness of the insulation ensures good draft.
Step 1
Initial installation stage:
- connection to the outlet pipe of the tee;
- connection of a horizontal or vertical section without insulation, transition from an uninsulated pipe section to an insulated one;
- installation from below of an element with revision and a container for condensate drainage.
An area without insulation must be installed - the temperature at the point where the flue gases exit the furnace is very high, any insulation will simply bake and damage the pipe. Often in this place it is necessary to install a heater, coil or container for heating water - to select and rationally use the heat of the exhaust gases. The wall of the bathhouse made of flammable materials near the stove and chimney is covered with non-combustible materials - stone, tiles, mineralite.
The pipe is attached to the wall with special clamps or brackets, the lower part of the pipe is also attached to the wall (you can place it on a special stand). The distance between the clamps should not exceed 1 m, it is advisable to make it smaller - 0.5–0.7 m.
The elements are simply inserted into each other, the connection point is fixed with a crimp clamp. Before connecting two pipes, a special sealant is applied to the joint.
Step 2
Holes are cut or punched in the ceiling of the bathhouse using a hammer drill or grinder. The lower flange of the passage unit is attached, a pipe (or sandwich structure) is laid, insulation is laid, the upper flange of the passage unit is installed on the ceiling and attached to the ceiling structures (occasionally to a bracket). The stage ends with the installation of the pipe in the attic.
Step 3
A hole in the roof of the bathhouse is cut in the same way as in the ceiling. It is extremely undesirable to cut the rafters when leading the pipe through the roof, therefore, when designing the installation site of the heater and the passage of the chimney, this circumstance should be taken into account: a curved chimney and set to the side can worsen the draft. In any case, before installing a chimney, it is necessary to draw a diagram of the placement of the stove and pipes in the bathhouse, taking into account the optimal passage of all ceiling and roof structures.
A roof sheet is attached to the underside of the roof. A roof section is fixed on top - an unloading platform with a cone. A chimney is passed through the groove, and the groove inside is filled with insulation. The joint between the groove and the pipe is covered with a cone-shaped apron. Silicone sealant is used to seal all joints - it withstands the temperature on the surface of the pipe.
The top of the cut is covered with a galvanized sheet or roofing material, and roofing material is placed under the bottom.
Step 4
Lastly, the master flush is installed - an elastic device made of high-quality durable EDPM rubber or silicone. Silicone is less resistant to ultraviolet radiation, so it is advisable to cover the master flush with a steel cap. The master flash is secured with self-tapping screws, they are screwed into an aluminum strip around the perimeter of the flash. All joints are sealed. Usually the roof under the master flush is covered with galvanized steel so that it fits tightly and seals the roof groove well.
The installation sequence of more complex roof trim for all needs is shown in the video.
Making boxes
Many people are afraid to make a metal box for the chimney pipe themselves. But it doesn't contain much complexity.
When making a box you need the following tools:
- Metal scissors.
- Galvanized sheet.
- Self-tapping screws.
- Compass.
- Drill.
Further sequence of actions:
- The hole is being prepared. Its edges need to be secured with support beams. They will create support for the box.
- A couple of parts are cut from a galvanized sheet. Along their edges, at a distance of five centimeters, a 90-degree bend is made. These U-shaped parts are fastened with self-tapping screws to prepared holes in the ceiling covering.
- Two more U-shaped blanks are prepared in the same way, and they are overlapped onto the existing sheets. The result is a solid frame for the exit made in the ceiling covering.
- The next part of the action is the bottom for the box. An element is cut out from the same galvanized sheet, the dimensions corresponding to the opening made. In its center, draw a circle with a compass for the entrance of the smoke exhaust billet.
- From the central part of the bottom of the box, 4 fasteners are placed (each of them has a two-centimeter width). Next, they are cut out and bent at an angle of 90 degrees. As a result, a base is formed with a hole and 4 strips for fastening.
- The bottom is attached to the walls. A chimney is inserted through the exit and secured with a clamp. The empty space is filled with an insulating layer.
Using the suggested instructions, making a box is not difficult. If you follow everything exactly, the work will not be difficult even for an inexperienced layman.
How to choose thermal insulation material for a chimney
The best option is sandwich pipes. Their high-quality and carefully calculated insulation is covered on the outside with a reliable steel casing to protect against wetness and wind. In all other cases, insulation for chimneys in any case comes down to heat-resistant and non-rotting mineral wool, or even better - mineral wool shells. No plastic insulation can withstand the temperature on the surface of a single-layer steel chimney.
The top of the mineral wool must be covered as tightly as possible with a casing made of galvanized or stainless steel, and the joints must be sealed to prevent precipitation and atmospheric moisture from entering. Mineral wool picks up moisture and loses its thermal insulation properties, and if it freezes it can damage the chimney.
For external insulation of brick chimneys, you can use polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam in the form of sheets or by applying foamed liquid hardening compounds. The temperature on the surface of brickwork is not very high, and plastics can withstand it. But plastics must be protected from ultraviolet radiation and mechanical damage (snow, hail). Pipe cleaning methods
To maintain the functionality of the chimney hog in working condition, it is necessary to clean the hog of soot and tar deposits twice a year (read: twice during the heating season). If you use resinous firewood, such as pine, then you will have to clean the chimney more often.
Methods for cleaning chimney walls from soot are divided into mechanical and chemical. Mechanical - using all kinds of brushes or pipe cleaners. Chemical - using special logs, copper chloride, table salt, PHC (anti-carbon chemical composition) and even potato peelings.
Some chemicals contribute to the shedding of soot from the walls, some - the burning of soot on the walls. In this case, the temperature rises significantly and the chimney may be damaged. Therefore, the mechanical cleaning method is preferable.
Relevance of thermal insulation
Moisture and smoke generated during fuel combustion are aggressive factors affecting a brick chimney. The temperature difference during the cold season and the accumulated moisture settling on the walls fills microcracks with water, and the stone structure collapses from the inside. Small ice crystals press from the inside and destroy it. An insulated chimney can eliminate this. During the combustion process, condensate is formed on the surface of the flue, which contains a chemical series of oxides. When interacting, the elements form weak acids (carbonic, sulfuric, etc.) that can destroy the metal surface. It is for this reason that chimney insulation is necessary. Proper installation of thermal insulation helps prevent indoor fires and prevents the roof from catching fire. Well-heated chimney pipes improve draft in the fireplace, boiler and stove, and there is less tar and soot residue left in it. The efficiency of the heating unit increases significantly.