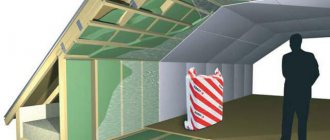
Why is insulation needed?
Inter-crown insulation is a universal material, therefore it is widely used for houses and baths made of rounded logs, profiled or laminated timber. In this case, the density of the insulation can be about 750 g/sq.m. with a thickness of up to 11 mm.
To reduce heat loss, the insulation is laid in one layer. It is important to remember that when using uneven or under-dried timber, the insulation is laid in several layers.
Insulation promotes timely vapor and heat insulation of wooden structures and high-quality air exchange in rooms.
When building a log bathhouse or house, an important condition is to minimize possible gaps between logs and beams. It is for this reason that work is being done to seal it with high-quality insulation.
Such measures are aimed at effectively protecting the building from adverse climatic conditions.
Other
Of course, the three examples we have given are not a complete list of insulation between logs. For these purposes use:
- Sheep wool;
- Jute;
- Polytherm.
We will talk about all these materials in separate publications. For example, many people are interested in what is better to use, flax or jute, for inter-crown space.
And someone asks: what is better, jute or moss?
We will devote a separate article to jute insulation in the near future.
Performance characteristics
High-quality insulation, which is laid between the crowns of logs or beams, must meet high standards of quality and safety of use. Therefore, the main performance characteristics of the material include:
- High elasticity and density, maintaining properties throughout the entire period of operation. Thanks to its elasticity, the insulation is able to take the desired shape, and its density is able to fill existing gaps between the crowns.
- Low thermal conductivity for effective protection of walls from heat loss.
- High moisture and vapor permeability.
- Resistance to mold, fungi and harmful microorganisms that arise when exposed to increased moisture and heat.
- Resistant to ultraviolet exposure and adverse weather conditions.
Advantages of jute
Compared to other types of insulation, varying in price, quality and composition, jute has a whole list of undoubted advantages: – The unique hygroscopic properties of the capillary fibers of jute provide excellent waterproofing in the bathhouse. Jute is not completely saturated with dampness, but actively absorbs it. – Jute fiber does not wrinkle or compress, so it is ideal for filling grooves and any gaps. – Jute insulation “breathes”, providing air circulation, but retains heat perfectly, creating a microventilation effect. The composition of the air inside the building is qualitatively improved. – The increased strength of jute fibers guarantees durability in use. – For supporters of a healthy lifestyle and the use of natural materials, jute suits perfectly, even harmonizing in color with log walls. – Jute fiber contains an increased amount of the unique natural polymer lignin, which makes this material incredibly resistant to dampness and rotting. – Jute felt is not pulled apart by birds, and moths do not grow in it. – If the thickness is properly selected, the jute does not blow through and does not require re-caulking. – Jute insulation is inexpensive and will allow you to save a lot of money.
Safety
The insulation must be safe for human health. In the bath we enjoy the smell of natural wood and get healthier, so the materials used should not contain any harmful components.
Fire resistance
The insulation for a bath should not flare up from every little spark. Experts recommend using materials no higher than the second flammability group.
Biological resistance
The insulation should not attract the interest of birds and allow the emergence and proliferation of various fungi and bacteria.
Vapor permeability
In a steam room, humidity and temperature constantly fluctuate, and water condensation in the inter-crown space can only be avoided by using materials with a good ability to transmit moisture without rotting the wood. Therefore, pay attention to the vapor and air permeability coefficient of the material.
Country bathhouse
Durability
Good insulation lasts as long as the structure itself, and at the same time maintains its integrity and elasticity throughout the entire period of use.
What should you pay attention to?
It is recommended to insulate the walls in the bathhouse with materials that can transmit (not accumulate) moisture. This group includes jute, moss, flax, that is, all heat insulators of natural origin.
Experienced craftsmen advise not to be fooled by advertising or the experience of your neighbors, but to rely on the features of your building. The first thing you should pay attention to is the density of the insulation. For one-story baths made of profiled timber, the recommended thickness of the heat insulator is 3-4 mm with a density of 300-400 g/m2. If the building includes 2 floors, then the density of the material should be 700-800 g/m2 with a thickness of 8-10 mm.
The ratio of density and thickness plays an important role. For example, if insulation with a density of 300-400 g/m2 is laid with a thickness of 6-7 mm, then “voids” will soon appear. And vice versa. Installation of material with a density of 700-800 g/m2, laid with a thickness of 5-6 mm, will be considered too rigid. In this case, the insulation will not be able to evenly fill all the voids of the timber after shrinkage is completed.
What to choose
Since ancient times, natural and durable material – wood – has been used to build a real Russian bathhouse.
However, many years of experience show that it is impossible to achieve an ideal joint of materials either in manual cutting or in production, and this entails heat loss directly through the walls.
In this regard, even at the first stages of construction, each of the rows is laid with inter-crown insulation.
This allows you to completely eliminate heat loss through cracks in the walls.
Today, the most popular materials used as inter-crown insulation for baths are:
- Linen;
- Moss;
- Jute;
- Other insulation materials.
Let's look at each of the categories in more detail.
Important! All internal components of the wood structure must be dry and properly treated with antiseptics.
Felt (sheep's wool)
A natural material for insulation, which in its performance properties is superior to tape insulation made from plant fibers.
Felt is a worthy option for buildings made of profiled timber. It is simply irreplaceable for insulating residential buildings and baths, although it is not cheap.
During the production process, the felt seal is carefully treated with special fire-retardant compounds, as a result of which it absorbs moisture well and quickly releases it when heated.
It is resistant to mold and mildew and does not cake during use.
Choosing interventional insulation for a bath
In Russia, the bathhouse is traditionally built from wood. Wood absorbs moisture over its entire surface, followed by its distribution along the fibers and gradual removal through the ends of the log houses. This causes periodic changes in the volume of wood. In spring and autumn, the tree, gaining moisture, swells, and in summer and winter, when it is lost, it dries out. The result is the appearance of gaps between the crowns.
Due to the impossibility of ensuring a tight fit of logs or beams to each other, cold bridges are formed between the crowns, increasing the ventilation of the walls and inevitable heat loss. To eliminate the problem, insulating inter-crown spacer materials are laid between the logs or beams. Let's consider the most commonly used insulation materials, and which inter-crown insulation is best for a bathhouse built from timber and log frames.
What requirements must materials for baths meet?
To ensure long-term comfortable temperature conditions at high humidity during hygienic and health bathing procedures, interventional insulation must have the following quality properties:
- not contain or emit substances harmful to human health during operation;
- ensure uniform and tight closure of the seams between the crowns;
- low thermal conductivity;
- absorb and release moisture similar to wood;
- not affected by mold, mildew and insects;
- resistance to temperature changes;
- do not arouse interest among birds as a material for constructing nests;
- durability.
Natural:
- Natural moss. For thermal insulation of joints in wooden baths, red (cuckoo flax) and white (sphagnum) are used. The first type of moss has excellent properties, but is quite rare, which makes it difficult to harvest the required volumes. The parameters of sphagmum are somewhat lower (especially in terms of durability), but it is found everywhere. Due to the long time it takes to collect and properly dry the material, moss is gradually being replaced by other insulation materials. But it continues to be widely used in places of its mass growth, especially in the northern regions.
- Jute. It is obtained from the stem of a tropical shrub of the same name. Has all the above characteristics. The high content of natural resin (lingin), while giving the material excellent properties, makes it somewhat rough. Available for sale in the form of tow, jute cords, felt and flax-jute. The last two varieties are tape with the same density along the length. This is an excellent inter-crown insulation for a log bathhouse, but the difficulty of filling uneven grooves between logs with such a tape practically precludes its use as an inter-crown insulation for a log bathhouse (tow is used for such baths). The main disadvantage is the high cost.
- Linen. In addition to traditional tow, which, like moss, has been used since ancient times, it is produced in the form of a ribbon of interwoven flax fibers, called flax batting or “euro flax”. Can be used in any wooden baths, but is ideal for buildings made of timber.
- Sheep's wool. Rarely used due to high cost.
In all natural insulation materials, the presence of synthetics in the composition or adhesive compositions is unacceptable. It is recommended to purchase tow made of moss and jute in the form of rolls, which greatly simplifies its installation.
Artificial:
- PSUL is a polyurethane foam tape impregnated with acrylic mixtures to increase elasticity and strength.
- Polytherm is a tape consisting of thermally bonded polyester organic fibers; in fact, it is a padding polyester designed specifically for baths.
- Foamed polymers (spray foam, polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam and others).
- Mineral wool TechnoNIKOL.
- Silicone sealants.
To ensure comfortable conditions in the bathhouse, it is recommended to use only natural insulation materials in Russian bathhouses.
The main thermal insulators used: pros and cons
The origin of the word “caulk” is associated with hemp, from which hemp and twine for sealing cracks were made hundreds of years ago. Products based on this plant are still produced in separate nonwoven fabric factories. But sphagnum moss and “cuckoo flax”, which were once the most popular sealants in Russian wooden architecture, are now perceived as exotic. We will limit ourselves to considering what is present on the shelves of construction supermarkets and specialty stores.
Rolled flax insulation
Inter-crown linen seal
This inter-crown insulation is made from flax fibers using needle-punched technology. We can order any strip width from 3 to 40 cm in 0.5 cm increments. The thickness at a density of 700 g/m² is 8 - 10 mm.
Linen wool (as this thermal insulator is also called) is one of the best means for residual elasticity, heat conservation, environmental friendliness, and aesthetic properties. In addition, flax fiber tape is currently the most inexpensive way to efficiently caulk a chopped bathhouse. Rolled flax is easy to use. The strip is laid in the groove of the crown and adjusted with staples. The log can then be mounted. Wind is not a hindrance to installation.
Among the disadvantages of flax, it is not the best biostability. Birds happily take it out of the cracks to build nests. Some insects also live in this material.
Rolled jute insulation and jute-linen materials
Jute inter-crown seal
Thermal insulation made from jute is a coarse, homogeneous non-woven fabric produced using the same technology as the insulation made from flax. Jute inter-crown insulation is a durable and relatively rigid tape, which, in addition to good heat-shielding and hydrophobic properties, is distinguished by the presence of 20% lignin in its composition. Lignin is a resin similar in properties to the resins of coniferous trees. Thanks to its presence, jute exhibits both positive and negative qualities.
How to choose interventional insulation - the pros and cons of each type
Since ancient times, log baths have been insulated exclusively with caulking - when natural material was manually pushed between the logs. And this method, of course, has its undoubted advantages. But the downsides are not encouraging either: not only is all the work on caulking quite labor-intensive, requires special skill and takes place in more than one stage, but many bathhouse attendants have gotten into the habit of pulling out the caulking itself by birds. Why do experienced builders immediately recommend covering such a bathhouse with expensive siding - but why would it even be built from environmentally friendly, beautiful logs? But, fortunately, today there are already other types of interventional insulation - no less environmentally friendly, even more practical and not at all expensive. This article will help you decide which modern inter-crown insulation is better.
Inter-crown insulation: how to choose? What is the best inter-crown insulation for a bathhouse? These questions cannot be answered unambiguously - each has its pros and cons, and some advantages.
Inter-crown insulation made of sheep wool
A good inter-crown insulation for profiled timber is made from sheep wool. It is simply ideal for insulating a wooden bathhouse - although it costs quite a bit. But it does not cake at all and is significantly superior in quality to all modern tape insulation materials.
Tape inter-crown insulation
This insulation is quite new for the Russian market, but has already gained popularity. Its main advantages are that, in general, the entire assembly of the structure occurs quickly, labor costs are reduced, and the insulation itself does not accumulate moisture, is not blown, is hypoallergenic and is not at all attractive to birds. High-quality tape insulation is glued together after laying the walls.
Its composition is interesting: natural fibers are pierced by special needles with barbed hooks, and, intertwining with each other, these fibers form a fairly dense substance, which in its structure resembles felt. Its standard dimensions are as follows: length – 10-50 linear meter, width – 100/125/150/200 mm, and thickness varies from 5 to 15 mm. This insulation also has a different surface density – 300-800 g/sq.m.
But the most important thing is to correctly determine the thickness of the tape insulation, because... it must be selected depending on the thickness of the log house. So, for chopped wood you need insulation 15 mm thick, for ordinary timber - 8-10 mm, and for glued timber - 5 mm.
There are also some peculiarities of laying such insulation. So, if the timber is uneven, it is better to lay the tape in two layers.
The tape insulation itself today is made from flax or jute, or in a combined version - flax and flax wool, the percentage of the ratio of materials in which can be different. This is what determines their quality and scope of application.
Inter-crown insulation made of jute
The popular jute inter-crown insulation is today considered an excellent alternative to expensive caulk. It is a tape with a thickness of 5/10/15 mm, quite dense and uniform. You need to roll it directly along the groove, fixing it along the way with a construction stapler. And after laying the log house, the jute will become even more compacted - its fibers will stick together and acquire enviable resistance to wind and moisture.
Walls with this insulation turn out beautiful, with perfect seams, warm and do not need any other finishing. And jute fiber, unlike flax, is of uniform thickness and easily spreads over the crowns.
Intercrown linen insulation
Although this material also has its advantages. For example, it quickly absorbs and quickly releases moisture, and the walls really “breathe.” Linen is not allergic and not hazardous to health, does not create a static charge and is good at preventing the appearance of fungus on the walls. In addition, if the inter-crown insulation for the timber is made of flax, the bathhouse does not need any other ventilation. And the most important thing is that such insulation does not have a sharp edge, and therefore the bundles can be made by hand of any length and shape.
And finally, you can’t think of a more environmentally friendly material for wall insulation - it’s not without reason that even linen clothes are considered healing.
Combined insulation: interventional insulation flax wool
As for the combined options, the more jute in the tape insulation, the less water permeable it is. After all, this plant material contains a special lignin polymer, which holds together those same cellulose fibers in wood. But flax contains only 2% of this substance, and therefore it is more susceptible to moisture. In addition, the more flax in the insulation, the more likely it is that moths will eat it, but the pest does not like jute. And jute is blown much less than flax.
How do you know that there are no flax additives in inter-crown insulation? Easy - by color. It should be golden, i.e. light brown, but gray inclusions indicate that flax was added to it.
In general, combined materials for insulation can combine very different qualities, and therefore they are called universal. Their only drawbacks are rigidity and fragility, which, however, is regulated by the addition of flax to them.
So, have you made your choice? And now the most important thing is to lay the material correctly: slowly, carefully and without sparing the material. Then your bath will look beautiful and delight you with freshness and pleasant aromas.
stroy-banya.com>
What insulation is suitable for a bath?
Beginners often ask themselves the question: what insulation to choose for the walls of a bathhouse?
For a bathhouse, it is recommended to use inter-crown insulation for timber made of natural fibers. This seal does not accumulate moisture, provides good air exchange, and is resistant to rotting and destruction.
The best representatives are insulation materials made of moss, jute and flax, as well as their derivatives. They are successfully used for caulking wooden houses and baths.
To understand which is the best insulation for a bathhouse, you should pay attention to the main characteristic of the material – density.
For timber structures, insulation with a thickness of 4 mm and a density of 350–450 g/sq.m. is used.
For steam rooms made from rounded logs, products with a thickness of 5 mm and a density of at least 600 g/sq.m. are better suited.
For houses with 2–3 floors combined with a bathhouse, material with a thickness of 9–11 mm and a density of up to 750 g/sq.m is used.
To choose a quality sealant, you need to know what type of wood is used to build the log house.
For bathhouses made of timber and rounded logs, you can choose materials up to 10 mm thick - jute felt, flax felt, a combined version with jute and flax.
For a chopped-type bathhouse, it is better to choose insulation up to 15 mm thick - felt made of jute and flax, tow in ribbons and bales made of flax or jute, moss.
Necessity
This material performs several important functions at once:
- Reliably isolates the space between the crowns of the house, inaccessible for inspection, from water and moisture, which, over time, can seriously damage the house;
- Does not allow air to blow through the cracks between the logs;
- Compensates for changes in wood volume that occur due to seasonality and changes in temperature and humidity.
The timber is insulated both at the construction stage and after, the so-called caulking of the log house.
As a conclusion: the inter-crown seal serves not only as a heat insulator, but also:
- Performs waterproofing functions;
- Increases the service life of the building.
The choice of such material must be approached very carefully.
Methods for sealing inter-crown gaps
Regardless of what type of material was chosen for insulating a wooden structure, installation work is carried out in several available ways:
- No bends;
- With a bend on one side;
- With a bend on both sides.
Laying insulation without using bends is characterized by high quality of fit and small technological gaps.
The material is laid out around the perimeter of the log house on the base, and the next element is laid on top. Fixation is performed with a construction stapler.
For timber buildings, a one-sided bending installation method is used. To do this, take a compactor whose width is twice the width of the log. The strip is mounted with a one-sided bend on the lock. An additional rope made of jute or flax is installed on the outside of the wall.
Installation of insulation with a double-sided bend is carried out for buildings made of wild logs, fire monitors or rounded logs.
Often, such building materials are characterized by uneven dimensions at different ends.
The inter-crown insulation for the timber is fixed using a stapler, while the strips are folded in half and shifted in width. This allows for correct installation between different sized ends. In addition, this method prevents complete shrinkage of the wood.
The choice of the best insulation option for a house or bathhouse depends on many factors that experienced craftsmen take into account at the beginning of construction.
How to properly insulate a bath using jute tape insulation
A bathhouse is a room that should retain heat as long and well as possible.
You need to think about preserving heat in a bathhouse at the very beginning of its construction and select the best insulation for a bathhouse in advance.
- The first is laying in a groove without deflection.
laying inter-crown insulation in a groove without deflection
laying inter-crown insulation in a groove without deflection
When insulating a bathhouse, jute tape greatly simplifies the insulation process due to the fact that it is easy to unwind, adjust to size and fits neatly into the groove, and a wide product range allows you to select sizes without further adjustment to your bathhouse.
Basically, the insulation of a bathhouse depends on the preferences of the specialist and the features of the structure; a particularly important point is when after 7 - 9 months the bathhouse shrinks and tape insulation is required again. The fact is that after the construction of the bathhouse, shrinkage occurs, which entails the appearance of cracks and cracks between the logs; in this situation, they are simply caulked using jute tow, i.e. drive the tool into the cracks.
With the help of tape insulation and tow, you can insulate a bathhouse so well that for the next 10 years you will not think about the fact that good steam will come out.
Source of the article: https://mezhvencov.ru/statyi/materialy/dzhut-dlya-bani-uteplyaem-svoimi-rukami.html
Do-it-yourself finishing caulk
After the log house has been subjected to shrinkage, finishing caulking is carried out at home. During the shrinkage process, the previously laid layer of insulation is deformed, voids can form in the inter-crown cracks, and vertical cracks can form in the corners of the frame. The operation is performed from the outside and inside. Caulking is a labor-intensive process that requires diligence and attention; the main tool is a wide wooden chisel or rubber mallet. To avoid damaging the integrity of the fibers, it is better to blunt the chisel. The operation begins with the lower crown along the entire perimeter, after caulking of the first crown is completed, they move on to the second, etc.
How to insulate a bathhouse from the inside?
All work on internal insulation is divided into three stages: floor, walls, ceiling. Often the procedure begins with a pre-prepared base. Its base can be either concrete or ordinary soil. In the latter case, you will need to make a sand and gravel cushion on the ground with a layer thickness of no more than 40 cm.
Creating a warm base
Which wooden bathhouse is the warmest, with a dirt or concrete floor? Of course, the option with cement mortar is more modern and practical, so we will insulate it.
- Cover the concrete base with roofing felt or bitumen mastic;
- Secure the support bars under the joists;
- Install the logs on the supports so that their ends meet the walls;
- The resulting cells between the logs are filled with expanded clay;
The thicker the expanded clay layer, the lower the level of heat loss
- Cover the floor frame with waterproofing film;
- Install insulation between the joists, put mineral wool in the steam room, and foam plastic or expanded polystyrene in the dressing room;
- On top, the structure is covered with a vapor-proof membrane;
- Afterwards, a rough version of the floor is knocked down, onto which the desired material is mounted.
Please note: ceramics and solid boards are used most often in the bathhouse, tiles are not afraid of dirt and deformation due to moisture, although wood swells, it is warmer.
Wall decoration
This algorithm of actions will help you figure out how to properly insulate a steam room, dressing room and other rooms in a wooden bathhouse:
Do it right! All work on wall insulation is carried out from the ceiling to the floor!
- Initially, the surface is impregnated with biocidal impregnation;
- Next, the seams are processed - place the material in the grooves between the beams and caulk it thoroughly;
- Apply a moderate layer of sealant on top of the fabric;
- Afterwards, a special frame is installed, similar to what was done outside;
- A heat insulator is placed in it - only material resistant to high temperatures can be installed in the steam room; gypsum fiber, magnesite boards and mineral wool will do;
- A vapor barrier is placed on top - is it worth using foil? It’s not just worth it, it has practically no alternative, well, if you don’t take into account the innovative foil penotherm;
- Next, a frame is mounted to secure the cladding, taking into account the required two-centimeter gap from the vapor barrier layer.
There is no need to rack your brains for a long time about how to insulate the ceiling. From the inside the procedure is similar to the walls, but from the attic it looks a little different.
Ceiling insulation
A little outdated, but still effective ceiling insulation.
Experts say that to minimize heat loss, sealing the outside of the ceiling is mandatory! Let's look at this simple technique:
- Place fiberglass on the ceiling to prevent moisture from entering;
- Mix a solution with high thermal insulation qualities - for this you will need clay, chopped straw, water and sawdust. All ingredients are mixed until thick in one to one proportions;
- Fill the space between the beams with mortar, controlling the level of moisture insulation on the inside of the ceiling;
- Leave the work for several weeks until the solution dries completely;
- Then, dense insulation and a moisture-proof membrane are laid;
- A thin cement screed is poured on top - fixing it.
At this point, the complex of work on capital insulation of the bathhouse can be considered completed. Many will wonder whether it is necessary to make so many unnecessary movements for the sake of short-term pleasure? Anyone who wants to feel the real heat of an old Russian bathhouse will definitely say - it’s a must! Moreover, such leisure also has a healing effect.
What is jute insulation
Jute is a kind of annual short- and long-fruited shrubs, herbs and plants of the Malvaceae family, and is a spinning crop.
Jute mainly grows in India, Asia, Africa, America and Australia; there are about 80 species of this plant. Jute insulation is traditionally used for insulating walls, eliminating gaps and cracks in a wooden house because... Over time, cracks and gaps appear, and it is in them that moisture accumulates, in addition to blowing heat out of the house.
It is tape insulation that is best suited for insulating a bathhouse or home; it perfectly absorbs and releases moisture that penetrates and accumulates in the cracks, and also prevents the process of rotting.
Changes in the size of walls and the appearance of gaps in them occur due to the fact that wood absorbs moisture very well; in addition, moisture gets into the cracks of the wood and the process of rotting of the house occurs.
In order to avoid these problems, in the construction of wooden houses, inter-crown insulation is used; it is an excellent insulator thanks to which the joint of the log becomes airtight and helps to normalize the moisture absorption process.
Advantages and distinctive features of 100% jute insulation
The distinctive features of jute insulation are: it contains only primary jute fiber without the addition of firewood, flax and other materials that lower the price of jute, but at the same time reduce its quality.
The correct jute insulation is made only by the needle-punched method, without thermal bonding, due to which there are no impurities of fusible polyester in its composition and its thickness and width are uniform throughout the length of the entire roll.
It is precisely thanks to the needle-punched method of jute production and the fact that it was brought to our company straight from Bangladesh that it has absolutely no foreign odor or impurities, and also does not wrap around the drill.
Jute insulation in rolls can be easily unwound and cut, making it easy to place it between a log house and insulate a bathhouse or house.