On the eve of winter cold, the question of how to prepare water for heating systems becomes especially important. Proper water preparation is doubly important for owners of private suburban areas that are not connected to a heating plant and receive water from wells or wells. If the water is hard and contains foreign impurities, for example, iron or manganese, this can lead to failure of not only plumbing fixtures and household electrical appliances, but also damage to heat exchangers, corrosion of pipelines and radiators.
Heating system of a country house.
The first and most important stage of work
The main thing that should be done before planning water treatment measures for a heating system is to conduct a chemical analysis of the composition of the water.
Known (a) and proposed (b) schemes for preparing water for heating: 1 - water heater; 2 — steam-water heater; 3 - refrigerator; 4 - nutrient tank; 5 - high pressure manifold; 6 - low pressure manifold; steam; condensate.
You can carry out tests at home using test kits for aquariums (they are sold at any pet store). However, in order to obtain more accurate values and most effectively prepare water for heating, you should use the services of a certified laboratory.
Water for analysis is collected in a 1.5 liter plastic bottle from non-carbonated drinking water. It is unacceptable to use bottles of sweet carbonated water and other drinks. The cork and bottle are washed well with the same water that is taken for analysis; no detergents should be used. The water is first drained for 10-15 minutes to prevent stagnant water from entering the sample, as this may affect the test results.
To prevent water from being saturated with oxygen dissolved in the air, it is drawn in a thin stream so that it flows down the wall of the bottle. Water is poured under the neck. The bottle is tightly wrapped with a cork to prevent air from entering under it. Oxygen causes chemical processes to occur, and this can also affect test results. If it is not possible to immediately take the samples to the laboratory, then the water can be stored in the refrigerator (not in the freezer!), but no more than two days.
Heating system.
A comprehensive water analysis includes checks for the following indicators:
- rigidity;
- iron;
- manganese;
- pH (degree of acidity);
- permanganate oxidability (indicates the presence of organic substances in water);
- mineralization;
- ammonium;
- oxygen saturation;
- turbidity, color, smell.
If necessary, samples are taken for the presence of microorganisms. Some of them, such as legionella and amoeba, not only can cause serious harm to health, but can also settle inside pipes, forming a slimy microbial film. This promotes corrosion and degrades heating quality.
Related article: Frame country house: do-it-yourself installation
First stage
The first stage of preparing water for the heating system is the most important. First you need to conduct a chemical analysis of the water that will flow into the heating system. Before filling the heating system with water, such studies can be organized at home, however, more accurate results can only be obtained in laboratory conditions.
Tip: To collect water for analysis, you need to prepare a plastic bottle in which water without gases was stored. The volume of the bottle should be one and a half liters.
The bottle and stopper must be thoroughly rinsed with the same water that will be used for research. Detergents should absolutely not be used. Before filling the bottle with water, you need to wait 10 minutes so that stagnant water does not get into the bottle. It is best to pour water in a thin stream, as this will prevent it from being saturated with oxygen. The water must be taken for analysis as quickly as possible, and if this is not possible, it can be stored in the refrigerator for some time, but not in the freezer. The shelf life is no more than 2 days.
Distilled water for heating
A comprehensive water analysis will help check its following characteristics :
- The presence of iron or manganese in its composition;
- Acidity level;
- Oxygen saturation;
- Smell;
- Color;
- Level of mineralization;
- Permanganate oxidation;
- Rigidity;
- The presence of ammonium in the composition.
In laboratory conditions, you can also take samples for the presence of various microorganisms. Some microorganisms, such as amoebas or legionella, can not only cause damage to human health, but also settle in pipes, thereby forming a microbial film of a mucous nature. The quality of heating can be significantly reduced and, in addition, microorganisms can contribute to corrosive effects.
Tip: The water in the heating system should not be too hard or too soft. A good option is distilled water in the heating system.
The normal hardness level should be from 7 to 10 mEq per liter. If the indicator is exceeded, it means that the water contains various salts. The most common are magnesium or calcium salts. When water is heated, these salts will be converted into scale, which can significantly reduce the efficiency of the heating system. Scale can also lead to faster wear of the heating system elements and you will have to drain the water from the heating system and change some of them.
Tip: Hot water from a heating system that is too soft can be just as harmful to the heating system components as hot water that is too hard.
Water too hard and too soft
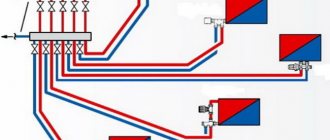
An example of a boiler room diagram for a heating system that provides quick installation and comfortable heating and hot water preparation in a private house, cottage, or country house.
Normal hardness values are 7-10 mEq/l. If this value is exceeded, it means that the water contains an excess amount of calcium and magnesium salts. When heated, the salts form a precipitate known as scale. Accumulating inside pipes and radiators, scale interferes with heat transfer and contributes to wear and tear of the heating system.
The most affordable way to soften water is boiling. During heat treatment, carbon monoxide is removed, and therefore calcium hardness is significantly reduced. However, some calcium remains in the water, so boiling will not completely remove hardness.
Another cleaning method is to use filters with scale inhibitors (neutralizers), such as lime, caustic soda, soda ash. Hard water is also passed through ion exchange resin filters, replacing potassium and magnesium ions with sodium ions.
The use of magnetic softeners is a reagent-free method of water softening. Under the influence of a magnetic field, the properties of water change so that potassium and magnesium salts lose their ability to form as solid sediment and are released in the form of loose sludge. However, salts still remain in the water and need to be removed. In addition, this method is not as effective at water temperatures above 70-75 degrees (that is, the temperature common for boilers, water heaters and boilers).
Rough cleaning and deferrization of all water, water softening for heating and hot water supply (DHW) systems.
Reverse osmosis purification involves forcing water through a special membrane that traps harmful substances. This allows you to completely remove calcium and magnesium salts, which cause scale. But this method also has disadvantages: the high cost of treatment equipment and the consumption of a large amount of water during cleaning (for 1 liter of clean water, approximately 2 to 10 liters are drained into the sewer).
Too soft desalted water, for example, rain or melted water, is no less harmful to the heating system than hard water, since the calcium salts contained in the water neutralize acidic reactions, slowing down corrosion. Therefore, before using rain or melt water for the heating system, you should let it settle for several days and refill it only after making sure that its pH level is in the range of 6.5-8, but not lower. This is especially important if the wiring was made from non-galvanized pipes, which were initially susceptible to corrosion.
Article on the topic: Do-it-yourself children's attic bed using the tongue-and-groove principle
Softening hard water: take care of your health!
We are taught hygiene from childhood, and the procedures of hand washing, washing, morning/evening shower, and taking a bath become mandatory. One way or another, much in our lives is connected with water. But many people do not even suspect the harm that water that has not undergone the necessary purification causes to humans.
Softening hard water: make everything as safe as possible!
Let us dwell on the properties of water in which the content of calcium and magnesium salts – hardness salts – is increased.
For hard water, softening is a necessary procedure, because otherwise the liquid from the tap can cause great harm.
Hard water is extremely dangerous for people: it contributes to the accumulation of salt in the body. This leads to problems with the joints (diseases such as arthritis and polyarthritis can develop), the formation of sand and stones in the urinary system (kidneys, bladder) and gall bladder. This happens not only when you drink hard water, but also when you take a shower or bath. Therefore, softening hard water is a necessary process for those who care about their health.
Hard water is also dangerous for heating and water supply systems, pipelines, boilers, boilers, as well as household appliances, since it leaves scale on the walls of pipes and on heating elements.
Not only the health of the owners and household appliances suffer from untreated water in a private home or cottage. Hardness salts have no less influence on the condition of the skin and appearance of a person. This can be understood by paying attention to how you feel when washing your hands and face. Hard water dries the skin and hair, causes a feeling of tension, and requires a large amount of detergents and various cosmetics to moisturize. In this case, the protective layer of the skin is damaged, which again requires restoration measures.
Isn't it better to think about properly softening hard water than to deal with the consequences of exposure to hardness salts?
Softening hard water: how to properly deal with hardness?
A hard water softener filter can solve all these problems. There are several types of such devices, but the most practical and inexpensive is a filter based on ion exchange. As a result of softening hard water with such a filter, calcium and magnesium salts remain in the filter, and clean water flows directly into the house.
Methods for deferrizing water
Rough cleaning, reagent disinfection and deferrization of all water, elimination of excess chlorine and sorption additional purification of water, water softening for heating and hot water systems.
The maximum permissible iron content in water for technical needs, in particular for the heating system, should not exceed 1 mg/l. The ideal value is 0.3 mg/l. An excess of iron leads to silting of the internal surfaces of pipes and the proliferation of bacteria in the ferrous sediment, which occurs especially actively already at 30-40 degrees Celsius. This leads to rapid wear and tear of the hot water supply and heating system.
The easiest way to deferrize is settling. Under the influence of oxygen, the iron contained in the water oxidizes on its own, forming a rusty sediment. To carry out iron removal yourself, you will need a large tank with a capacity of 200-300 liters and a device for pumping oxygen: a spray unit or a compressor (for small tanks a regular compressor for aquariums is suitable).
To deferrize water, the same method is quite applicable as to soften it - using the reverse osmosis method. Filters with ion exchange resins are also used. To prevent the proliferation of iron bacteria, chlorination (50 mg/l) is used, but first you should find out how resistant the installed water supply facilities are to chlorine.
If the iron content in water is over 5 mg/l (which is not uncommon for water from wells), then filters with glauconite sand enriched with manganese oxide are used for purification. After passing through a filter medium that serves as an oxidation catalyst, the water gets rid of iron, manganese and hydrogen sulfide, which precipitate. When such a filter becomes clogged, it must be washed with solutions that restore its oxidizing capacity (potassium permanganate solution). It should be remembered that with this cleaning method, harmful chemicals are discharged into the sewer system, so it can only be used if there is a centralized sewer system on the site. Removal of mechanical impurities, manganese, microorganisms, oxygen
Rough water purification, removal of dissolved gases, deferrization, sorption purification, water softening and disinfection.
To remove foreign impurities (sand, peat fibers, phyto- and zooplankton, fine clay, dirt, organic substances, etc.), various mechanical filters equipped with washable or removable cartridges are used. For very heavy contamination, pressure filters with granular loading are used (quartz sand, expanded clay, activated carbon, anthracite).
The most obvious sign of the presence of manganese in water is a black precipitate. Its concentration rarely exceeds 2 mg/l, but already at a concentration of 0.05 mg/l, manganese can deposit on the walls of pipes, gradually clogging them. Typically, manganese is dissolved in water along with iron, so that with the de-ironization of water, demanganation also occurs simultaneously. To remove manganese, filters with ion exchange resins are used.
Related article: Glass sink: advantages and selection criteria
To disinfect water, that is, remove viruses, bacteria, protozoan microorganisms, ozonation, chlorination, and irradiation with ultraviolet rays with a wavelength of 200-300 nm are used.
Rough cleaning, reagent disinfection and iron removal, water softening, elimination of excess chlorine and sorption purification of water, final fine cleaning.
The ultraviolet irradiation method is the safest method of water disinfection among the above, since it does not affect its chemical composition, affecting only harmful microorganisms. Water disinfection using UV units occurs in a few seconds.
The corrosive activity of water strongly depends on the presence of oxygen dissolved in it. The dissolved oxygen rate for closed and open heating systems is the same and is no more than 0.05 mg/cub.m. To reduce the oxygen content in water, deaeration units and columns are used.
To prevent oxygen from entering heating systems in other ways (with air), you need to monitor the overall integrity and tightness of the system and not fill it with water too quickly, as this contributes to the formation of air locks. If pipes made of gas-permeable materials, such as polyethylene or polypropylene, are used, they must be protected with an anti-diffusion layer of aluminum.
Methods and methods of water preparation
Many negative factors are eliminated by preliminary heat treatment and filtration. In other cases, the preparation of water for a heating system includes several stages of purification with additives and reagents to give the coolant the desired characteristics.
Methods that can be used before filling the heating system:
- Adding reagents. These are certain chemicals that reduce the excess content of certain components that negatively affect the system.
- Catalytic oxidation. Required when there is a high content of iron impurities. The oxidative process binds impurities and removes them as sediment.
- Filtration. Various mechanical type filters are installed for the process. The filling of the units depends on the chemical composition of the water.
- Softening through the use of electromagnetic waves.
- Freezing, boiling or settling water for a certain period of time. The result is distilled water for heating, which is considered the best coolant.
- Deaeration process. This is necessary when there is an excess of oxygen, carbon dioxide and other gases.
Important! Pre-filtration removes impurities and sediments. When the percentage of impurities is small, flushing or replaceable cartridges are sufficient; if there are a lot of impurities, then filters with a multilayer composition of quartz sand, activated carbon, anthracite or expanded clay are required.
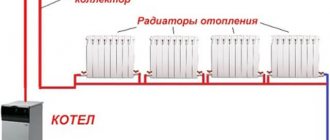
Flushing the heating system from scale
Rough purification and deferrization of all water, water softening, elimination of excess chlorine and sorption post-purification of water, ultraviolet disinfection.
Proper preparation of water for heating systems includes: mechanical cleaning of contaminants, softening, deferrization, removal of manganese and, if necessary, disinfection and deaeration. Distilled water, settled water, melt water or rain water is suitable for filling into heating systems. Heating water with corrosion and scale inhibitors is sold in specialized stores. It is good because it does not need to be prepared before pouring it into the heating system.
The most thorough water preparation does not eliminate the need to monitor the heating system, especially in a private home. If there is a noticeable deterioration in the quality of operation of the heating batteries, the system is flushed. To do this, the water is drained, then the radiators are dismantled. The bottom of the bathtub is covered with rags, the sewer hole is covered with a mesh to prevent fallen pieces of scale from getting there. Then a radiator with the plugs removed is brought into the bathroom and installed.
Washing is carried out using a flexible hose, removing the shower head from it. The radiator should be turned over periodically when flushing. A metal rod is used to remove large pieces of scale. Flushing is completed when pieces of scale stop being washed out of the radiator and the water becomes clear.
Preparing water for the heating system
When designing your own home or private project, you cannot help but take into account the very impressive costs of the heating system. But not only do you need to select the most optimal system and decide on the power source, but preparing water for heating systems in a private home will be a costly issue. Both the quality of heating and the longevity of its operation depend on how high-quality, soft the water in the heating system is.
Heating systems: how not to get confused with the choice?
There may not be so many heating systems. But you will have to choose one and each consumer will have to do it independently. In central heating systems, the choice is not great, what can a given budget be spent on, or what are the possibilities for a certain object or objects that will have to be heated, that system will be installed. Private owners are forced to make decisions and bear responsibility on their own.
The table below shows the features of the use of various heating systems. This way, any user can get his bearings at least at first, which can be immediately dismissed.
A heating system is understood as a set of equipment for generating, transmitting and delivering heat to the end consumer. In general, the heating system consists of a heat source (as can be seen from the table - different types of gas, electricity, diesel fuel), heat pipes directly from the heating devices. In an apartment, these could be radiators or batteries.
Heating can be done using liquid or hot steam. They can heat with ordinary water or with a special antifreeze liquid that does not freeze. And since heating comes with water, all the problems associated with it result in problems of softening and preparing water for the heating system.
Choosing a heating system should, first of all, solve the question: what source will the consumer use? That is, will the water be heated using wood, gas or electricity? By the way, the water treatment system also depends on such nuances, because the influence of heat from electricity and heating of water from firewood has different spheres of influence on the surface.
Based on the selected source, the corresponding boiler is selected. After this, it is already chosen how heat will be supplied to the end consumer - immediately or through radiator pipes. Immediately - these are warm floors, warm walls, that is, there is no branched heating system through pipes. But the most popular heating systems are still boiler houses. Boilers can be single or double circuit. That is, they can heat the coolant directly or they can also heat water for the coolant.
When working with heating systems, it is important to remember the features of their operation. Such systems are used in Russia, for example, for an average of 210 days a year. For the rest of the time, the system is preserved, first preparing it for this process. In the same way, before the start of the heating season, the system is prepared again. Rinse. Remove debris and do light cleaning.
After installing the system, check the pipes for the presence of debris in them. After this, cold water is run into the system at maximum pressure and washed for no more than three hours. The water from the system should come out clean after such flushing. This way they get rid of construction waste after installation, and after conservation they wash out the lime, which is often left inside the system so that bacteria do not breed there and silt-like growths do not form.
After this, the first batch of water is heated and water at boiling point is introduced into the system. Flushing with boiling water helps remove oily residues from the system and partially wash away rusty residues. Even if there is a water purification system, the heating system will have to be flushed at least twice a year, before conservation and before starting the system.
How to properly prepare water for use in a heating system?
It turns out that if you operate a heating system, then very high demands should be made on the quality of water. If after twenty years the consumer does not want to endure the costs of pipes covered in dirt, rust and scale, then it is very important to install the correct treatment system and use exclusively treated water for heating. And such water should enter the boiler, for example, for heating.
When working with low-quality, especially hard water, there is a high risk of rapid failure of heating systems. Therefore, preparing water for a heating system is, first of all, softening, provided that the water is supplied from a centralized water supply system.
If you do not use cleaning, you will have to spend quite a lot on constant descaling so that the pipes do not clog and the boiler does not explode. And caustic chemicals harm equipment and are expensive.
Therefore, it can only be prepared by purifying the water. Although progress has gone far ahead, the main stages of cleaning remain the same:
- Mechanical cleaning – removal of any solid impurities;
- Settlement or sorption;
- Cleansing from harmful bacteria and foreign salts, including ferrous ones;
- Direct water treatment for heating and water supply systems.
In short, the ideal option for preparing water for a heating system will look like this. If the heating system is located in frosty areas, then additional antifreeze will be added to it without fail. If these are hot countries, then the water can be supplemented with special substances so that silt does not form and algae do not grow due to the heat.
A variety of devices can be used as softeners in such a system. Electromagnetic water softeners AquaShield are extremely popular because of their simplicity. They not only make the water softer, but also thoroughly clean the internal surfaces of the equipment from old scale.
Good old cationic resins are often used for softening. There is no substitute for them for water treatment. Nothing will make the water softer than these devices. But over time, the quality of such cleanings decreases and the resin needs to be changed. After replacement, the quality of cleaning returns. But such replacement parts are quite expensive and are expensive for heating systems. True, in industry such systems are used with recovery tanks. Then the costs are reduced, although not by much.
You can soften water using conventional chemicals. But in this case, there is a risk of getting other growths on the equipment. And it’s not clear how to delete them, because... it will no longer be scale.
Oxidizing agents are used to remove iron deposits. Iron salts become heavier after reaction and can be easily removed from the equipment.
And another fairly common stage in heating systems is deaeration. It is used to remove dissolved gases from water.
We learned that preparing water for heating systems is a complex multi-step process that allows us to obtain water of a certain composition that would not lead to the formation of various harmful growths inside the equipment.