Supply and exhaust ventilation units are efficient, reliable and durable. But! They are expensive.
Therefore, many homeowners, faced with a lack of clean air in their apartments, try to solve the problem on their own. They build forced ventilation with their own hands. The seemingly simple task of “how to properly make forced ventilation” is fraught with many pitfalls. It is not enough just to select powerful fans and lay inconspicuous air ducts. It is necessary to calculate all elements of forced ventilation, their proper placement and layout.
About forced ventilation
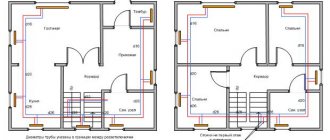
in a private house, ventilation equipment is usually placed in the attic.
The air flow generated using mechanisms and supplied to the room is called a forced ventilation system. In the direction of air movement it can be:
- supply;
- exhaust;
- supply and exhaust.
By air delivery method:
- with air ducts;
- without air ducts.
Many apartment owners limit themselves to forced ventilation, when the air supplied by a fan creates increased pressure. This enhances the displacement of exhaust air through centralized ventilation ducts.
Another way to improve air exchange is forced exhaust ventilation. The outlets of the ventilation ducts in the kitchen, toilet and bathroom are equipped with exhaust fans. They create rarefaction in the air. To make up for the shortage, air enters the apartment through vents or air supply devices.
On the upper floors of high-rise buildings, the above methods rarely fully satisfy the need for fresh air.
The most effective is a forced supply and exhaust ventilation system. In which both the supply and exhaust of air are provided by mechanisms. Assembling it yourself is not so difficult, especially if you use our tips.
Forced ventilation device
the snail fan is very powerful, but noisy.
A forced ventilation device in an apartment or cottage is a combination of elements for various purposes, which all together perform one task:
- Air intake grilles. They protect air ducts from mice, insects and debris. Attached to the outside of the air ducts;
- Filters. Cleans the air from dust and fluff. Especially thin ones even deposit plant pollen. There are many modifications of filters of different shapes and degrees of purification;
- Air valves. Necessary for adjusting the air flow supplied from outside. In the cold season, protect the system from icy gusts of wind;
- Fans. Create a constant air pressure in the ventilation ducts;
- Sound absorbers. These are materials that absorb mechanical noise and aerodynamic noise in air ducts;
- Heaters. They heat the supply air in winter;
- Ventilation ducts or air ducts are pipes through which air moves;
- Automatic block. When doing forced ventilation in a private house with your own hands, as a rule, this unit is neglected. Automation controls the system, turns fans and heaters on and off. The most advanced modifications change the speed of the blades.
Ventilation device
Artificial ventilation differs from natural ventilation in its ability to forcibly create and control the movement of air flows of the required intensity. This category includes both ordinary household fans for exhaust vents and expensive complex air conditioning systems.
When choosing the optimal system option, it should be taken into account that its effectiveness depends on operating conditions. Inexpensive types of household mechanical ventilation are usually designed for installation on standard ventilation ducts. More complex systems require separate ductwork, increasing not only efficiency but also overall cost.
The device for domestic forced ventilation is quite simple. It is a combination of various elements that activate or improve the quality of air exchange. The classic elements of the system are:
- Protective grilles for ventilation ducts. They protect the exhaust openings from the entry of debris, insects, and small rodents, but do not impede air movement.
- Air filters. A forced ventilation system equipped with an air filter allows you to protect the room from fine dust and flying debris. There is a huge variety of filters of varying degrees of purification.
- Air valves. They help regulate the air flow coming from the street through the air intake. Provide additional protection for ventilation elements during the cold season.
- Mechanical fan. The main pumping element of each forced-air system, on which the ventilation performance indicator depends.
- Sound absorbers. Allows you to reduce the noise level during system operation.
- Heater or recuperator. They help equalize the temperature between incoming and outgoing air flows. Using a recuperator reduces energy costs for heating the room.
- Air ducts and ventilation ducts. Air duct pipes are an essential element of any ventilation system. They supply fresh air from outside, regulate movement through the building and remove it from the premises.
- Automatic climate control devices. They differ in variety, cost and range of functions. For example, the compact and inexpensive tion o2 fresh air breather allows you to forget about ventilating your apartment or office, providing round-the-clock freshness with the windows closed.
We recommend that you read: Equipment for cleaning ventilation in apartment buildings
A forced system is needed when natural ventilation cannot cope. The easiest way to organize a mechanical hood yourself. But the best option remains the use of automatic climate control devices. They allow you to control a whole range of parameters of incoming air under any weather conditions.
The optimal choice of equipment for creating a high-quality forced ventilation system depends on the type of room in which it will be used. The garage does not need an air ionizer or a system for maintaining optimal temperature around the clock. A typical apartment rarely needs a separate recuperator. But it helps to significantly reduce home heating costs. There is a recommended set of devices for each room.
Selecting a forced ventilation scheme
- Combined. With such a system, forced exhaust is combined with natural air supply or vice versa. The most widely used ventilation device in an apartment or private house. Installation is quite simple and does not require special care. We have already mentioned the disadvantages above.
- Forced supply ventilation with cooling requires the introduction of an air conditioner into the system. Such equipment is installed directly on a riser or a private house; it is quite expensive and cumbersome.
- Forced supply ventilation with air heating. The easiest way to organize it is to install a recuperator. It will save energy costs by using the heat from the exhaust air. The downside is that the recuperator is quite expensive.
- Supply and exhaust forced ventilation with recirculation. Exhaust air is filtered, partially mixed with street air and returned to the room. Such a forced ventilation device is quite complex, so only experienced craftsmen undertake to do it in an apartment with their own hands.
In the house
High-quality mechanical ventilation in the house is an important condition for the comfort of country real estate. The construction design of apartment buildings initially includes ventilation ducts hidden in the walls. And for country cottages they are often considered as a separate additional element of comfort. The presence of an attic space opens up many possibilities for ventilating a private home, allowing you to choose an option of any complexity within your means:
- Combined system. A combination of forced exhaust and natural air supply into the room. It is easy to install and maintain, but often leads to increased energy costs for cooling or heating the incoming air.
- Forced supply ventilation with cooling. It involves installing an air conditioner at the inlet, supplying immediately cooled air. Increases the comfort of living in the house during the summer heat.
- Forced supply system with heating. The ventilation ducts are upgraded with a heat exchanger or recuperator, which helps equalize the temperature of the incoming air with the outgoing air. Efficient, economical and comfortable, but quite an expensive option due to the high cost of the recuperator.
- Supply and exhaust unit with air recovery. It uses a special supply and exhaust ventilation unit that can heat or cool the incoming gas by mixing air coming from the room. Thanks to heat exchange, the fresh air temperature approaches the optimum, allowing you to save on heating or cooling to comfortable values.
- Air conditioning system. An effective but expensive option in which supply air is supplied and serviced by an air conditioner. Depending on the power and set of functions of the device, the incoming air masses can be cooled, heated, subjected to ionization, cleaned of dust, bacteria, and qualitatively improved in any other way necessary for the user.
We recommend that you read: Do-it-yourself ventilation in the garage: photos, videos.
The simplest and most inexpensive ventilation device in a private home is a supply valve. The device consists of a damper with an air filter and is easy to install yourself.
When choosing the optimal ventilation option, keep in mind that high-quality gas exchange not only helps create a comfortable atmosphere in the house. It prevents the appearance of mold, dust, bacteria inside the rooms, maintaining the health of residents and the normal operational characteristics of the property itself.
Calculation of forced ventilation
compact installation for forced ventilation
If you are planning to make forced ventilation in a private house with your own hands, you should first carry out calculations. Quite complex calculations are required for forced supply and exhaust ventilation:
- Performance;
- Power and number of fans;
- Noise level;
- Air duct cross-section;
- Power and types of auxiliary devices: heaters, recuperators.
Before doing forced ventilation, it is important to carry out the calculations correctly.
Calculation by multiple
This is one of the main quantities used when calculating a forced ventilation system. The air exchange rate shows how many times the air in the room should be changed in 1 hour. For example, a multiple of “2” means that the air will change twice in an hour.
Air expansion table according to SNiP
| Purpose of the room | Temperature in winter | Exhaust air volume or multiplicity |
| Outflow | ||
| Bedroom, living room | 20 | 3 cubic meters of air per 1 square meter of living space in a room |
| Shared bathroom | 25 | 25 cubic meters per hour |
| Toilet | 18 | 25 cubic meters per hour |
| Bathroom | 25 | 25 cubic meters per hour |
| Pantry | 18 | 1.5 (multiplicity) |
Calculation by area
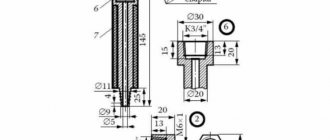
selection of the cross-section of the air duct
This calculation is suitable for home craftsmen who decide to assemble the forced ventilation of a private house or apartment with their own hands. Calculation of forced ventilation averaged for rooms with a height of about 3 meters: air flow per 1 sq. meter of total area is 3 cubic meters per hour.
Calculation of the area of ventilation ducts
The cross-sectional area of the air ducts is also very important for the effective operation of the forced ventilation system. The cross-sectional size is affected by the volume and speed of exhaust air.
Now we choose with our own hands which type of hood: forced or natural, which is better for ventilation. In the first case, the air speed should be about 3.5 m/second, in the second - about 1.5 m/second.
To select the correct cross-sectional area of the air ducts, use our diagram.
Calculation by area
Calculating mechanical ventilation by area is the second way to calculate the overall performance of a future forced air exchange system. This option is often used to calculate a DIY installation. During calculations, it is recommended to adhere to the general recommendation, regardless of the size of the premises. It consists of the following - for any room with a ceiling height of no more than 3 meters, the final air flow is three cubic meters per square meter of area per hour.
We recommend that you read: Ventilation in the incubator
Calculation of the cross-section of air ducts
Calculating the area of ventilation ducts is an important point in the design of each ventilation system, regardless of complexity and performance. The cross-sectional area of the air ducts is a parameter that directly affects the maximum speed of movement and volumes of exhaust air.
For natural ventilation, the normal speed of air flow is one and a half meters per second, for forced ventilation - 3.5 m/sec. It is not difficult to calculate the optimal cross-section of the air duct, knowing the operating capacity of the assembled structure. The second option for carrying out calculations is to use diagrams for selecting air duct sections containing standard recommended values.
Air distribution
The efficiency of forced ventilation in an apartment assembled with your own hands is often reduced due to poor air distribution.
With well-planned air distribution, there are no “dead zones” with standing air in a house or apartment. The lower the air exchange rate, the higher the likelihood of this phenomenon.
For inflow into the living room, install 2 supply distributors on the side of the outer wall, and 1 or 2 exhaust distributors on the opposite wall.
The best air distributors for forced ventilation systems not only quietly supply air to the room, but are also discreet. The simplest distributor is a metal plate drilled for a “colander”. Having thought it through and calculated well, you can make holes directly in the air duct.
You can hide the supply openings behind curtains, under a sofa or closet, or between ceiling levels. Exhaust grilles should be placed as high as possible.
The ratio of inflow and exhaust depends on the nature of the room and the lifestyle of the household. For example, in a living room for smokers, the exhaust fan should be more powerful than the supply fan. This creates a vacuum in the air and prevents smoke from penetrating into adjacent rooms.
The ventilation of the kitchen and other rooms with high humidity levels is calculated using the same principle.
Selection of equipment for forced ventilation
an approximate set of components for home ventilation
When starting to make forced ventilation in a private house with your own hands, you can choose one of the options:
- Inexpensive systems assembled from disparate components;
- An improved forced ventilation system in an apartment, often containing a recuperator.
Most home craftsmen with skills opt for the second option. It is better to overpay for high-quality equipment and install it, saving on installation.
Installation location
distribution of exhaust fans in the kitchen
The location for the ventilation unit should be as far as possible from bedrooms, children's rooms and recreation rooms.
Options:
- Kitchen;
- Hallway;
- Balcony.
It’s much easier for owners of private houses; they also have attics. And the neighbors are far away.
Equipment with good sound insulation is almost inaudible behind 2 closed doors.
Air balance
When calculating forced ventilation, a positive balance should be maintained. This means that the volume of supply air is greater than the volume of exhaust air.
The main rule: air moves from clean rooms (bedrooms, living rooms) to dirty ones (kitchen, bathroom).
If it is customary in the house to tightly close doors with baseboards, you need to equip them with grilles for ventilation. Then the air can circulate freely from room to room.
Air is supplied and removed mechanically into enclosed spaces.
The ratio of supply and exhaust in premises for various purposes.
| Purpose of the room | Innings | Outflow |
| Living room | 200 cubic meters/h | 200 |
| Bedroom | 250 cubic meters/h | 200 |
| Corridor | — | 50 |
| Kitchen | 100 cubic meters/h | 150 |
| Combined bathroom | 50 cubic meters/h | autonomous |
| Total (required minimum) | 600 cubic meters/h | 600 |
DIY forced ventilation
You can assemble a completely professional ventilation system with your own hands.
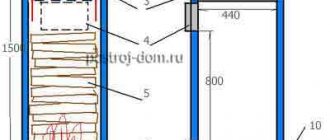
For ease of assembly and fastening, you will have to replace the double-glazed window facing the balcony. The new one should be 20 cm lower, and close the resulting hole with a polyurethane foam insert.- Carefully cut the 125 nipple into the polyurethane foam. If you do this correctly, you don’t even have to seal the insertion point.
- Away from the PPU insert, we install an FVK or FV filter at 125. The window on the loggia will serve as an air valve.
- We connect the filter to an NK type electric heater using a semi-rigid hose. The distance between the filter and the heater can be any. The heater should be placed away from flammable surfaces or its body should be insulated. The case can heat up to 70 degrees, and the cover will have to be removed periodically.
- Attach the fan at a distance of 250 mm from the electric heater. To make it work silently, insert it into the box and fill it with polyurethane foam. Before doing this, strengthen two sections of the air duct and provide a power connection.
- Next, we install a direct air duct in the apartment with our own hands for forced ventilation, where the air flow will be leveled, and install a sound muffler. 60 cm will be enough, but if there is a place better than 90 cm. The total length of the forced ventilation system, assembled with your own hands, will be about 150 cm.
- The air supply to the rooms will be through air ducts into which 10 x 15 cm grilles are cut, at least three for the entire forced ventilation system in the apartment. If the length of the air duct is more than 5 m, you should use a galvanized pipe.
- We automate the forced ventilation system in the apartment. To do this, we connect the temperature controller according to the diagram using a three-wire cable. All electrical equipment is equipped with circuit diagrams that need to be used. A duct temperature sensor is installed in the middle part of the air duct, no closer than 1.5 meters from the electric heater. The equipment is powered from a standard electrical outlet.
As you can see, it is not too difficult to make forced ventilation in the house. The scheme we presented is suitable for a two-room apartment. Properly done forced ventilation will work with an open window or good exhaust hood. As a hood, it is enough to install a household fan with a power equal to the supply fan into the ventilation grille of the bathroom.
Installation of mechanical ventilation
Depending on the type of system being installed, it is necessary to prepare holes of the required diameter in the walls and/or floors of the house. This must be done with care so as not to damage the supporting beams.
Next, air ducts are laid into the holes so that the horizontal sections are as short as possible; they make the draft weaker.
One way or another, horizontal sections should be secured with hangers or clamps using self-tapping screws and/or dowels.
The gaps between the wall and the system are filled with glue or sealant.
Then comes the installation of fans: in a ducted system they are installed in front of the ventilation grille (most often the grille is already built into the duct), in a ductless system they are mounted directly into a wall or window. If you need a hood in an apartment, then you can limit yourself to a regular fan.
It is necessary to widen the vent hole so that the fan housing fits into it. If it is too wide, then you need to narrow it with plaster mortar, then insert the fan into the hole and fix it. The cracks along the edges of the ventilation grill are filled with silicone sealant.
The outlet pipe is led out into the street through the roof. If the pipe is higher than the roof ridge, then mechanical ventilation will be supplemented by natural ventilation - draft will appear even without the fan running. But this is provided that there are no horizontal sections.