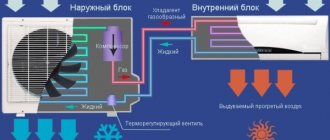
Cooling power of air conditioners
To determine the cooling area of the unit, a parameter such as cooling power, abbreviated as MO, is used. Very often, consumers confuse it with power consumption, which leads to confusion when choosing equipment. Typically, the cooling power exceeds the energy consumption by several times. The ratio of these parameters expresses EER - the energy efficiency of the air conditioner. The standard for household devices can vary between 2.5-4.
Variety of types of air conditioners
MO can be determined in several ways:
- The simplest is to study the labeling from the manufacturer, comparing the data with the parameters of the room (area), which we will talk about a little later;
- A less complicated option is to use a special calculator, which can be found on the Internet;
- Using formulas, take into account all heat sources in the room, comparing them with the volume;
- And the most complex method, close to the scientific approach, is to take into account the heat sources that provide energy to the room from the outside, as well as the thermophysical properties of objects in the room.
Of course, no one will use the latter method due to its complexity, and we don’t need such accuracy - but comparing the device data not with the area, but with the volume of the room will be just right. We will discuss the calculation methodology further.
If the air conditioner can't handle the cooling, it starts to cause a lot of inconvenience.
What happens if the power of the air conditioner is selected incorrectly? It all depends on which way you went wrong. If the power is not enough, then the device will not cope with cooling; the desired temperature may not be established, since the heat sources actively counteract the process. In this case, the air conditioner itself will work for wear and tear - it overheats, which is fraught with premature breakdowns. All this leads to additional costs for repair and maintenance of the device.
Find out how to turn on warm air on air conditioners from different manufacturers in a special article on our portal.
When an air conditioner, on the other hand, is more powerful than needed, it will not be used to its full potential. Accordingly, you will overpay for the purchase and installation. Such a device will create a lot of noise in a small room. The consequences are not the same as in the first case, but the unpleasant moments always remain so.
It is important to choose the right air conditioner
If the power is selected incorrectly
The consequences of an incorrectly selected climate system are unpleasant indoor conditions. The result is predictable - the room will be either too cold or too hot. But there are other pitfalls of an incorrectly selected air conditioner.
Excess power
Despite the advice to round the power up when making calculations, you should not go too far in this matter. A powerful air conditioner will quickly create the necessary conditions in the room, which means that it will have to be turned off to prevent it from getting cold. Frequent starts and stops of the device have a bad effect on its performance. This means that the next time you turn it on, the air conditioner may fail.
If the power is excessive, the room will be coldSource pbs.twimg.com
The second unpleasant side is financial. The more powerful the split system, the more it costs and the more electricity it consumes. The result is an expensive device that will exhaust its service life ahead of schedule, which again will lead to unnecessary costs.
The third unpleasant effect is that the more powerful the device, the more intensely moisture condenses from the air in it. This means that the room will be stuffy, dry, but at the same time cold air, in which bacteria can easily spread.
This video shows how to measure the current consumption and power of an air conditioner:
Lack of power
A weak split system will not be able to fully perform its job or will work at its maximum capacity. As a result, it will break faster, or you will have to keep it on all the time, which again leads to breakdowns. If the air conditioner fails to cope even with constant operation, the room will be hot, and only under the device itself a strong air flow will blow.
If there is not enough power, the air conditioner cannot cope Source i.ytimg.com
In the video there is additional information on how to choose an air conditioner:
The power of an air conditioner is the main indicator of its operation. If it is calculated incorrectly, the buyer risks, at best, wasted money, and at worst, his performance and health. After the power of the air conditioner has been calculated, you can proceed to choosing its remaining characteristics - appearance, ease of use, etc.
Calculation of cooling capacity by square meters
So, the same split system model is available in several variations, designed for different room volumes. Naturally, each manufacturer labels its products so that everything is clear to sales representatives, installers and end customers. But if the first ones know how to navigate the notations, then not all consumers have such information.
The number highlighted in the marking will tell us the cooling power
Devices are marked according to their cooling performance. This parameter is expressed in kWTU, one unit of which per hour is 293 W. The photo above shows an example of such marking - all data is contained in the exact name of the model. What options could there be:
- 07 – the power of the device will be 2 kW. Such a device can be installed in a room of 18-20 square meters. Please note that 7 units are indicated, not 0.7 units, otherwise you will get confused in the calculations;
- 09 – here the power increases to 2.5/2.6 kW. Manufacturers recommend them for rooms no more than 26 square meters;
- 12 – is the most powerful option for household split systems. It can effectively cool a room up to 35 square meters.
Some companies use different labeling. For example, Toshiba has representatives with values of 10 and 13 in its model. To calculate their power, we multiply these numbers by 293. That is, 10 will be 2.9 kW. Another Japanese company, Mitsubishi, uses square meters in its labeling. At the same time, the parameters of the devices remain the same, but the markings are more clear to end consumers.
When choosing an air conditioner, the individual characteristics of the room will be of great importance.
However, a pure calculation by square meters is fraught with inaccuracies, which the seller is unlikely to tell you about in the store, since he himself may not know, or simply does not want to waste extra time, since you may not have the necessary data at hand. Now we are hinting at the height of the ceilings in your rooms, because it is logical that in rooms with ceilings of 2.7 and 3.4 m there will be different volumes of air, and the difference is significant.
For this reason, the following adjustments need to be made to the methodology described above:
- If the ceiling in the room is no higher than 3 m, then 100 W of cooling energy per square meter will be enough to effectively cool it.
- From 3 to 3.4 m this parameter increases and is already 120 W;
- 3.4-4 m – 140 W per meter;
- Above 4 m – 160 W.
There are no higher values, since higher ceilings are usually not installed in residential premises - industrial split systems are used there.
Industrial split systems
The specified cooling energy parameters are designed for a room in which there are no additional sources of temp, which we humans are also. Therefore, when making an accurate calculation, you should definitely calculate how many people on average can be in a refrigerated room. We also add household appliances: TVs, computers, stoves (if you need to install the system in the kitchen) and so on.
The calculation here is rough and average, but it still helps to significantly improve the result. For one resident and one household appliance, an average of 300 W of thermal energy is released into the surrounding space.
Let's give a simple example of calculation. Let's take a hypothetical room of 20 square meters, in which there are always two people, one of whom works on a computer, and the other just lies on the sofa and relaxes. The ceilings in the room are no higher than 3 m, which means we take 100 W per unit area. As a result, we get 2 kW from the area of the room and another 900 W from people and equipment. Total - 2.9 kW. To cool such a room, according to calculations, we will need 09,10 or 12 according to product labeling.
Attention! We said that the indicators are average. In fact, a person at rest emits no more than 100 W of energy, with little activity this parameter rises to 130 W, and with serious physical activity it rises to 200. The same applies to household appliances. It generates a lot of heat under maximum load. In normal operation, the performance is not very high, so in our example, it would be reasonable to limit ourselves to 9, while 7, which is designed for the specified area, will perform poorly.
When choosing an air conditioner, it is important to consider the height of the ceilings
What does power consumption depend on?
What generally determines the energy consumption of an air conditioner during use? Several factors are important here:
- compressor potential;
- temperature difference between indoors and outdoors;
- function performed;
- cooling capacity, i.e. cold load.
Although it is worth noting right away that the dependence of air conditioner consumption on these reasons occurs only for inverters. Models operating in start-stop mode (temperature reached → switched off; temperature changed again → switched on) have unchanged electricity consumption values, but require more time to achieve the specified parameters.
Compressor potential
comparison of the operation of an inverter and a start-stop air conditioner
The lower the compressor speed, the lower the energy consumption. Such energy-efficient air conditioners most often have an inverter method of controlling the operation of the compressor, when a saving mode of energy consumption is automatically activated when the set temperature values are reached.
That is why inverters are considered a more profitable purchase compared to conventional start-stop units, which always operate in the same power mode.
We recommend: Bath blocks: which ones are better?
Temperature difference
The greater the temperature difference between the room and the street, the greater the power consumption of the air conditioner in kW. If it's 40°C outside and you want to set your home to 22°C, the costs will be higher than if it's 25°C outside.
For an air conditioner with linear energy conversion, the power consumption per hour itself will not change, but when the set temperature is reached, its compressor will turn off and turn on when it rises.
Different functions performed
Different functions require different time commitments. In principle, there is an analogy here with the previous paragraph. There will be no changes in the power consumption of the air conditioner in kW per hour, but with large time expenditures, the number of kW that the air conditioner “ate” will increase, therefore, the cost of paying for utility bills will be higher.
Working in the cold
How is the relationship between cooling capacity and how much power is consumed by the air conditioner from the network? In fact, the relationship is simple - the higher the cold load, the higher the electricity consumption.
Cooling capacity calculations based on room volume
We are gradually moving to more complex and accurate calculation options. Let's look at how to correctly select the power of a split system based on the actual volume of the room.
When selecting, using not square meters, but the specific cold parameter per 1 m³, you can obtain the most accurate data. The main calculation parameter will be the specific power, denoted by the Latin letter q. Its value may vary depending on the lighting conditions that are most often observed in the room. So, if it is shaded q will be 30 W/m³, if the illumination is average, not very bright - 35 W/m³, if the windows face the sunny side - 40 W/m³.
Table 1. Calculation instructions
| Meaning, formula | Description |
| Step 1 - parameter Q1 | Q1 is the required power of the device, which will compensate for the heat flows that pass through building structures. V for us is the volume of the room, which can be calculated using mathematical formulas known from school by multiplying the height of the room with its width and length. |
| Step 2 - parameter Q2 | Q2 is the “resistance” to the heat generated by human bodies. We have already indicated the average value earlier. You can use it, or use more realistic parameters. |
| Step 3 – parameter Q3 | Q3 is cold energy aimed at compensating for heat from electrical appliances that emit heat of approximately 30% of the amount of electrical energy they consume. For example, your computer consumes 200 watts per hour every moment. During this time, it will release about 60 W of thermal energy into the surrounding space. This also includes heat from lighting fixtures, especially if incandescent lamps are still used. One such 100 W bulb will heat the air in the room no less than a computer, if not more. |
| Step 4 - Q parameter | Q is the sum of the energy of all heat sources in the room. |
As you can see, the whole difference in the calculations, by and large, comes down to calculating the Q1 parameter, the rest is done according to the same principle, however, the difference in the results obtained is sometimes significant, especially in cases where large rooms are involved.
Specific parameters
If you think that in your calculations you have come close to the most accurate result, then you are mistaken - they still remain, if not approximate, then with a large error. If a specialist carried out accurate calculations, he would take into account the following parameters:
- The thickness of the walls and ceilings in the room and the material from which they are made.
- The floor where the desired room is located.
- The presence of non-standard windows - perhaps the room has a transparent roof or their area is very large.
- Types of windows and their energy efficiency.
- The average number of people and the activities they engage in most of the time.
- Infiltration of external air, that is, how often the room is ventilated - many people do not have enough cool air from the air conditioner, they want natural odors.
Let's look at the last point in more detail.
An open window significantly reduces the efficiency of the cooling unit.
If you open the window, air from the street will directly enter the room, which can become very hot in the hot summer. As a result, your split system receives additional heat load, in other words, you begin to cool the street. The instructions for any air conditioner say so - the device can function normally only with the windows tightly closed. Heat loss through the ventilation system is included in the calculation of the unit's power.
In practice, it often happens that users first turn on the air conditioner, then, after turning it off, open the window, and when it gets hot again, they start the ventilation. This approach is extremely inefficient - you are, in fact, constantly heating and cooling the room. The device will not suffer from this, but a comfortable atmosphere inside will never be established.
Another situation is when the air conditioner operates simultaneously with an open window. The person sitting next to you seems to feel cool, but as soon as you turn off the device, it immediately becomes stuffy again. As a result, the split system works non-stop, which leads to its accelerated wear and overheating.
During continuous operation, the system can quickly fail
If this is how you use air conditioners, then it is not possible to accurately calculate their power when purchasing, since the air flow cannot be calculated - it depends on a lot of factors.
Advice! If you absolutely cannot live without fresh air, then you need to ensure that there are no drafts in the room so that air from the street flows in in a weak stream. To do this, set the window to the window or micro ventilation mode and close the front door.
Also, when selecting an air conditioner (calculating its power), you need to consider the following:
- Parameter Q1 needs to be increased by 20-25%. This will compensate for the additional heat gain from the street.
- The air conditioner's energy consumption increases by 10-15%.
- When it is really hot outside, it is still better to close the windows in the room so that the device does not wear out.
- Take a look at inverter units, which can automatically change their MO depending on the actual heat load.
Advantages of Inverter Air Conditioner
Here it is worth giving a little explanation. Conventional air conditioners have a built-in thermal sensor that constantly measures the ambient air temperature level and blows according to the settings until it reaches the temperature you set. Inverter units can easily be called smart. They can correlate the temperature difference, calculate how much “effort” they need to put in to achieve the desired result in the shortest possible time, run at the required power, and so on. That is, if you buy a seven, it will not blow stronger than what is built into it, and it will not cool any less, but the inverter split system will cool effectively and save electricity if necessary.
Prices for popular air conditioner models
Air conditioners
Energy efficiency indicators
Most modern split systems combine the functions of cooling and heating air. In each of these modes, the equipment consumes a different amount of energy resources. The exact consumption depends on many factors.
Device energy efficiency factors
The ratio of the power produced by a device to the energy consumed, which is necessary for its generation, is called the energy efficiency coefficient. It is this indicator that expresses the energy efficiency of climate control equipment.
Split systems have two of them:
- Refrigeration coefficient. Allows you to determine the energy consumption required by the device in cooling mode.
- Thermal coefficient. Makes it possible to assess the level of energy consumption when operating for heating.
To calculate the energy efficiency coefficient, you need to know the parameters of consumed and produced power in different modes, indicated in the equipment characteristics.
It is worth considering that the COP (heating power) value usually exceeds the EER (cooling power) value. This is due to the operating characteristics of the compressor. While working, it heats up and transfers heat to the refrigerant circulating in the system. In heating mode, the heat generated by the compressor serves as an additional source of energy
For example, let's take one of the models of split systems from AUX - ASW-H07A4.
Let's calculate its EER using the following formula:
K = Q/N,
Where:
- K is the required value;
- Q – power of the device in cooling mode (amount of generated energy in kW);
- N – power consumption (the amount of energy taken from the network in kW).
We get: K = 2.1 / 0.65 = 3.23
Therefore, the EER of the model taken is 3.23. The higher the final indicator, the more economically the device uses electricity.
The thermal coefficient COP is calculated using a similar formula. These values must be indicated in the technical data sheet of the device. They can also be obtained from the sales consultant at the time of purchase.
The values of the split system power consumption and output declared by the manufacturer, as well as COP and EER, may differ to one degree or another from the real ones. It all depends on the conditions in which the device is operated.
At enterprises where testing and calculations of energy efficiency of equipment are carried out, conditions are close to ideal. In practice, they are not always observed.
Therefore, it is important to take into account some rules for operating air conditioners to prevent excessive consumption of electricity. We'll look at them in more detail a little later.
The parameters of the considered COP and EER coefficients are fundamental when dividing split systems into energy efficiency classes according to the generally accepted scale.
Energy efficiency classes of split systems
The level of efficiency or “anti-efficiency” of split systems, like many other household appliances, is clearly demonstrated by the energy efficiency scale.
The classification of energy efficiency parameters involves marking devices with special symbols - Latin letters from “A” to “G”. According to the requirements of international quality standards, the designation corresponding to the device must be present on the packaging
Since the category of climate control equipment under consideration is characterized by two types of output power, it is also assigned two energy efficiency classes. Of course, this applies only to those devices that are designed for both heating and cooling of rooms.
The most economical group of equipment is considered to be the models marked “A”, the most energy-consuming – “G”. As existing technologies are constantly improving, manufacturers have begun to produce devices whose efficiency exceeds Class A.
We recommend: How to choose foamed polystyrene?
In this regard, the scale was expanded, adding the designations “A+”, “A++”, “A+++”. Such models are an order of magnitude more economical, but also much more expensive than others.
Factors of minor importance
In addition to coefficients and energy efficiency classes, there are a number of additional factors that influence how much electricity the split system will consume:
- compressor type;
- thermal power of the device;
- room area;
- difference between internal and external temperatures.
The air conditioner's flow rate is largely determined by the compressor installed in the device. The amount of energy required depends on the frequency of its rotation. Conventional mechanisms operate on a start/stop principle.
When the sensor detects temperature changes above or below specified levels, the electronic unit starts the engine. After reaching the desired temperature values, it turns off again. In standby mode, virtually no electricity is consumed.
Inverter models smoothly maintain the temperature within the specified values. Therefore, they do not need to completely cool the entire air volume the next time they are turned on. They consume almost half as much electricity, last longer, and can operate for heating even in severe frosts.
The scheme according to which inverter split systems operate is considered more efficient and economical. In these models, compressors operate non-stop, smoothly changing rotation speed and, accordingly, power consumption.
The only drawback of equipment with inverter compressors is the high price. However, judging by user reviews, it pays for itself quite quickly.
The larger the area the air conditioner serves, the higher its consumption will be and the greater the thermal power it should have. This parameter is measured in BTU and is designated in numbers - 7, 9, 12, 18, 24, etc.
For average apartments, the first three options are most suitable.
The rest are installed in large houses and administrative buildings:
- “Seven” corresponds to a value of 7000 BTU (1BTU ≈ 0.3 W). That is, its performance is approximately 2100 W. Such a unit can efficiently serve premises with an area of 20-25 m², while consuming about 0.7 kW/h.
- "Nine" has a power of 9000 BTU or 2700 watts. It is designed for objects with an area of 25-30 m² and consumes electricity within 0.8 kW/h.
- “Twelve” with a performance of 12000 BTU or 3600 W is intended for rooms up to 40 m². Its consumption is about 0.95-1 kW/h.
If you do not compare the thermal power of the device with the area of the room and buy an air conditioner with a lower value than is actually necessary, you may encounter unpleasant consequences.
First of all, this is fraught with increased energy consumption and a shortened service life of the device due to excessive loads.
To ensure uninterrupted and safe operation of the air conditioner, you should ensure that there is an outlet with a power coefficient corresponding to its power, check the parameters of the safety plugs in the electrical panel, and make sure that the wiring is in good technical condition
The temperature outside the window, or more precisely, its difference with the temperature in the room served, also affects the amount of energy consumption.
For example, the outdoor thermometers have risen to +40 °C, and the room needs to be cooled to 22 °C. In this case, the air conditioner will consume more energy than if it were 32 °C outside.
How to calculate power using calculators
If you have neither the desire nor the time to do calculations, then you can use the services of some Internet resources that have special calculators. In theory, of all the methods, this should combine the optimal simplicity/accuracy ratio, but in practice, not everything is so simple. We don’t know what algorithms are embedded in the program code, we don’t know which heat sources are taken into account and which are not. Some resources, based on the results of verification, provide indicators with a significant margin, which will force you to overpay when purchasing.
Calculator for calculating air conditioner power by room area
Skip to calculations
For these reasons, we recommend using calculators only for rough calculations. If you are not “scared” by the power reserve, then calculators will help you quickly calculate the level of ventilation and other characteristics that you have not even thought about.
These resources will also help you choose the type of air conditioner depending on the room in which it will be installed.
Video - Calculation of air conditioner power
How to choose the right split system
So, let's summarize everything we talked about during today's article. Suppose that you have chosen your optimal calculation method, and you have obtained a certain value, let it be 2.4 kW for a room size of 20 m² - let’s slightly reduce the result from the example given earlier, since we have one person resting, and the second one also sitting at the computer and makes a minimum of movements.
Technically, all calculations were performed correctly, but the fact that the device cannot constantly operate at full capacity has not yet been taken into account - this is an extreme operating mode. To relieve the equipment from additional loads, 10-15% of the reserve is added to the obtained result, 20% is possible, but then the point in accurate calculations is a little lost. We consider that 15% of 2.4 is 0.36. In total, the figure rises to 2.76 kW.
Air conditioning - a device for maintaining and setting a certain temperature in a room
From the data given earlier, it becomes clear that an option of at least nine will be required. This situation can confuse many people, since the air conditioner will consume a lot of energy. There is no need to worry, since the efficiency of split systems is quite high, since freon condenses and steam generation occurs. In fact, this results in energy consumption reduced by 2.5-3 times.
Prices for freon for refilling air conditioners
Freon
So, we looked at different methods for calculating the power of split systems. The material is presented in a clear and easy-to-learn form. We hope you find it useful!
Finishing the toilet with PVC panels will greatly simplify the improvement of the interior of the toilet. In a special article, we’ll look at how to finish wall panels in a bathroom, and we’ll also figure out how to choose the right material.
Video - How not to make a mistake when choosing an air conditioner
Technical condition of the air conditioner
The efficiency of an air conditioner very much depends on its technical condition and can sometimes drop almost to zero if the air conditioner is dirty or malfunctioning.
Air conditioner dirty
If the filters, fan and heat exchangers of the external and internal units of the split system are dirty, then the efficiency of the air conditioner decreases.
Moreover, if the pollution is very strong, then it is noticeable to the eye - the air conditioner blows “warm air”, and if it is not too strong, then no, but the air conditioner still treacherously increases the electricity meter.
The main recommendation in this case is to clean the filters more often.
Filters must be washed under running, not hot water; if necessary, you can use neutral detergents, such as dishwashing detergent.
We recommend: Insulation of a country house for winter living: outside and inside, choice of materials
The amount of freon in the air conditioner
The cooling efficiency of a room air conditioner also depends on the presence of freon in its refrigeration circuit.
Moreover, its quantity should be optimal for the refrigeration system.
The efficiency of the air conditioner drops both when freon leaks and when it is refilled!
The “bigger is better” principle does not apply to an air conditioner.
And even if the air conditioner cools normally, this does not mean that it is operating in its optimal mode.
The only way out for a non-specialist in this case would be to carry out regular maintenance.
Those who want to learn how to diagnose and repair an air conditioner on their own can study our constantly updated section “Do-it-yourself air conditioner repair”
Thermal insulation of copper tubes
The external and internal blocks of the split system are connected by tubes through which freon circulates; its temperature is much lower than the ambient temperature and therefore losses also occur through them.
And the longer the route, the greater the heat loss.
Thermal insulation on the tubes may not be partially applied during installation; birds love to peck at it, using it to insulate their nests, and it also loses its properties over time.
So you need to monitor the integrity of the thermal insulation and restore it.