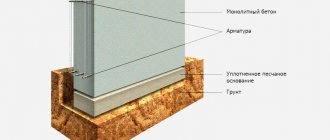
The foundation is designed to evenly distribute the load created by the weight of the building and transfer it to the ground.
When erecting it, it should be taken into account that it must lie on naturally compacted soil slightly below the freezing depth. Depending on the type of soil, the size of buildings and a number of other factors, foundations are divided into floating, strip, pile and columnar. In this article we will take a closer look at the technology of constructing a floating foundation.
In what cases do you choose a floating foundation?
The foundation of any building is intended to distribute the load and transfer the weight of the entire building to the ground. Today there are several types of them depending on the type of soil and the size of the building. Let's consider the so-called floating foundation; its production is used in the following areas:
- with low groundwater levels;
- on bulk and weak-bearing soils;
- on heavy, heaving soils.
Another name for such a foundation is a floating slab, since its construction uses the technology of a monolithic reinforced concrete slab, as shown in the figure.
It is possible to make a floating foundation in the form of a concrete strip:
Let's build our own house
Recently, when constructing low-rise buildings, developers often choose a slab (floating) foundation as the foundation. This type of foundation is a suitable option for most types of foundation soils and buildings, as it allows you to avoid problems that arise during the shrinkage of a wooden frame or profiled beam. There are several types of slabs for a floating foundation: flat; ribbed However, the second type is most often used, which has the ability to maximally withstand the loads from a wooden house. Moreover, if you plan to lay a ribbed slab foundation yourself, then remember that this process is more labor-intensive compared to the first type. In general, building a floating foundation is not a huge problem. Its construction does not require heavy special equipment; usually only a few people can handle the laying. A monolithic floating foundation for a private house must be created if the groundwater lies very close to the surface. It is also advisable to build it when the continental soil on which the piles must rest is deeper than 200-250 cm. The need to build a floating foundation The foundation is the most important foundation of every structure. How correctly it is laid determines the future ability of the structure to withstand natural elements and time. In other words, the durability and strength of the house depends on the choice and the right decision. You should choose the design of the base especially carefully, because freedom of choice in this case does not exist. Each of its types is determined by the following parameters: the future load of the structure itself; climatic characteristics of the area; hydrogeological indicators of the landscape; bearing capacity of the soil, etc. Accordingly, there are as many different methods of laying a foundation using different types of building materials. For example, in places where the soil is subject to various seasonal deformations - uneven subsidence, swelling - conventional technologies are not suitable. In order to make the right decision on the type of foundation, it is better to seek help from a specialist who will help you understand the terrain, study the surrounding buildings and suggest a more optimal option. You should not do this yourself, because correct geological exploration, including the presence of a peat or water pocket, can only be carried out by a professional.
Impact on the foundation The supporting part of the structure is designed to directly transfer the load from the structure itself to the soil located under the house. The type of foundation, its depth and building materials depend on the climatic conditions of the area, the nature of future loads, where the construction site is located (depth of soil freezing, groundwater level, etc.) and on the characteristics of the house (presence of a basement, shape of the building, number of floors, etc.). P.). The forces that act on the foundation are divided into two types: 1. acting from top to bottom (load of the building structure): constant (weight of walls, foundation, roof, ceilings, as well as other loads: weight of furniture, people, equipment, etc. ); temporary (mass of snow, wind). 2. from bottom to top (load from the soil): constant (soil resistance force, depending on the nature of the occurrence, its composition and bearing capacity); temporary (the force of soil heaving during frost). The fact is that during periods of sub-zero temperatures, groundwater is converted into ice and, accordingly, increases in volume. Thus, in addition to the compressive load, tangential forces begin to influence the foundation, tending to push it to the surface. If the soil freezes below the depth of the foundation, then a lifting force is added to all this, which acts on the foundation. In order to avoid negative consequences on the foundation, serious measures must be taken: the foundation walls must be covered with sliding building material (for example, roofing felt); the foundation walls should not be built vertically, but in the form of a trapezoid; the base of the sole needs to be expanded; It is better to cast foundation walls from reinforced concrete; the base of the sole must be laid below the freezing level of the soil. Creating a continuous foundation slab allows you to evenly distribute the loads that act on the sole. It is laid at a certain depth, and the soil underneath is replaced with sand, thus creating a sand cushion that absorbs forces from the soil. It is precisely such a foundation that is able to perceive them, like some kind of “barge” rocking on the waves. Floating foundations are used for the construction of a variety of buildings on all types of soil, including peat, heaving, subsidence, bulk and weak-bearing ones, as well as at different depths of groundwater. A floating foundation is a special technology that was developed for construction in problem areas. It is a reinforced concrete monolithic slab, which is located under the entire house - vk.com/wall-72891995_273. This concrete base is sometimes called poured concrete. It is made from a pure mixture without the use of stones. The filler is fine and medium gravel or crushed stone, which is spread and compacted into the formwork. To improve the properties of concrete, it is advisable to use special vibrators that perfectly strengthen the foundation.
A slab floating foundation should ideally match your structure in size and shape. How to build a floating foundation, technology: 1. Slab foundation. Stiffening ribs should be created along the perimeter of the foundation; from crushed stone, coarse sand or mixtures thereof, lay a base (300-400 mm), moisten it and compact it; Formwork (250-300 mm high) is knocked down from boards and secured from the outside with pegs; create grooves for filling the stiffeners, and lay sheets of roofing felt, glassine or roofing felt on their bottom; reinforcement is distributed along the base and along the grooves; then poured with a concrete composition of Portland cement grade 400 mixed with crushed stone 1:2; then lightly compact the surface and level it. The floating foundation slab is poured in one step. Creating a fill in parts is strictly prohibited. Upon completion of the work, the surface of the slab is covered with film. So it should stand for 10-14 days. The site needs to be moistened periodically. 2. Foundation design. After removing the formwork, a brick base is created along the perimeter of the base, in which vents are equipped. It is simply necessary to do this, otherwise mold may form in the house. They are placed 150 mm above ground level. Floating foundation: disadvantages and advantages The main disadvantages are the complexity of the work and its high cost. Advantages: walls are protected from shrinkage cracks; the foundation can support even heavy buildings; durability. The slab foundation is also the subfloor of the first floor.
Advantages and disadvantages of a floating foundation
A foundation built in this way will be:
- strong and durable;
- practically does not shrink;
- able to withstand very heavy structures;
- the load-bearing slab can be the floor in the basement.
It also has disadvantages, which are limited mainly by the high cost and labor-intensive nature of the work. However, a practical approach to construction operations can significantly reduce the cost of work. You can, for example, abandon the use of a concrete pump and use the unloading trays of concrete mixers or hire low-skilled workers (under supervision, of course). Thus, the cost of a floating foundation can be slightly reduced.
Some types of floating foundations
An excellent solution would be to lay a floating foundation on clay soil. Being close to the surface, clay deposits are easily washed away. In this case, the constructed foundation itself is exposed. A reinforced concrete floating slab as a foundation is just right for such soil: the movement of clay due to various processes will not affect the walls of the building in any way.
When constructing light premises, various foundation configurations are used, for example, the “floating column” method. Floating columns are used in the construction of wooden baths. To do this, the space is filled with sandstone, a concrete slab is laid, and columns are mounted on it, filled with concrete inside.
An approximate diagram is as follows:
The lower crown of the bathhouse or beam frame is installed on top of the structure:
This construction option is simple and does not require spending a lot of money.
How to pour correctly
To independently erect a slab, it is necessary to evaluate the soil composition and groundwater level (GWL); compaction of the sand backfill with water and a vibrating plate plays a special role. Next, you should definitely initially plan communications with duplication, for problem-free drainage (gutter). For a floating slab, plantar and ring drainage is provided. The insulation is ordinary dense polystyrene foam.
How a floating foundation is laid
Before you start making it, you need to find out the composition of the soil on the site and make calculations for the house design.
Important. The bottom of the dug pit must be compacted. It is unacceptable for there to be areas with loose soil, sand or crushed stone.
A floating foundation is made with your own hands in several stages:
- The foundation pit is prepared in accordance with the project.
- Geotextile materials are placed at the bottom of the pit, creating a barrier that will prevent sand from being washed out.
- Then a layer of sand and gravel is poured, which is moistened and compacted. Typically this layer is 20-30 centimeters.
- The next layer is a concrete base with reinforcement, its thickness is about 10 cm.
The structure of a floating foundation is shown in the figure:
To have a clear idea of how the foundation is poured, it is worth watching how a floating foundation is made, video on YouTube
In order to make the calculation it is necessary to take into account:
- The thickness of the concrete slab. For light buildings, it is enough to make a slab 15 cm high.
Attention. You should not make a floating foundation too thick in thickness. Even for a two-story frame house with reinforced concrete floors, the thickness should be no more than 20 cm.
- Thermal insulation. The insulator is applied under and above the floating slab; polystyrene foam is suitable for this.
- Water protection. If groundwater lies below 1 meter, waterproofing is carried out using moisture-proof membranes.
- A pillow consisting of two layers. Above is gravel, below is sand. Important! Exactly in that order. After all, if groundwater gets under the slab, the gravel does not allow it to linger for long and the water flows into the sand and then into the soil.
Marking and arrangement of the pit
To mark the foundation the following are used:
- cord;
- pegs;
- construction level;
- roulette;
- triangle.
At the construction site, one corner is marked along the perimeter of the future foundation. A peg is driven in. A triangle is placed on it, and along one side the length of the building is marked, and along the other - the width. Pegs are driven in at the resulting points.
Next, the axis lines are determined and the 4th peg is driven in. Correctness is checked using a triangle - the resulting diagonals are compared. If the stakes are installed correctly, the difference between the diagonals will not exceed 2.5 cm. If the sizes do not match, it is necessary to make an adjustment by moving the corners.
A cord is stretched between the driven pegs to obtain visual contours for the foundation.
After preparing the markings, you can begin arranging the pit. The size of the finished pit should exceed the size of the slab by 110 cm around the entire perimeter. This is required for arranging an insulated blind area and drainage of the base.
Important! When digging a pit, it is necessary to take into account the soil loosening coefficient. Rocky soil doubles in volume, sand triples, crushed stone and gravel quadruples.
When constructing a pit, a slight slope of the walls should be observed in a ratio of 1 to 0.25 to prevent possible soil shift.
The laying of utilities is carried out at the initial stage. In this case, water pipes are installed with a depth of 150 cm, sewerage is buried 80–100 cm below the soil freezing level.
To protect a floating foundation from soil heaving, the following methods are used:
- arrangement of drainage wells;
- waterproofing sand or gravel cushion 55 cm high;
- an insulating layer of polystyrene foam boards 15 cm thick;
- waterproofing layer made of polyethylene film.