The most common foundations are strip and pile, but their installation is not always possible. On problematic soils, a strip foundation with bored piles can be a salvation. It performs especially well on soils that are susceptible to heaving. The structure can withstand the influence of forces and become a reliable support for any home.
Such a foundation distributes the load onto that layer of soil that is incompressible and located deep. This article fully covers the topic of constructing such a foundation and identifies its positive and negative aspects.
Pros and cons of a bored foundation
The drilled version has the following advantages:
- There is no need for additional work on leveling the soil and constructing a trench or pit. If we compare it with a foundation such as a strip foundation, the foundation on bored piles requires less preparation costs, since a strip type device requires a flat surface and a large amount of excavation work is carried out.
- Low cost of installation work, low consumption of materials compared to a slab base.
- High speed of work completion. They can be completed in 12 hours, depending on the characteristics of the object and the properties of the soil on the site. It takes 8 days for the concrete mixture to harden, while the strip foundation will harden within a month.
- There is no need for additional waterproofing, which also helps reduce costs.
In addition, with a bored-type device, there is no need to look for a place to store piles, which is especially important in a small area. The service life of the foundation is 100 years. For private construction and frame houses this is a long period.
But this type of foundation also has a drawback: piles of the same type can differ in their load-bearing capacity even in the same geological conditions - the difference in indicators is 30%. This makes it difficult to calculate the bearing capacity of piles.
Flaws
- A bored strip foundation can normally serve a little less than 100 years, after which it will have to be strengthened. For people who intend to build a house “to last forever,” such a foundation may not be suitable.
- There are problems with the arrangement of the ground floor. Of course, when carrying out certain work, the strip part of the foundation can partially fulfill the role of a plinth, but this is quite difficult, and in some cases, impossible.
- This type of foundation cannot support massive buildings; Designed for light weight buildings. The maximum load will have to be taken into account during construction and subsequent life in the building.
Bored or screw piles: which is better?
When building on subsiding, swampy and soft soils, both bored and screw foundations are used. It is difficult to unequivocally answer the question of what is best.
It is believed that screw piles are a more reliable structure that can withstand high design loads. Their installation is faster than the installation of bored piles; they are immediately ready to bear the full load, and no additional time is required for the solution to harden.
Bored piles.
Screw piles are subject to repair, but the process is considered simple. They can also be reused if necessary. But at the same time, they have a significant disadvantage compared to a bored foundation - they are more expensive.
Waterproofing
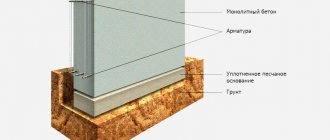
The construction of a bored foundation requires protection from the negative effects of the environment. Proper waterproofing will ensure the preservation of the entire structure. High-quality coating materials are used for its construction. They will be able to protect the concrete grillage from excess moisture. It is covered with several layers of material. The technical characteristics of rolled waterproofing and the properties of the building material of the walls are taken into account.
As coating materials, you can use bitumen mastic with various fillers. It enhances the strength of the coating. Waterproofing cannot be neglected if the groundwater level is below the base of the house. The use of coating materials will provide the necessary barrier to the penetration of moisture into the structure of the structure.
Properly executed foundation construction ensures special strength of the building and prevents its destruction. The house can be used for several decades. The use of advanced technologies allows us to build a very strong and reliable structure and maintain its high technical parameters.
Calculation and layout of bored piles
If the developer decides to make a bored version with his own hands, he needs to understand the design features of such a foundation. Thus, bored piles are installed in rows under all load-bearing walls; the piles must be located at the corners of the future house.
In order to calculate the diameter of the piles, their number and the required distance between them, you need to take into account the soil structure and the weight of the structure. Semi-rocky and rocky soils have the best bearing capacity. Clayey, sandy, loamy soils require more piles.
To determine the weight of a future building, you need to calculate the weight of the building materials used in its construction (including the roofing “pie”). For this, there are special reference tables and SNiPs.
The more the house weighs, the more piles will have to be installed and the smaller the distance between them should be.
The distance between the piles should be at least 3 of their diameters. If the supports are installed at a smaller pitch, this will reduce the load-bearing capacity of the base.
Step-by-step instructions for installing a bored foundation
First, the future foundation is marked. To do this, knock down casting boards from boards and beams. This design consists of 2 levels: the first indicates the height of the piles, the second - the upper edge of the grillage.
Determine the landmark from which the count will be made, this could be the border of the site or a fence installed on it. Then the base lines of the foundation are marked - this is where the walls of the building will go. After this, the dressing boards are installed, and a string is pulled between them.
It is important to check the angles between adjacent partitions - they must be straight.
The location of the piles is marked in accordance with the project, lowering a plumb line from the string, and reinforcing pegs are driven under it.
Then the following types of work are performed:
- drilling of the wells;
- installation of casing pipes;
- reinforcement of piles;
- their concreting;
- cutting casing pipes.
At the final stage, the construction of the ground part of the foundation of the future house is carried out.
Drilling wells and installing casing pipes
Drilling in private construction can be carried out either using a hand drill or using special machines.
A hand drill allows you to construct a well with a diameter of 15-45 cm. It is necessary to drill to a depth of at least 1.5 m, so that the wells are at least 0.3 m below the soil freezing level.
Well drilling
After the well is ready, a casing pipe is made. For its construction, you can use roofing material. The diameter of the casing pipe should practically coincide with the well, and its length should be 50 cm greater than the depth of the well. For the upper part of the pipe, several layers of roofing felt are used and they are tied together with wire. The result is formwork for the future pile, which is placed in the hole until it stops.
Reinforcement of bored piles
If in industrial or multi-apartment residential buildings the length of the pile can be several tens of meters and the diameter - at least 1 m, then in private construction piles with a diameter of 0.35 m and a length of 2.5-3 m are most often used.
In this regard, when reinforcing such a foundation, it is important to remember several rules:
- The total length of the reinforcement cage can be less than the length of the pile by no more than 10 cm.
- The tying of longitudinal reinforcement with horizontal jumpers should be done every 70 cm. In this case, welding is not always used for connection; sometimes tying wire is sufficient.
- For reinforcement, use either 3 rods of corrugated reinforcement with a cross-section of 14 mm, or 4 rods with a cross-section of 12 mm. For transverse lintels, smooth reinforcement 6-8 mm in diameter is used.
Reinforcing blank.
The calculation of the required amount of reinforcement is carried out at the design stage.
Concreting of bored piles
Scheme of a bored pile.
After the bundle of reinforcement has been installed, the pile can be concreted, that is, concrete can be poured inside the casing. It is best to use a mixer for these purposes, since it is designed for large-volume concrete work.
The selection of a suitable material is made at the design stage; standard concrete of a grade not lower than M100 is used for these purposes.
It is recommended to process each layer with a deep vibrator so that voids do not form inside the mass. It is better to prepare concrete in small portions simultaneously with compacting the previous layer.
The structure of the heel - the base of the bored support
In order to increase the load-bearing load of the pile by 5-10%, you can widen the base of the support - the heel.
Two methods can be used for this:
- expansion of the soil at the wellhead, after which intensive compaction is performed, and then the concrete mixture is poured;
- casing pipe of such a design that it widens at the bottom.
In the first case, it is difficult to control the quality of the resulting design. In the second, the quality will be higher, but the labor intensity of the work will increase, since a wider well will have to be drilled.
When building a relatively light private house, such widening is not necessary.
Trimming casing pipes and fittings
Pipe and fittings are cut using a grinder. The reinforcement bars should protrude from the finished pile, but all should be of equal height. This is necessary in order to connect the piles with the ground part of the foundation.
Pile-slab foundation
In such a foundation, 2 methods and schemes are combined. The parts of the pile structure account for approximately 85% of the load, and the slab - the remaining 15%. This is associated with the difficulty of independently drawing up a project, since even a specialist is not always able to perform the correct calculations.
There are several options for pile-slab foundation.
The pile-slab foundation combines 2 different foundation schemes
One of the common methods is to decouple the grillage from the slab. The method allows you to reduce the cost of work due to the possibility of reducing the thickness of the slab.
The installation technology is that the first thing you need to do is install a pile foundation, and then a slab that will strengthen and connect the piles. In this case, it is not necessary to make a solid grillage. This is the best option for one- or two-story buildings.
It is advisable to install a pile-slab foundation in the following cases:
- In regions with high seismic hazard.
- On problem soils. In this case, most often an ordinary pile foundation is erected. However, there are some limitations. If the house is massive or it is planned to increase its number of storeys over time, then it is recommended to strengthen the piles. For example, you can make a slab base.
- The foundation is suitable for buildings for which vibrations are unacceptable. For example, if a private house is made of foam blocks or using a frame method.
- It is recommended to install the base under an extension to a previously manufactured house.
- In the absence of reliable data about the territory (soil characteristics, groundwater occurrence, etc.). If in doubt, it is better to choose a pile-slab foundation.
Before moving on to manufacturing, it is recommended to study the nuances of constructing pile and slab foundations separately.
Construction of the ground part of the foundation
The execution of this part of the work depends on which project has been selected.
The bored version can serve as a support for several types of foundations:
- Pile-monolithic, that is, a combined version, when a monolithic slab is made on top of the piles. This type is suitable for dense soils; it is most often used for buildings that exert high loads due to their large mass. The cost of pouring such a foundation is quite high, which is associated with a large amount of work, so it is used only where high load-bearing capacity is required.
- Pile-tape. This option is considered optimal for private construction. In this case, with the help of formwork, a concrete strip is poured, which rests on the installed piles, thereby transferring up to 40% of the weight of the house to the supports. Although this type of foundation is considered simple to implement, it is not always suitable for the site; for example, on marshy soils it cannot be considered reliable enough.
- Pile-grillage. The design of this base resembles a pile-tape, but instead of a tape, a grillage made of metal is installed. This type of foundation is most often used for relatively small country houses, since its load-bearing capacity is lower than that of the options listed above.
When choosing the type of foundation, it is best to consult with a specialist or entrust all related calculations to a professional in order to choose the most reliable option.
grillage
Plus, if you install bored piles with a grillage, the foundation will require almost no reinforcement, since initially their stability and strength, as well as their load-bearing capacity, will increase. But on the other hand, you will have to make additional calculations, taking into account the density of the soil, the depth of its freezing, climatic conditions and many other factors that can be omitted when installing conventional piles. However, it's definitely worth it.
Typically, piles are buried below the level where the soil finally freezes - and just in case, it is covered with additional roofing felt protection in order to maximize the load-bearing capacity. Also, such protection plays the role of waterproofing and reduces external pressure, which in winter can reach such limits that it pushes part of the pile out of the soil.
There are two types of grillage:
- hanging;
- recessed.
In the first case, a distance of about 1 cm is left directly between the grillage and the soil, because of which the foundation turns out to be slightly higher than the ground level, in a suspended state - and this protects the building itself from the cold of the ground, moisture, and also from possible soil deformation due to any weather phenomena or climatic features.
If we take the second case for consideration, then the grillage simply goes 2 cm deep into the ground.
It is also important not to forget about reinforcement. In the vertical version, the rods are brought out minus a couple of centimeters by the length of the grillage - and this outlet turns out to be higher than the pile itself. If the soil is too heaving, then the grillage is placed somewhere 15 cm above the soil surface.