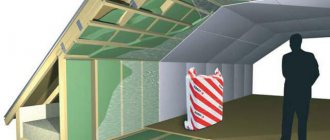
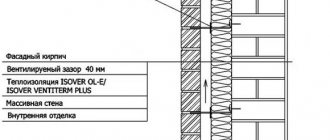
How does the work itself happen?
To begin with, it is worth noting that quite serious requirements are imposed on safety precautions, without strict compliance with which it is impossible to insulate a metal hangar.
When working, be sure to use protective shoes and gloves, a gown, goggles, and a respirator. And the material itself is better protected from exposure to UV rays and moisture.
Preparatory stage
Mandatory preparation of the premises will be required before starting work. It must be degreased and completely dried, free of dust. Grease and dust reduce adhesion, or the ability to adhere to other surfaces.
And if there is excess moisture, then chemical reactions will not proceed correctly. Metal surfaces are first completely cleaned of rust; only after this can spraying begin.
Getting the mixture
First, the material is brought to the construction site. It is usually stored in barrels with two components - polyol and isocyanate.
The liquids are mixed with each other, using a high-pressure dosing reactor up to 150 atmospheres.
Sputtering
After this, the hangar is covered with an even layer of a fine aerosol mixture. It clogs all holes and cracks and penetrates even the most inaccessible places. Violent chemical reactions begin inside the mixture after it comes into contact with the surface.
The substance immediately begins to foam, but then quickly turns into a solid state. The insulation reaches 95 percent strength literally after two hours, but it completely reaches the desired state in no less than 24 hours.
Specifics of warehouse premises
Hangars have become quite popular in recent years, but during operation their advantages can turn into disadvantages.
For example, heat does not stay inside such a building, because its walls are only 1-2 millimeters thick. And the formation of condensation due to low temperatures can harm the metal itself, which is susceptible to corrosion. You will either have to spend additional money to protect the base material, or pay serious money for electricity.
But there is another way out - insulating hangars. This procedure will reduce the cost of their maintenance and protect them from harmful environmental influences. But this is not without its own nuances.
Insulation of hangar with Tepofol
Thermal insulation Tepofol is a material made of polyethylene foam and polished foil or metallized film. Tepofol combines thermal insulation, waterproofing and sound insulation qualities. Its reflectivity is very high, thanks to the presence of polished foil, which provides up to 97% reflection of thermal energy rays. And its porous closed structure completely eliminates the possibility of absorption or stagnation of moisture and steam. The low thermal conductivity of polyethylene and its high reflectivity reduce heat loss by more than 30% and effectively protect the surfaces of treated walls from blowing and dampness.
Advantages of Tepofol:
- exceptional elasticity characteristics;
- stability of the original form;
- the material is absolutely safe for human health;
- good hydrophobicity;
- excellent vapor permeability;
- durability and wear resistance (with proper installation, the material will last for decades);
- resistance to corrosion and mechanical damage;
- resistance to atmospheric precipitation;
- high degree of noise and heat insulation;
- biological stability - the material is “not interested” in rodents and insects, mold or mildew does not appear on it;
- ease and convenience of transportation and installation;
- no need for additional care;
- Possibility of combination with different building materials (gypsum, cement, lime, concrete).
Thermal insulation Tepofol retains all its original properties and characteristics even after many years of use.
Tepofol is produced in 2 types:
- Tepofol foil - provides reflective thermal insulation and has good noise absorption.
- Tepofol metallized - has a high degree of resistance to organic solvents and acids, and also has good mechanical strength.
Both types of material can be made either as a single-sided or double-sided version - when there is a reflective layer on both sides of the coating. Tepofol is also produced on a self-adhesive base (when there is an adhesive coating on one side, which simplifies installation) and Tepofol NPE, in which there are no additional upper layers at all.
Tepofol is used as the main insulation (from 40 to 150 mm) and additional insulation (from 2 to 10 mm) of any structures.
In some cases, it is not necessary to retain heat, but rather to keep the cold inside the hangar (for example, in ice complexes). Tepofol is perfect for this!
For more information on how to insulate a hangar with Tepofol, watch the video:
What requirements must insulation for a hangar meet?
How to insulate a hangar if its design features - material and shape dictate some requirements that the thermal insulation material must meet:
- plasticity - under the influence of temperature changes, the metal surface of the hangar “plays”, i.e. it contracts and expands, so the insulation must be sufficiently plastic so as not to crack from such changes;
- high adhesion – a hangar is a large metal structure, and to insulate it you need a material that has good adhesion and is able to “catch” onto the smooth surface of the corrugated sheet;
- good thermal insulation properties - since the walls and roof of the hangar are very thin, the task of thermal insulation falls entirely on the insulation;
- light weight - frameless and frame hangars are usually built with a vaulted roof, i.e. the walls and roof are a single whole, and it is strictly forbidden to overload such a structure in order to avoid collapse.
All these requirements are met by insulating hangars with polyurethane foam (PPU).
PPU insulation: pros and cons of using technology
The PPU house insulation technology has a lot of different reviews, both positive and negative. Let's consider what is more, advantages or disadvantages, and whether it is worth giving preference to this type of insulation.
To spray polyurethane foam it is necessary to use high-pressure equipment
The main advantage of this method of providing a building with high-quality thermal insulation is its high efficiency. Thanks to its cellular structure, this material retains heat perfectly. But there are other advantages that should not be overlooked:
- the absence of seams and joints eliminates the occurrence of such a phenomenon as “cold bridges”, which has a positive effect on heat conservation;
- You can spray polyurethane foam onto any surface, even one that is complex in design or texture;
- the low level of hygroscopicity of the material has a positive effect on the waterproofing properties of the surface;
- Polyurethane foam adheres to any surface except polyethylene. It is interesting that this quality, which is positive at first glance, can also be considered a disadvantage, since it is almost impossible to wash polyurean foam, and there is no solvent for it. The only way to get rid of it is to peel it off by hand, and this almost always results in significant damage to the surface on which it was applied;
Insulation of the attic with polyurean foam
- The service life of polyurethane foam with full preservation of all technical characteristics of the material is 25 years. After this, the thermal insulation continues to operate, although the thermal conductivity of the spraying increases;
- spraying is done quite quickly, so carrying out all the necessary work will not take much time;
- the material is self-extinguishing and does not support combustion even in the event of a fire;
- the vapor permeability coefficient is 0.05-0.06, which allows you to effectively remove excess moisture after insulating the walls with polyurethane foam.
Spraying hard polyurethane foam
Disadvantages of polyurethane foam insulation: pros and cons
As you can see, the number of positive characteristics of this material is large, and we can say that all these positive aspects fully justify its use as insulation. However, PPU also has disadvantages, and it is better to know about them in advance:
- the cost of spraying polyurethane foam is approximately 1.5-2 times higher than if you use mineral wool as insulation;
- compliance with spraying technology directly determines the life and quality of its service. Only if you have high-quality equipment and appropriate duster experience, is it possible to obtain the desired result;
- Do-it-yourself insulation of polyurethane foam is a very complex and often unjustified process. This is largely due to the high cost of the required equipment, as well as the lack of proper experience in this area;
- polyurethane foam does not burn, however, in the event of a fire it emits a lot of dangerous acrid smoke;
The flammability of polyurethane foam is quite low
As a result of exposure to ultraviolet rays, the foam deteriorates, losing its original appearance, changing color from white to dark brown.
Fortunately, most of the proposed shortcomings can be neutralized, for example, by inviting an experienced specialist to work with his equipment and providing the surface with a finishing finish, which will further protect the polyurethane foam layer. But the main limiting factor for insulation with sprayed polyurethane foam is the price, which, nevertheless, is fully justified by the long service life of the coating.
Insulation with polyurethane foam (PPU)
Polyurethane foam is an environmentally friendly material, the warranty period of which is more than 30 years . With a relatively small thickness, it has fairly high thermal insulation characteristics. The advantages also include high resistance to the negative effects of alkalis and acid-aggressive substances.
Please note that liquid polyurethane insulation is in quite high demand both for insulating houses and garages, and for insulating hangars. The thing is that 1mm of polyurethane coating is similar in characteristics to 50mm of mineral wool . This option is considered by experts to be the most optimal, especially when it comes to insulating large arched hangars.
Its huge advantage is that it can be sprayed onto a surface of any shape. A continuous layer of spraying eliminates the occurrence of cracks, cold bridges, and leaks. After rapid hardening, it strengthens the structure and hides minor defects in the profiled sheet. The thickness of the spraying is selected depending on climatic conditions, which allows saving consumption in warm areas. PU foam prevents the spread of rodents and is resistant to fungus and mold.
Internal and external insulation
There are external or facade insulation of walls with polyurethane of the following types:• plaster facade• ventilated facade• brick facade.
For external insulation of walls using the “ventilated facade” type, it is necessary to install a sheathing made of metal profiles or wooden blocks. Further application of insulation will be no different from the insulation of a plaster facade.
The thermal insulation layer can be installed both outside and inside the wall. For most materials, external thermal insulation is preferable.
This is due to the fact that it allows the dew point (the area where condensation forms) to be moved away from the wall, preventing the destruction of its components. When using this method, the usable area of the premises is not reduced.
But it also has disadvantages: the appearance of the facade changes, and installation work can only be carried out in dry weather.
Internal thermal insulation does not affect the appearance of the facade, and you do not need to wait for good weather to install it. But the shift of the dew point into the inner space of the wall and the reduction in the usable area of the premises do not allow making a clear choice in favor of this method.
IMPORTANT!
When installing internal thermal insulation, you need to bring out sockets and other internal communications without walling them up.
The effectiveness of a particular method also depends on the selected material. Polyurethane is laid in a relatively thick layer, and its installation on the inside of the wall significantly reduces the amount of free space in the premises. Although the material is moisture resistant, the formation of condensation cannot be ruled out when the dew point is shifted inside the wall.
Dew point
These factors make it preferable to choose external thermal insulation when using polyurethane.
Description of the main functional features of insulation
The main purpose of thermal insulation materials is to reduce heat loss from structures in winter and slow down the heating process of buildings in the warm season. In addition, proper installation of thermal insulation allows you to:
- save on heating;
- extend the period of operation of housing, industrial premises and other structures;
- minimize deformations of load-bearing elements that occur under the influence of changing temperatures;
- reduce the consumption of building materials used.
The necessary materials are selected strictly individually, taking into account a comprehensive assessment of their characteristics. These include porosity, vapor permeability, hygroscopicity, fire resistance and a number of other parameters, discussed in detail below.
Thermal permeability coefficient of purchased building materials
One of the most important characteristics of each insulation is its ability to prevent heat loss. A low value of the indicator allows the minimum thickness of the insulator layer to be used in the work.
According to statistics, the leading positions in terms of the parameter under consideration are occupied by 2 types of materials: mineral wool and polystyrene foam. Their maximum values are 0.041 and 0.039 W/(m•°C), respectively.
Vapor permeability, or the ability to “breathe”
The presence of the described property allows TIMs to remove excess moisture vapor from buildings, thereby minimizing the possibility of rotting structures. Penoizol and various types of cotton wool are characterized by high coefficients. Plates made from extruded polystyrene foam practically do not have these properties (their indicator is 0.013 Mg/m*h*Pa).
The leader in vapor permeability is mineral wool, the coefficient of which is 0.60 units.
Strength, biostability and porosity
The three properties included in the subtitle are also among the most important. The first of these indicators allows us to determine the possibility of using materials in elements with additional loads. To find out which products are the most durable, you should listen to the opinions of experts - large construction companies. These specialists, who use the largest percentage of the total number of products produced in their work, consider basalt slabs and expanded clay to be the best (in terms of the property under consideration).
Only inorganic TIMs have the ability to resist decomposing biological processes, including the influence of rotting bacteria, fungi, and the influence of coating-destroying insects.
The highest porosity rates - a coefficient that affects a number of additional characteristics and determines the number of voids present in the material in relation to the volume (total) - are found in mineral wool (up to 97%), as well as insulation materials made from plant fibers and asbestos.
Product susceptibility to water
Among the properties that all materials possess without exception is the ability to absorb moisture, or hygroscopicity. The lower the indicator, the less tendency TIM has to shrink. The most reliable types of thermal insulation in this regard are polymer insulation, which absorb water in a minimal amount (from 0.05%). Mineral wool is recognized as the most hygroscopic, quickly losing its insulating ability at high humidity.
Fire resistance or fire resistance
The non-combustibility of thermal insulation is a determining factor in ensuring the fire safety of any structure. Fire-resistant types of insulation include fibrous inorganic materials; flammable - polyurethane foam; low-flammable - polystyrene foam.
No shrinkage and maintain durability
When analyzing the characteristics of materials declared by the manufacturer, you should pay attention to the strength of the insulator. With a long-term (complete) absence of shrinkage, the product retains high thermal insulation properties and prevents the formation of temperature bridges (areas with reduced thermal resistance)
The service life of the insulation should be close to the service life of the structure.
Additional properties of thermal insulation that do not require an extended description include:
- environmental friendliness;
- level of toxicity of products released during combustion;
- smoke generation;
- frost resistance;
- bending strength.
The main advantages of thermal insulation with polyurethane foam
Despite the high cost, polyurethane foam thermal insulation has a number of important advantages. It allows you to protect the hangar room from heat loss, street noise and other negative factors.
Environmental friendliness
PU foam does not contain formaldehyde or phenolic resins, which are found in expanded polystyrene or mineral wool products. Therefore, it can be used to insulate buildings where food, vegetables and grains are stored.
Polyurethane foam does not contain phenolic resins.
Chemical resistance
Polyurethane foam is not afraid of exposure to solvents, chemicals, alkalis and acids. In addition, its composition and density do not change upon contact with steam or water.
Thermal properties
The material has increased thermal insulation properties. With identical thickness, it is 2 times more efficient than traditional solutions. Therefore, developers can reduce the thickness of the insulation layer while maintaining optimal thermal conductivity.
Polyurethane foam has good thermal insulation properties.
Physical and mechanical features
Polyurethane foam is distributed over the surface without installing additional fasteners. After the surface hardens, it becomes monolithic and rigid. This increases the safety margin of the hangar structure and allows it to withstand heavy loads.
Lifetime
Using polyurethane foam, you can form a monolithic coating with a long service life. The service life declared by the manufacturer is 30-50 years. Minor defects and mechanical damage can be eliminated by filling a new portion of the solution.
The service life of polyurethane foam is 30-50 years.
Types and features of hangars
Cold frame hangars cannot be insulated
Hangars are built with or without a frame base. Each model has its own positive and negative characteristics. Installation technology, operation and maintenance of different structures have much in common.
Frame
The models are buildings based on a metal frame. The hangar is installed on a foundation and covered with cladding. The frame is subject to assembly and disassembly. Structural elements are fastened with bolts. The functionality and economy of the building depends on the form.
The basis of the frame is made up of channels, I-beams and pipes, as well as other metal components. The structure is treated with a primer of any color. Metal hangars can be cold or warm. The walls of cold models cannot be insulated.
Frameless
Frameless models are constructed directly on the construction site using special mobile devices. The construction involves profiling and corrugating rolled steel to give it the required radius. The arched element is connected into blocks using a beading machine. They are then lifted by a crane and installed on the finished foundation. The building elements are fastened together by spot welding and bolts.
What is PPU?
Polyurethane foam or polyurethane foam or PPU is a unique thermal insulation material. It is 90% air, enclosed in tiny bubbles. The shell of the bubble is made of the thinnest polyurethane film.
Foam is applied to the surface using a special apparatus in which the components of the future insulation are mixed. The finished mixture is fed into the sprayer under high pressure. As soon as polyurethane hits the surface, it enters into a chemical reaction with atmospheric air and begins to foam. Due to the capture of air molecules, its volume increases 80-100 times.
Advantages and disadvantages
Let's start with the advantages:
- Today, polyurethane foam insulation is the most effective. This is due to the cellular structure of this insulation and the carbon dioxide contained in the cells. Ideally, this system gives a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.02, which is even lower than that of air (0.022).
- Continuous, seamless spraying, which eliminates the presence of cold bridges, further increasing the efficiency of insulation.
- Possibility of spraying on surfaces of any, even the most complex shapes.
- Low hygroscopicity. Simultaneously with insulation, you improve the waterproofing characteristics of the surface. This property is used for insulating foundations, wells and other similar structures.
- Excellent adhesion to any surfaces and materials except polyethylene. Excellent adhesion (adhesion) in some cases can be considered as a disadvantage - it cannot be washed off with anything, since there is no solvent for polyurethane foam. It can only be cleaned mechanically, often with fragments of the surface on which it was applied.
- Long service life - up to 25 years with the declared characteristics, later carbon dioxide is replaced by air, thermal conductivity increases, but not catastrophically, sprayed thermal insulation continues to work.
- If during the first year the insulation with polyurethane did not cause any complaints, there will not be any for the next couple of decades.
- When using high-pressure installations, polyurethane spraying takes a short period of time, without compromising quality.
- The vapor permeability of polyurethane foam is quite high - 0.05-0.06, which allows excess moisture to be removed through the walls, as before insulation (if the walls are vapor permeable).
- Does not support combustion (self-extinguishing).
As you can see, there is a decent list of advantages that contribute to the fact that thermal insulation with polyurethane foam is gradually becoming more and more popular. But there are also disadvantages:
- High price - 1.5-2 times higher than when insulating with mineral wool. But if you calculate it per year of service, it won’t be more expensive.
- The final result depends greatly on the equipment used and the experience of the duster. Good results are achieved only with full compliance with the technology.
- Due to the use of high-tech equipment, polyurethane foam insulation is very, very difficult to do with your own hands. There is a way out - to buy equipment together for several owners - there is a reason for this, considering the prices. But the question of experience remains - achieving normal performance on your own is very difficult.
- The material does not burn, but when burned it emits a lot of caustic and harmful smoke.
- Fear of ultraviolet radiation. When exposed to sunlight, the foam melts and the white surface turns dark brown. But a film of a certain thickness protects the underlying layers from further destruction, so if the polyurethane foam is thick enough, it can even be left open. But the appearance of the surface insulated with polyurethane foam is far from the best, so finishing is still required.
The main limiting factor in the spread of polyurethane foam insulation is the high price. Although, when compared with the cost of insulation with extruded polystyrene foam, the prices do not seem so high, and this despite the fact that sprayed thermal insulation is installed many times faster and gives a better result. Overall, if you are planning to insulate your home, this technology is worth exploring.
Vestiges of the past
The price of insulating a hangar or warehouse using polyurethane foam spraying will depend primarily on the area of the structure and the complexity of its configuration. But given the large volumes, it cannot be low. Therefore, some contracting organizations, caring more about their own benefit than the benefit of the client, propose, in order to save money, to insulate the hangar using mineral wool, polystyrene foam or hot bitumen. But this is a dubious benefit - these materials have already lost their relevance, since their use is less effective compared to spraying polyurethane foam and has a number of limitations.
Mineral wool - the material is very hygroscopic, i.e. strongly absorbs moisture and can retain it for a long time, and wet cotton wool loses up to 90% of its thermal insulation properties.
Formally, it is considered fireproof because it does not burn. But under the influence of high temperature it releases toxic formaldehyde, which is a strong carcinogen.
It will not be possible to insulate a hangar made of corrugated sheets with mineral wool, since this is a heavy material and thin metal sheets of the walls, and even more so the roof, will not withstand such a load.
During installation, seams remain - the weak link in any thermal insulation chain.
Polystyrene foam is a very brittle material, so it is only suitable for covering flat surfaces. When installing it, anchors are used, which violates the integrity of the base; in addition, dew points form at the attachment point and at the joints of the sheets. This material is highly flammable and, when burned, releases extremely toxic substances, so in some rooms it is prohibited from being used by fire safety regulations.
Short-lived - service life is about 15 years.
The technology of insulating hangars with hot bitumen is used quite rarely. The material is too heavy for thin vaulted structures.
But insulating a warehouse with hot bitumen is quite possible. For example, a flat roof to avoid heat loss through the roof, or insulation of basements, which will serve as additional waterproofing.
Polyurethane foam: pros and cons
Hangars can be insulated using polyurethane foam. It has many advantages, including reliability, ease of installation, long service life, and resistance to various types of fungal formations. You can count on low thermal conductivity as well as benefits from an economic point of view. Polyurethane foam is quite common for the reason that it has the qualities of moisture resistance and resistance to temperature fluctuations. Insulating hangars with polyurethane foam is quite expensive, which is a disadvantage. Among other things, when choosing this material, you must be prepared for the only method of applying it - spraying, which will require special expensive equipment. Otherwise, it will be quite difficult to cope with the work.
Insulation of hangars with polyurethane foam: price
As we already mentioned, you are not buying a layer of insulation, but thermal resistance. And yet, in the table for insulating hangars with polyurethane foam, the price for guidance is given depending on the thickness of the foam layer for a volume of work from 500 m2 (for example, the surface area of a typical arched hangar 15 m long and 7.5 m wide is 648 m).
Begemot Group of Companies provides a 10-year guarantee. We have been working in the market for 14 years. We don't do anything offhand. For each object we carry out thermal engineering calculations and select an option that fully meets the task. You cooperate with us without risks.
After measurements and thermal engineering calculations, we will calculate an estimate, where we will indicate, to the nearest ruble, how much it costs to insulate a hangar with polyurethane foam in your particular case. For large volumes of work, preferential rates apply.
| Heat transfer resistance R – thickness of polyurethane foam | 2.5 (m2 °C/W) – 50 mm | 3.5(m2°C/W) – 70mm | 5(m2°C/W) -100mm |
| price excluding transport and other additional costs, rub. | 900 | 1300 | 1900 |
For questions about insulating a hangar with polyurethane foam, price , terms and dates for completing the application, please call 8-800-302-90-50, write a request by email or use the feedback form. Engineers will contact you at the time you specify.
Hangar construction
Insulation of hangars can be done using one of many existing technologies. Everything will depend on the design features of the building. Such tasks may be based on a framework, or sometimes lack it. In the latter case, it is possible to erect the structure quite quickly: there are no internal partitions, and a metal corrugated profile is used as the main material. In order to build a hangar, the area of which is 1500 m2, it will be necessary to employ about 12 people, which will take 24 hours. Such structures are completely waterproof, as they have reinforced seams, and the panels are coated with an anti-corrosion galvanized composition, which does not require maintenance.
If there is a need, the owners can install an additional waterproofing layer. The disadvantage is the lack of windows, which makes it impossible to use hangars as cowsheds. The construction of such buildings involves the use of steel or aluminum sheets, from which panels of the required length are made. The rectangular profile strips go into a machine, where they are shaped and become arched panels with a diameter of 4 to 40 m. Next, an automatic machine sews the panels together and forms waterproof seams. This allows you to form ready-made sections that are installed on the site.
If necessary, the structure can be moved using a hydraulic crane, and if small panels are used, their installation is carried out manually. The sections are placed next to each other using a machine, and no additional sealing is required - the hangar is waterproof. After installation, the sections are strengthened to the foundation by welding, and the structure is supplemented with doors and end walls.
The need for insulation of the hangar
Complex thermal insulation of the hangar expands its functionality. An insulated building can be used as a sports or shopping complex, or an administrative and even residential building.
Installation of modern insulators allows you to create a favorable microclimate and protect the building from negative environmental influences. Many materials meet fire and environmental safety requirements, and do not harm the human body. The process of insulating a hangar is accompanied by high costs, but they are justified.
Noise insulation
Structures made of metal sheets and profiles are not protected from external noise. At the same time, good noise insulation is an important aspect when using a hangar as:
- Vegetable storage facilities.
- Trade area.
- Dormitories.
- Workshop.
- Sports complex.
- Buildings for keeping animals.
The hangar needs good sound insulation.
In an insulated structure, the sounds of rain or hail, as well as various street noises, are not heard.
Heat protection
The next function of hangar thermal insulation is maintaining a comfortable microclimate throughout the year. In winter, insulation reduces the level of heat loss, and in summer it prevents overheating. Such features are important when using the structure for domestic purposes or storing any products.
Strengthening
Installation of several layers of thermal protection gives the hangar walls additional strength.
In addition, the insulated structure is not subject to corrosion, so it retains its attractive appearance longer without rust.
Roll insulation
When constructing hangars in our production, roll insulation is most often used (we work with trusted manufacturers URSA, Knauf). The products are characterized by high density, which allows for better insulation of objects with a large area, including those with non-standard geometry.
Insulation in rolls does an excellent job of maintaining temperatures inside the building. The advantages of this type include:
- — simple installation;
- — use on objects of any purpose;
- — resistance to external factors;
- - a light weight;
- — maximum adherence to surfaces;
- - low cost.
Twisted rolls are convenient to use for both external and internal insulation. There are materials that are designed specifically for lining pipes and communications.
Materials for floor insulation
In addition to insulating the walls, you will need to insulate the floors in the hangar. For this purpose, sheet materials, bulk mixtures or liquid compositions are used. Installation is usually carried out directly on the ground; additional basic structures are rarely used. It is technically possible to organize “warm floors” (both electrical and water systems) in the hangar.
Insulation materials for metal structures are selected based on the purpose and design of the hangar
Such an event will not be cheap even if insulated with economical materials, therefore more attention is paid to the effectiveness of thermal insulation
Farming activities are not complete without the use of a hangar, which is necessary for storing vegetables and grains. Among other things, such premises are used for the location of equipment and are used as places for keeping poultry and cattle.
Where are frameless hangars used?
Of course, frameless arched hangars are the most popular in industry - they are used as warehouses and workshops, as markets, bases and storage facilities, for temporary or permanent placement of working equipment, and, if suitable conditions are provided, for personnel.
In addition, the arched hangar can be used as an indoor stadium or skating rink, parking lot, workshop, gallery, studio - the range of possible uses is so wide that there is no point in using it completely. However, let’s consider possible ways to use this structure in a private sector:
- garage is the most popular and cheapest option for placing cars, trucks, agricultural and other types of equipment;
- a barn is an ideal option for owners of country and village houses and farms. The range of applications is extremely wide - the hangar can be used as a storage area for harvested crops, a chicken coop, a cattle pen, etc.;
- attic floor - in this case, a frameless arched hangar is installed directly on the roof of the house, provided there is a flat roof. This is very convenient if, for example, you want to build an insulated greenhouse - the structure is compact and has extremely low weight, putting almost no load on the building;
- a work space - a hangar - may be suitable for an entrepreneur to place a temporary office. This use has many advantages, in particular, placement in almost any location with low space consumption and savings on rent;
- room for leisure – in winter, the insulated hangar can be used as a children’s playground, gym, tennis court or indoor swimming pool.
Set of elements elements, components of the structure
The delivery set includes not only an inflatable hangar, but also the following types of kit components:
- stretch marks;
- air blower;
- packaging bag;
- repair supplies.
For inflatable frame structures, constant pumping is not required, since all elements of the structures are absolutely sealed. They provide for the presence of heating, lighting, and ventilation systems, which is necessary to create adequate conditions for the normal functioning of the facility. The shell of the structure contains 3 main layers:
- Insulating.
- Protective.
- Interior.
Inflatable structures have customized automation, so their operation is not associated with constant monitoring of the operating mode of such structures.
Thermal insulation properties of liquid and traditional insulation materials
If you have not read the material on the question of which insulation is better, then let us very briefly look at the thermal conductivity coefficients of the main and most common thermal insulation materials.
- Mineral wool: 0.06 – 0.07 W/(m*K). The difference in values is very dependent on density.
- Sheet foam: 0.037 – 0.05 W/(m*K). Also, when using sheet foam, there will be heat loss at the joints.
- Penoizol: 0.06 W/(m*K).
- Expanded polystyrene: – 0.03 W/(m*K).
- Polynore: 0.025 W/(m*K);
- Thermal insulation paints: from 0.0012 to 0.025 W/(m*K). Of course the manufacturer and modification matter.
You also need to understand the fact that during the actual operation of the material, its thermal conductivity will differ for the worse due to a number of different reasons.
Comparison of thermal conductivity of various materials
Advantages and disadvantages of the material
Cotton wool has been used for building insulation for many, many years. The advantages of this type of insulation include:
- cotton wool does not burn well, it does not support combustion;
- low thermal conductivity (0.035-0.045 W/(m*K) depending on the brand) - for comparison, polyurethane foam has 0.022-0.041;
- sound insulation;
- no deformation during heating and cooling;
- mineral wool is not damaged by rodents and insects, it does not rot;
- wear resistance and long service life - more than 50 years.
The permissible heating temperature also varies depending on the type of mineral wool. Thus, basalt wool is most resistant to high temperatures.
Due to its good fire safety, mineral wool is often used to insulate arched hangars where people, livestock, and explosive substances are constantly stored. This insulation is perfect for gyms, agricultural complexes, office and retail premises, and workshops.
The main disadvantage of mineral wool is that it absorbs moisture well and becomes heavier, which puts enormous pressure on the frameless arched structure. As a result, the design may fail. Thermal insulation properties decrease, thermal conductivity increases due to moisture absorption. Moisture is formed due to condensation on the metal. The problem is solved by laying waterproofing.
Despite the fact that the technology for installing mineral wool is not complicated, it takes considerable time. So, for example, polyurethane foam can be sprayed in 3 hours, and mineral wool will be laid on the same area in 2 days.