The essence of the method
Recycling organic matter in this way involves converting heavy waste into lighter waste. There is no access to oxygen, an anaerobic reaction occurs. The pyrolysis process is accompanied by an increase in temperature to 200–400°C. The pressure corresponds to atmospheric pressure.
The mechanisms of transformation of substances by anaerobic heating have not yet been sufficiently studied. Conventionally, all pyrolysis reactions are divided into primary and secondary. The first type of transformation is to reduce the molecular weight of compounds. This is how heavy substances are broken down. The process is accompanied by the release of a large amount of gases.
The secondary reaction is the conversion of low molecular weight compounds into heavy ones. This chemical process is characteristic of the last stages of pyrolysis. Gas emissions are reduced. Two types of reactions occur at the same time, so the classification is arbitrary.
In theory, water is pyrolyzed. As a result, hydrogen and oxygen are formed. But in practice, such a task is not feasible, since the required heating temperature is thousands of degrees. This is technically labor intensive and expensive.
Chemists also allow gas pyrolysis. First, the less stable bonds of carbon atoms are destroyed, then the bridges between this microelement and hydrogen disintegrate. According to the pyrolysis formula, methane is the last to decompose.
What is pyrolysis - description of the process
Theoretically, you can burn any substance that includes compounds of carbon and hydrogen, for example:
- coal;
- natural gas (methane, propane, etc.);
- biomass – fresh, dry;
- wood products, cellulose, ordinary firewood;
- various types of plastics;
- rubber made from natural or artificial rubber;
- oil, its derivatives;
- other carbon-containing waste.
At the output you will receive a certain amount of thermal energy, depending on the initial moisture content of the burned mass. To describe the processes, we use the chemical formula:
Combustion is a rapid oxidation reaction. Under ideal conditions, each carbon atom combines with two oxygen particles, and 2 hydrogen atoms interact with 1 oxygen particle. As a result, harmless compounds are formed - carbon dioxide CO2 and water. The latter evaporates when heated, taking away part of the released heat.
Even in a fire, pyrolysis gases are released - they burn above the main flame, combining with free oxygen
Pyrolysis is a decomposition reaction of a substance that occurs when heated and lack of free oxygen. This principle is used in gas generating plants:
- Fuel (in particular, wood) is placed inside a closed metal vessel - a reactor.
- The container is heated from the outside to 500...900 degrees, and a dosed amount of air is supplied through special holes - tuyeres.
- Under the influence of high temperature, the substance decomposes into 3 main components - carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2) and solid or liquid carbon residue. At the same time, a small amount of carbon dioxide and water vapor is formed.
- The volatile products constitute pyrolysis gas, a flammable mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide that leaves the container through a separate pipeline. The separated gaseous fuel is purified, cooled, and then pumped into the tank.
Diagram of the simplest gas generator installation with a water seal
Combustion and pyrolysis are 2 different processes that can occur simultaneously. Example: during intensive burning of wood, a small volume of carbon monoxide is formed in the boiler furnace, while harmless CO2 is much larger. And vice versa, in smoldering mode, firewood releases a lot of hydrogen and carbon dioxide, some of which manages to turn into CO2 and oxidize. That is, it all depends on the amount of oxygen involved in the reaction.
Watch this video on YouTube
Application of the method in the Russian Federation and in the world
The first pyrolytic enterprises in Russia opened in the last decades of the 19th century. Kerosene was processed there. The resulting products were used to make gas for lighting. The first patent for this method was received by a scientist from St. Petersburg. During the First World War, toluene, a raw material for TNT explosives, was created using the pyrolytic method.
Pyrolysis waste processing plants are located all over the world. Gas, as one of the recycling products, is a source of energy for heating water and heating. Ethylene and propylene are produced using high-temperature processing. The leader in creating a product for producing ethyl alcohol at this stage is the USA. They extract more than 27,000 tons of this substance in 1 year. In Russia they receive 3,000 tons.
Pyrolysis is more popular in the world than in the CIS countries. This is due to the high cost of installation and technical difficulties of operation. New enterprises are not being built; old ones, preserved from the times of the Soviet Union, are being reconstructed.
Pyrolysis equipment for waste processing can be easily purchased on the Internet. The price for one installation starts from 10 million rubles.
The high-temperature processing method has long gone beyond the industrial field. You can find ovens with eco-pyrolysis function. The essence of the mode is that for simultaneous preparation of a large amount of food, a minimum of energy is required.
Classification
There are 2 main classifications of the pyrolysis method. The first is based on the duration of the process. There are fast and slow pyrolysis. The first is like water in hot oil. In this case, the liquid boils instantly. And slow processing is like heating water in a pan. It happens gradually.
Fast pyrolysis has a number of advantages over slow pyrolysis:
- since the products are not tarred, the output is cleaner;
- waste recycling requires the least amount of energy;
- heat release reactions exceed absorption, resulting in the production of energy;
- there is no need to interrupt the technological process.
Waste treatment by anaerobic digestion is divided depending on the level of heating inside the plant. In this way, low- and high-temperature pyrolysis is isolated. In the first case, heating is achieved from 450 to 900°C, in the second - above 900°C.
During low-temperature processing, gases come out in small quantities. But a lot of solid waste remains. The high-temperature method is accompanied by abundant synthesis of gases and a minimum of resins. A distinctive feature of this type of processing is that the solid residue is zero.
In chemistry, a distinction is made between oxidative and dry pyrolysis. The first type is used for recycling waste of a pasty consistency, sediment, raw materials in fuel oil or ash. Dry pyrolysis of waste has become more widespread. It is used for solid waste disposal.
Prospects for the development of pyrolysis
When using catalysts, the cracking process increases sharply and the yield of products increases. In this case, difficulty is caused by the emerging process of coking of the catalysts themselves. Scientific developments in this direction are underway.
The use of process activators or inhibitors that inhibit secondary reactions is also at the experimental stage. But this method of process optimization is also difficult due to contamination of the output product. Currently, methods are being developed to physically accelerate pyrolysis using electromagnetic fields.
In everyday life, heating furnaces based on cracking are becoming widespread, consisting of two chambers, in the first of which sublimation occurs by cracking, and in the second the combustion itself takes place.
Processed products
The volume and type of pyrolysis products vary. The material that was processed, the amount of raw materials, the duration and temperature of the process play a role. As a result of combustion, the following pyrolysis products are formed:
- pyrolytic oil;
- electrical and thermal energy;
- diesel fuel;
- pyrogas;
- Picarbon is a solid residue that is essentially charcoal.
Pyrolytic oil is used as furnace fuel. In fact, it is an analogue of fuel oil. The product is also used as raw material for recycling.
All these products should be obtained in theory. But in practice this cannot always be achieved. To obtain diesel fuel, it is necessary to carefully separate the waste. It is almost impossible to extract raw materials from unsorted residues.
Garbage processing stages
Before burning waste, it is prepared: crushed and dried. Drying is the process that requires the most energy. When processing wood, it is dried to 15%. In addition to removing water from the wood, some components are replaced.
Only after preliminary preparation do they begin to pyrolyze the waste. The most unstable parts of the garbage decompose first. Their splitting occurs at temperatures up to 300°C. At this time, acetic acid, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide are released.
When the temperature rises above 300°C, most of the solid waste decomposes.
This process is exothermic, that is, it is accompanied by abundant heat. Methanol, hydrocarbons, ammonia, and ethers are actively formed.
At the last stages of pyrolysis of waste paper and other wood residues, the substances remaining in the installation are calcined. At this moment the temperature reaches 500°C and continues to rise. A resin with a high molecular weight and volatile gases are released. For example, hydrogen, carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide. The end result is charcoal.
Recyclable Products
The use of pyrolysis is widespread. Thus, obtaining petrochemical products is possible only using this method. Coke used in metallurgy is a product of pyrolysis. Landfills for household waste have been developed, where their destruction occurs using thermal decomposition. The good thing about this method is that it is waste-free; this is relevant in the conditions of the Earth’s polluted atmosphere.
Obtaining petrochemical products
When organic complex compounds decompose under the influence of temperature, simple hydrocarbons are obtained. This process produces ethylene and propylene , and various derivatives from them. Based on them, various IUDs are subsequently obtained by polymerization and synthesis. Cracking in petrochemicals occurs at 800–900 degrees.
Wood cracking
The profession of charcoal burners has long been known, who burned wood without access to air underground and obtained charcoal. At a temperature of 5000, dry sublimation occurs, which produces valuable products - acetone, resin, acetic acid and methanol. In this case, the carbon remains in a solid state and is called charcoal. Such a product is subsequently used as a high-calorie fuel or an activator of chemical processes.
Pyrolysis begins at a temperature of 200 degrees with the release of carbon oxides. It should also be noted that if the decomposition products are subsequently burned in an air atmosphere, then the total calorie content of their combustion will be much higher than the energy spent on pyrolysis.
Wood chemistry is a science that initially developed only in Russia, and the first cracking experiments belonged to Russian scientists.
Destruction of household waste
The use of pyrolysis to destroy household waste and obtain energy through this is promising. The main obstacle is the content of toxic volatile components in waste - chlorine, phosphorus and sulfur. These are active elements that can bind with other pyrolysis products and create dangerous compounds. Recycling tires and polymer materials allows obtaining secondary products and is economically justified.
During pyrolysis in the apparatus, the processed product goes through the following stages:
- drying process;
- cracking;
- burned the remainder in the atmosphere;
- gas purification in absorbers.
At the same time, the waste incineration plant has different modes and settings designed for a particular process.
To completely process waste, gas products are sent to special absorption plants, where they are cleaned of toxins. obtained as a result of pyrolysis is a valuable product , as it contains rare elements that are used for further processing.
At the same time, at a waste processing plant you can get:
- thermal energy;
- electrical energy;
- Tire and polymer processing products.
Recycling production during waste sorting will become economical. In the meantime, everything is taken to landfills, even mercury waste ends up.
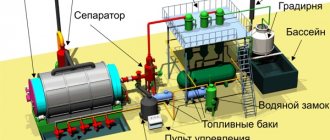
Description of the pyrolysis plant
The device for processing waste at high temperatures is dynamic. It can be moved to different parts of the room. A pyrolysis incineration plant has the following components:
- thermal reactor;
- a pyrolysis gas removal system, which includes a settling tank and a condenser;
- a set of devices for removal and purification of gases.
The main component in a pyrolysis installation is the reactor and its components (furnace and coal mine). The waste enters the top of the reactor, descending through the combustion process until it eventually ends up in the weld pit. High-temperature combustion occurs in the middle part of the reactor, and in its upper layers the waste is dried.
The combustion process consists of two stages: coking and thermal decomposition. Gases formed in the reactor do not immediately escape. To protect the ecological system, they must go through several stages of the pyrolysis line. The waste heat boiler is located first at the outlet of the reactors. Next, the gases enter the dryer and absorber. In the latter they are treated with lime milk. After this, the gases are released into the environment.
In the reactor of industrial pyrolysis furnaces for solid waste, sludge remains - municipal solid waste that has not been converted into gas, a mixture of salts and ash. It is completely safe. It is used in agriculture, industrial production as fuel or raw material.
Myths about pyrolysis TT boilers
The main design difference between a gas generator heater and a traditional direct combustion boiler is 2 chambers instead of one. A ceramic nozzle is installed between both fireboxes, and the air is forced into the air by a fan. The metal walls of the pyrolysis unit are protected by a lining of refractory bricks. How does he work:
- Firewood or coal is placed in the upper (primary) chamber and set on fire.
- Automation starts the boost fan.
- When the temperature in the firebox rises to 500 degrees, the release of pyrolysis gases begins.
- Entrained by the general flow of combustion products, these volatile compounds enter the lower secondary chamber, where they are burned in the presence of oxygen (supposedly).
Cross-section of a gas generator heater
In reality, the resulting synthesis gas begins to burn in the primary firebox, since the fan supplies excess air. Only a torch of flame is directed into the second chamber... and that’s all. Then the combustion products move through the flame tubes of the heat exchanger, heat the coolant and fly away into the chimney.
Addition. There is another design of heaters - without a fan, the secondary chamber is located at the top. From the point of view of pyrolysis, the concept is unworkable; the unit functions like a regular wood-burning hot water boiler, although it costs twice as much as its classic counterparts.
Supporters of pyrolysis heat generators (this includes manufacturers of this equipment, sellers and home craftsmen) attribute the following advantages to their TT boilers:
- the fuel is burned completely, the residue in the ash pan is practically zero;
- burning duration – 10 hours or more;
- low volume of harmful emissions into the atmosphere;
- high efficiency due to efficiency of 86...90% (manufacturers’ indicators) compared to traditional boilers with an efficiency of 75%.
Let's try to understand the veracity of these statements. Point one: if the firebox is loaded with dry wood (these are required according to the heater operating instructions), then after combustion there will be fine ash left. The air flow created by the fan and accelerated in the nozzle will simply blow the light residue into the chimney.
Due to the forced injection of gases from the side of the furnace, only a large fraction of ash remains in the secondary chamber
The result is an almost empty ash pan, the illusion of complete combustion. If you put dry wood into a classic turbocharged TT boiler, you will get a similar residue - a little ash at the bottom. That is, the completeness of combustion depends on the quality of the fuel, and not on the design of the heat generator.
Comment. Stacking raw firewood with a humidity of over 50% will give a negative result in any boiler. There is no point in considering such options.
Let us briefly answer the remaining statements:
- The burning time of 10-12 hours corresponds to reality. Another thing is that this indicator is achieved due to the size of the fuel chamber (100 liters or more), where a lot of firewood is placed. Pyrolysis has absolutely nothing to do with it.
- The assurances about the environmental friendliness of the boiler are true. The fan pumps air in excess, producing very little toxic gases. In standby mode, oxygen does not enter the firebox, the wood smolders slowly and the amount of harmful emissions increases.
- Boiler efficiency of 90% is fairy tales. In active combustion mode, the principle of operation of the boiler is similar to turbocharged versions of traditional units, whose efficiency does not exceed 75%. When the fan is turned off, the flame dies out and the smoldering coals emit little heat.
Conclusion. Purchasing a gas generator model of a solid fuel boiler is a very dubious undertaking. The unit is three times more expensive than conventional versions and twice as heavy due to the lining. Homemade heat generators, as a rule, are more reliable and cheaper than factory ones, but are too bulky. In terms of efficiency and other characteristics, they do not outperform classic TT boilers with a turbine or chain draft regulator.
Our opinion will be confirmed by a well-known expert practitioner in his video:
Advantages and disadvantages of different types of pyrolysis
Each type has its pros and cons. Low temperature pyrolysis has the following advantages:
- You can recycle waste without sorting it;
- minimal release of toxic sulfur and nitrogen oxides.
But this method has more disadvantages than advantages. Among them:
- high cost of installations;
- large dimensions of furnaces and complex design;
- operation requires a lot of funds and labor;
- High molecular weight compounds do not decompose.
Among the advantages of high-temperature pyrolysis are the following:
- gas is used as a raw material for thermal energy;
- at the outlet the gas has a minimum amount of impurities;
- liquid pyrolysis products (oil) are used as a substitute for oil;
- Ash is used in road construction.
High temperature processing is more profitable from an economic point of view. It requires less costs, and pyrolysis products can be reused.