What is a geothermal heat pump
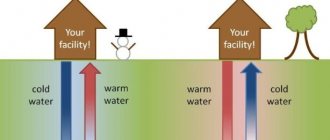
The product is an autonomous station that uses low potential thermal energy of earth, water, and air for operation. In reality, the TN looks like an air conditioner, but it works for heating. Due to the location of the pump manifold below the soil freezing level, the device also operates at negative ambient temperatures, which allows the station to be used in northern regions.
On a note! To ensure an uninterrupted supply of energy for heating the house and hot water supply, heat pumps are combined with solar heating systems.
Pros and cons of geothermal heat pumps
In conclusion, it is worth mentioning the strengths and weaknesses of geothermal heat pumps. Their advantages include:
- Economical. Geothermal installations are more profitable than gas, electricity, solid fuel, etc. The economic benefits are very significant. The costs are recouped in about 5 years;
- Functionality. Geothermal equipment can be combined with other systems designed for air conditioning and heating of premises. You can assemble an installation that works for cooling in the summer and heating in the winter. In addition, nothing prevents the parallel use of solar panels with a pump to generate the required electricity;
- The service life of the heat pump is 100 years with scheduled replacement of components. The first repair will be required after 30 years. After the scheduled replacement of worn parts, the pump will continue to operate in operating mode.
The disadvantages include:
- High requirements for the local area. Pumps cannot be installed anywhere. It is necessary to conduct reconnaissance to determine what would be more expedient, a horizontal or vertical contour ;
- High price. The purchase and installation of a medium-power pump will cost 300-500 thousand rubles. In some countries, there are preferential loan programs for the purchase of such systems;
- There are some problems with the circuit in the first year of service. This leads to a slight decrease in coolant circulation. Therefore, after a year it is recommended to inspect the water circuit, and this entails costs for improving the area around the house.
In developed countries, geothermal pumps are installed both in residential buildings and in industrial premises. There are many industrial centers that are heated using heat extracted from the ground or water. And the experience of using such devices shows that it is feasible and cost-effective.
Principle of operation
The functionality of the equipment is based on constant positive soil temperatures below the freezing level. As you go deeper into the earth, the temperature increases. The principle of operation is to use and convert the resulting thermal geothermal energy to warm up the coolant in the house.
The process is carried out as follows:
- an energy extraction circuit is installed;
- the pipeline is filled with propylene glycol;
- the circuit is connected to vertical geothermal zones buried in wells at 60-100 m or to a collection collector laid in the ground below the freezing point (from 1 m of depth);
- the salt solution moves in a closed circle between the probes and is heated to +5 C.. +6 C, then transported to the receiving compartment of the HP.
Now the heat pump comes into operation, taking and storing heat from the environment.
Structurally, the pump consists of several main and additional elements, where all processes of accumulation and transfer of thermal energy to the coolant take place:
- Closed circuit. The pipeline transports freon, which changes from liquid to gaseous state.
- Evaporator. The module is connected to a HP receiver and is needed to evaporate freon, which absorbs the heat of a heated brine solution (propylene glycol).
- Gaseous freon moves to the compressor part of the pump, where pressure is built up. Under pressure, the gas is heated to +65 C and injected into the condenser.
- In the condenser, the heated gaseous freon turns into a liquid state, while maintaining heating to high temperatures. Heat exchange is carried out through the walls of the condenser, due to which the coolant in the heating system of the building is heated.
Thus, a geothermal heat pump for heating a house provides heating of the coolant to maintain the room temperature to +25 C. This is enough to keep the rooms warm in winter frosts, when the thermometer outside the window drops to -30 C.
The most economical ways to heat a garage with your own hands
The heat pump is designed in such a way that it can be connected to heating systems with low-temperature incoming coolant, for example, to a heated floor circuit. Safe equipment has a lot of advantages, and in summer the device works to cool the house in air conditioning mode.
On a note! If the heat pump circuit is combined with solar panels, the system becomes energy independent. Autonomous heat supply and hot water supply are especially convenient for buildings located outside the city, where there is no possibility of connecting to central highways.
Functional features of the system
The operating principle and functional features of a geothermal heating system at home consist of the following steps:
- The solution located in the outer loop acquires additional heating in the ground by about 5 degrees. Its final temperature may be around 3.
- Having entered the heat exchanger of the pump, the solution transfers even its small energy to freon, for which it is quite enough for evaporation. Having passed into a gaseous state, freon enters the compressor, where it is compressed. The thermodynamic processes occurring in this case lead to a rise in temperature to 100. And the hot gas is supplied to the heat exchanger, where it transfers energy to the coolant of the internal circuit, most often water. Thanks to the scientific work of physicists and engineers, this process has been studied in detail and is embedded in the fundamental principles of the operation of various types of modern equipment.
- The coolant of the internal circuit reaches a temperature of 50-70 and enters the radiators and pipes. The cooled freon enters the expansion screen, its temperature and pressure drop to their original values and the entire cycle can be repeated again. The solution of the outer contour moves in the same way into the depths of the earth for a new portion of energy.
Ground-to-ground heat pumps
To maintain the operation of the circuit, it is necessary to ensure a constant supply of heat from the ground.
There are two types of contour layout with their own characteristics and efficiency characteristics:
- Horizontal type heat exchanger. Pipes for the geothermal circuit are laid below the freezing point of the soil. The method does not require the use of equipment for drilling wells; you can do it yourself - dig trenches to a depth of 1 m, lay pipeline loops. The downside is the increased loop size. For example, to warm up a room with an area of 220 m2, it is necessary to lay a circuit over an area of at least 600 m2 (six acres). Therefore, horizontal heat exchangers are only available if there is a large area around the house.
- Vertical type heat exchanger. The design involves immersing geothermal probes into wells that are deepened to a depth of 200 m. Wells can be drilled in limited areas, the advantage is maintaining a consistently high temperature - at depth the thermometer does not drop below +18 C. The downside is the mandatory use of drilling equipment.
On a note! The deeper the drilling, the higher the constant temperature of the soil.
Water-to-water heat pumps
This is an alternative use of a geothermal pump in which energy is extracted from water.
The circuit can be configured in two ways:
- Immersion of the heat exchanger to the bottom of the reservoir. The advantage is the absence of lengthy excavation work. The loops are laid out along the bottom of a nearby water source, which is located no further than 100 m from the house. The bottom depth must be at least 3 m.
Important! The optimal solution is to have your own pond. Placing loops in a river or lake will require special permission.
- Placement of probes in artesian wells. When pumping water from a well, the flows are driven through a heat pump, and the liquid is discharged into a second well, which also balances the pressure in the watered formations.
A simplified scheme for obtaining energy from water explains the popularity of water-to-water geothermal pumps.
On a note! If the option with artesian wells is used, then the costs of drilling wells are taken into account - in this case, artesian depths are required, and this is also from 180 m, so you will have to obtain permission to carry out the work and attract specialists.
Rules for choosing a heat pump
The VT model is selected depending on the installation conditions of the station. Limitations may be related to the terrain, groundwater level, lack of area for laying out loops, or the presence of a reservoir. For example, if the soil is rocky, then drilling to watered layers will result in significant costs - you will have to look for an option with a horizontal arrangement of loops, which means that large areas of the site are freed up, or the presence of a nearby reservoir.
On a note! In order not to make a mistake with the choice of arrangement scheme, you should contact a specialist. A professional will draw up a project and carry out preliminary calculations.
The most economical and cheap ways to heat a private home
What to look for when choosing a heat pump:
- COP. This is an abbreviation accepted in world practice and determines the profitability of installing a circuit, that is, the performance of the equipment in relation to the consumed power supply. For example, COP3 shows that for every 1 kW of current consumed, the HP produces 3 kW of thermal energy - the indicator is considered average.
- Contour layout. The design also affects the performance of the entire station. To clarify how much area is required to lay the pipeline in the ground, you need to calculate the heated area and multiply by 3. The final figure is an indicator of the size of the area for laying out the circuit. For example, if you need to heat 20 m2, then the size of the area for laying out loops is 60 m2.
- Functionality. In order for the house not only to receive heat in winter, but also to cool in summer, you should buy a split system.
Important! In terms of efficiency, geothermal pumps are ahead of any possible heating equipment. Modern models show a COP coefficient of 5. But an electric boiler produces only 0.09-0.99 kW of thermal energy per 1 kW of consumed current.
Ground source heat pump performance indicators
As in the case of air source heat pumps, their ground source counterparts have many modifications that differ in technical characteristics and efficiency parameters. Earth-Water pumps operating in open groundwater systems have an efficiency coefficient in heating mode in the range from 3.6 to 5.2, in cooling mode - from 16.2 to 31.1, respectively (see Fig. 2).
Rice. 2 – Efficiency indicators of a ground source heat pump (open system)
Closed-type ground heat pumps operating from underground pipelines have an efficiency coefficient for heating of 3.1-4.9, for cooling - 13.4-25.8 (see Fig. 3).
Rice. 3 – Efficiency indicators of a ground source heat pump (closed system)
The range of values shown in the figures demonstrates the performance of a typical range of ground source heat pump models. Typically, the higher the productivity, the higher the price of the equipment and, accordingly, the cost of associated costs for installation, commissioning, and maintenance. To have an idea of the full cost of purchasing and commissioning a ground source heat pump, you need to draw up a standard cost estimate, adapted to a specific equipment model. Do not forget that the energy consumption of different types of soil pumps can vary significantly: after all, it depends not only on power and performance, but also on the energy efficiency technology according to which this or that type of machine is designed.
Unlike air temperature, the temperature of the ground remains more or less constant, as a result of which the performance of the soil pump changes slightly in winter. The stable performance of the equipment makes it possible to select a soil pump model to suit the heating and hot water supply needs of a particular household.
Suppose, in the case of an air source heat pump, it would be completely inappropriate to rely entirely on it for heating, since its performance is too dependent on weather conditions and, in particular, on the street temperature. A ground source heat pump, as already mentioned, is subject to much less temperature fluctuations, however, it is not able to cope with the heating load alone.
The ideal option would be when the soil pump is designed to provide 60-70% of the total thermal load (total heating and hot water supply needs). On the coldest days of winter, the power of the soil pump may not be enough, so it is better to have a backup heat source on hand. The combined operation of these two heating systems will completely cover the household's domestic hot water and heating needs. Variable power soil pump systems with a two-stage compressor can satisfy all cooling and some heating needs at low power, and heat the house at full power during the cold winter months.
The Russian market offers a wide range of ground source heat pump models ranging in power from 7 kW to 35 kW, many of which are equipped with a hot water supply unit.
These articles may also be of interest to you:
- Heat pump for home: compare the pros and cons before purchasing
- Air heat pumps: operating principle, features, cost calculation
- Heat pump - a tool for controlling the microclimate of a home
- How to choose a suitable heat pump for a country house and cottage
Geothermal pump power calculation
The coolant heating rate is +65 C - this is the maximum level that the earth pump produces under constant extreme load. It is considered optimal to maintain the coolant mode within +45 C.. +50 C, which allows you to connect the station to a heated floor system.
Calculation of power parameters and circuit length is made taking into account the specifics of the application:
- To calculate the required power, the formula is taken as a basis - 0.7 kW of HP power is required per 1 m2. It turns out that to warm up a house with an area of 100 m2 you need to buy a pump with a power of 7-8 kW.
- The length of the contour is calculated taking into account humidity, soil looseness, and freezing point. To obtain 1 kW of thermal power, approximately 40-60 m of circuit laid in the ground will be required.
- Energy consumption is determined by COP. To ensure the operation of a geothermal pump, electricity is needed, which starts the pump into operation and ensures the injection of freon pressure into the compressor. A pump is needed to circulate coolant in the primary circuit. The higher the COP index, the less electricity the equipment requires.
On a note! All parameters are given conditionally, and for accurate calculations you should contact the equipment seller or the professional drawing up the project.
Heat pump manufacturers
It is believed that the best equipment models are produced by German manufacturers:
- Viessmann. They produce high-performance pumps that develop power up to 290 kW with a maximum heating of the coolant up to +60 C. The stations are supplemented with storage tanks for supplying hot water.
- Buderus. They produce household appliances with a power of up to 60 kW and heating of the coolant to +65 C. Low-noise pumps (40 dB) can be installed in the house, next to the living rooms.
- Vaillant. It produces all types of HP, produces a series of circuits for laying on the bottom of reservoirs, geothermal probes and circuits for laying in the ground. The maximum productivity of the devices is 46 kW, heating the coolant to +60 C. The disadvantage is the small selection of heat pumps, but the quality of the equipment remains high.
- Stiebel Eltron. The company's products are intended to partially or fully meet the heating needs of owners of private houses. The models are complemented by devices for integration into the ventilation system and work for cooling in the summer. The maximum power rating is 98 kW, a wide range of products and types of HP. When choosing, you should contact a specialist.
Important! Devices require particularly careful selection in terms of power and performance indicators. Purchasing low-power equipment will force the HP to work at its limit, and choosing high-power products will force it to function at half capacity.
Duty cycle in cooling mode
The cooling cycle, as a rule, repeats the operating algorithm in heating mode exactly the opposite. Through the operation of the check valve, the refrigerant flows in the opposite direction: it collects heat from the air in the room and pushes it out, in the case of DX-series soil pumps, into water or an antifreeze mixture. The heat is returned to an external reservoir or well in an open system, or to a network of underground pipelines in a closed system. When excess heat is generated, part of it can be used to meet the needs of hot water supply.
Unlike air source heat pumps, ground-based models do not require a defrost mode. After all, underground temperatures are much less subject to changes than air temperature, especially since the main unit of the soil pump is located indoors, so the problem of freezing practically does not arise.
Cost of VT and installation
To calculate costs, you need to take into account the following nuances:
- The price of the station depends on the manufacturer, power and averages 100-120 thousand rubles (from $1,600). The most expensive models are from German manufacturers, but they are also more reliable.
- Work on laying out the contour. Cheaper - horizontal layout, arrangement of a contour along the reservoir.
- Pump installation. This includes laying the pipeline and connecting the circuit. This requires a specialist and saving is not recommended.
On a note! If you contact a company that works on a turnkey basis, the cost of the work can be reduced. For example, all services for creating and connecting an equipment circuit for heating a house with an area of 80 m2 will cost from 350,000 rubles (from $5,300). Investments are one-time.