An autonomous heating system must have an expansion tank for heating, or a compensator. Its function is to compensate for the excess pressure that occurs in the system when the coolant expands due to heating. With a rapid increase in temperature, the coolant liquid expands and a pressure surge occurs, the so-called water hammer. It can destroy pipeline elements and connecting fittings. Other names for expansion devices: hydraulic accumulator, expansomat.
The choice of boiler and radiators for our house can be done as follows. When you use bead thermocouples, you can get all the heat you want. Practical and efficient, they are the perfect combination of comfort and savings. The special steel heat exchangers supplied transfer heat to your home's water supply, providing ideal conditions for your well-being.
Integrates with existing plant
The thermal pallet stove can be the main unit for heating and hot water, or it can integrate a traditional thermohydraulic or underfloor heating system and combine with solar thermal energy. Furnaces, depending on the model, can operate in manual or automatic mode. In the first case, you directly set the desired power level or water temperature. With automatic mode setting the water temperature, the electronics will regulate the power level.
Design and principle of operation of expansion tanks for heating
Heating systems can be open or closed. Accordingly, heating expansion tanks exist in open and closed types.
Open type tanks
An open expansion tank for heating is a parallelepiped-shaped container made of stainless steel. This tank is placed at the highest point of an open heating system, usually in the attic.
The thermal output is guaranteed by the characteristics of the fireplace, designed to provide high heat exchange and durable due to its remarkable thickness. The cast iron door with safety microswitch and wire mesh mounted gasket ensures perfect and consistent closure, preventing abnormal air intakes that reduce yield. High quality parts and materials.
All the details of the slab are the result of careful de-materialization and careful design of even the smallest details. The carbon steel boiler is fully insulated for improved performance. The homogeneity of building materials guarantees resistance to galvanic corrosion. The cuff made of stainless steel or cast iron, its shape, position and size of the air flow holes ensure a long service life and perfect combustion.
Pipes connected to the tank:
- mainline;
- circulation;
- alarm, with locking device.
In this type of heating system, the coolant (water) circulates naturally, without pumps. Despite the comparative cheapness and simplicity of such heating, it is gradually becoming a thing of the past due to numerous shortcomings.
Maximum compatibility and efficiency. The standard circulator provides maximum installation flexibility. It can be calibrated according to the requirements of the plumbing system. The electronic version of the control on some models regulates the amount of water immersed in the unit in accordance with the temperature of the water in the boiler, avoiding condensation. The product, when turned off and connected to a power source, is activated weekly for one minute without locking it out. Reduced energy consumption makes the electronic control of the circulator already compatible with the standards in force from.
- In an open tank, the coolant constantly evaporates, so you need to monitor the water level and add it as necessary. For the same reason, it is problematic to use another coolant, such as antifreeze - it evaporates even faster.
- It is possible for water to overflow from the tank, so it is necessary to ensure its drainage into the sewer or drainage system.
- An open expansion tank requires good thermal insulation so that the water does not freeze in severe frosts.
- Installation in the attic will require additional pipes and connecting elements.
- Air entering the system from the expansion device provokes corrosion of the pipeline and radiators, and also leads to the appearance of air locks.
A system with an open compensator is suitable for heating small one-story houses. Larger houses are heated with closed systems.
For maximum ease of use. The built-in safety and thermal safety valve in combination with the pressure gauge allows you to use the stove in complete peace of mind. Maximum installation flexibility. The standard expansion vessel provides maximum flexibility when installing any type of thermal implant.
Everything you need for a thermohydraulic system. Thermal furnaces are available in a wide range of equipment because they already have the components needed to integrate with the plumbing system, pipe plugs, safety valves and expansion tank.
Closed tanks
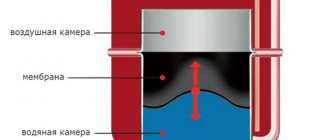
A closed, or membrane expansion tank of a heating system contains an elastic membrane inside, which divides the internal volume of the compensator tank into two compartments, gas and liquid. The gas part contains air under pressure (in some models - nitrogen or inert gas), and the liquid part receives excess coolant when heated.
Monitoring to check and manage parameters. The advanced electronic board provides continuous monitoring of the wardrobe by controlling and checking operating parameters. The pellet level in some models is constantly monitored using a device placed in the tank, which allows you to monitor the pellet content in real time and report its minimum level on the remote control display.
Frypot cleaning system. The cyclic cleaning system of the frypot during operation optimizes combustion and gives... Regular maintenance to be cool is so much more convenient and practical. Maximum functionality and remarkable savings. The thermal chamber is equipped with a display for controlling operation, power level and water temperature and a chronothermostat for the programmer with two daily time intervals.
Closed tank (membrane)
The higher the temperature, the more the liquid part of the accumulator is filled. At the same time, the gas part contracts and the pressure in it increases. When the threshold value is reached, the safety valve is activated and excess pressure is released. And when the heating system cools down, the reverse process occurs and the coolant returns from the tank to the pipeline.
As standard on some models, it monitors the operation of the oven, from turning on the temperature control to any alarms. Consumption is also under control as it allows you to schedule the chronothermost in daily, weekly and weekend modes with two fuses.
Automatic flame power control
The function is always active and automatically adjusts the power and intensity of the flame to achieve the set temperature by calibrating fuel use. They are a good alternative to geothermal heat pumps where drilling or burial is not possible, for example due to hydrogeological restrictions or undesirable soils.
Operating principle of a membrane expansion tank
There are two types of membrane compensators.
- With a diaphragm type membrane. These are small sized tanks. The diaphragm membrane in them is non-removable and cannot be replaced: if it breaks, you will have to completely replace the device.
- With a balloon (pear-shaped) membrane. It can be changed when worn out; it is used in large thousand-liter tanks.
The volume of expansion tanks for heating can vary widely from two to several thousand liters. The shape of the closed hydraulic accumulator is flat or cylindrical. In a flat expansion tank, the membrane-diaphragm is located vertically, in a cylindrical tank it is horizontal.
Even at temperatures below zero, the air in a room contains heat. With a "single machine" you will have a complete climate control system for your home! Ecological coolant absorbs heat from the air. The high pressure and temperature gas transfers heat to the hot water and condensate circuit: moving from gas to liquid.
We can get heat from the sun's rays through simple, environmentally friendly and convenient technology. In this way, hot water and heating can be produced by radically reducing the use of fossil energy sources. Less costs, less emissions, everyone's happier.
It is worth paying attention: a membrane compensator is sometimes mistakenly called a vacuum expansion tank for heating. However, this device does not use a vacuum. The heating system may have a vacuum deaerator to remove air microbubbles from the water.
Open type expansion tank
At the moment, this type of expansion tank is practically not used, because has the following disadvantages:
Open expansion tank.
- The coolant is in constant contact with air, which leads to airing of the system and the appearance of air pockets. Therefore, it is necessary to remove air regularly or install an air separator. Otherwise, the air can lead to corrosion of individual elements of the heating system, as well as a decrease in the heat transfer of heating devices;
- Due to the constant presence of the coolant in contact with air, it evaporates. You have to regularly add coolant to the system;
- Air microbubbles circulating through the heating system create unpleasant noise in pipes and radiators, and also lead to premature wear of circulation pump parts (blades and bearings). In addition, microbubbles “reduce the performance” of the circulation pump;
- Unlike a membrane tank, which can be installed at any point in the system (next to the boiler, in the basement,...), an open type expansion tank is installed only at the highest point. This leads to an increase in the cost of the system, because It is necessary to use additional pipes and fittings to mount the tank at the highest point.
Installing a membrane expansion tank
Unlike an open one, a membrane accumulator can be installed directly at the heating point, next to the boiler, for ease of maintenance. Usually it is placed in a straight section in front of the circulation pump, preferably so that water (or other coolant) enters the compensator from above. It must be equipped with a pressure gauge, a safety valve and connected to the return line.
Even less successful countries such as Austria and Germany have widespread solar thermal systems than Italy. Other sun-kissed countries such as Israel, Greece and Spain have long understood the economic and environmental benefits that flow from the use of this technology and use it with diffusion up to 40 times that can be found in Italy. this delay is due to the lack of adequate awareness of the economic and environmental benefits associated with the use of these plants and the high technological maturity they have achieved.
Hydraulic accumulators with a volume of up to 30 liters are mounted on the wall, larger ones are installed on the floor. When mounting on a wall, the tank should be securely fastened, since its weight increases sharply when filled with water.
Several membrane tanks in a heating point
The technology that converts solar energy into thermal energy has achieved remarkable levels of reliability and convenience in recent years. It is estimated that in the production of sanitary hot water these savings can reach 90%, while in solutions integrated with the heating system they can reach 40% of the total energy requirement of the entire building. The key element of the system that allows us to capture the sun's energy is the Solar Collector. This, through the photothermal effect, transforms solar radiation into heat, unlike a photovoltaic panel which converts it into electrical current instead.
Tanks for water supply systems
Unlike expansion tanks for heating, hydraulic accumulators can be oriented in space however you like, it doesn’t really matter. It will also be useful to install fittings on the supply line to the tank to cut it off from the network and empty it.
But the settings for cold and hot water supply are different. The fact is that the pressure in the pipelines is created by a pump that has an upper and lower shutdown threshold. You need to navigate by them. The pressure in the membrane tank operating in the cold water supply circuit must be set to 0.2 Bar less than the lower pump shutdown threshold. This will avoid water hammer in the system.
As for DHW, here the air pressure in the tank should be 0.2 Bar greater than the upper shutdown threshold of the pumping station. This is necessary to ensure that water does not stagnate in the container. You can find out more useful information by watching the video:
Important performance characteristics and compensator volume calculation
When selecting an expansion tank, take into account the maximum operating temperature and pressure. For example, the coolant can heat up to +120° C, and the peak pressure in the heating expansion tank can reach 6-10 bar (the usual average value is 2-4 bar). Therefore, the characteristics of the membrane, its durability, heat resistance, and compliance with sanitary standards are important.
There are three main types. Open plastic manifolds, mainly used for swimming pools where the required temperatures are relatively low and are used for seasonal use only. Flat plate glass collectors, built in endless variations, are by far the most commonly used since then, with the best performance.
Vacuum collectors, although several times with slightly higher efficiency, their price-performance ratio combined with their greater fragility make them marginal and only for special installations. This system does not use actual solar collectors, but instead consists of a dark plastic dome under a sanitary water tank that is heated for a greenhouse effect. However, at a very low cost, it has very low efficiency, coupled with the danger of winter frost, it reduces the seasonality of use.
The volume of the compensator depends on the volume of coolant as a whole in the system. It is not necessary to calculate the volume mathematically accurately; a simplified method is often used: select a tank with a capacity equal to 10% of the total volume of the coolant. And if this volume is unknown, then they proceed from the power of the boiler and the type of heating devices. The ratios are as follows: for heating radiators they take – 11 l/kW, for heated floors – 17.5 l/kW, for wall-floor heaters – 7.5 l/kW.
Its use is limited to the production of hot water and is so called because the circulation between the solar collector and the storage tank is determined by the principle of gravity rather than by a pump. The heat transfer fluid that is heated inside the manifold becomes lighter as it goes into the storage tank where, receiving its heat, it is returned to a large extent, thus creating a natural circulation cycle. For this to happen, it is necessary to place the storage tank on the roof at a slightly higher position than the collectors.
If the capacity of the selected compensator is insufficient, the safety valve will release pressure too often. In this case, it is enough to purchase and connect in parallel another expansion tank.
It is quite difficult to take into account all the nuances, especially since in each house the heating system necessarily has its own characteristics. In order not to make a mistake when choosing and installing a device, it is better to contact a specialized company.
For this reason, theoretically, in many modern homes, many applied restrictions are aesthetic and structural in nature related to weight. It can use all existing solar collectors and is so called because the circulation between the solar collector and the storage tank is determined by a pump. It is not associated with specific positioning protocols, so it meets a wide variety of technical, plant and architectural requirements. It can be built to any size and for any use, from domestic hot water production to heating system integration; from civil use to industrial use.
Video: installation of an expansion tank
Changing the temperature changes the volume of the coolant, which is fraught with dangerous consequences.
Despite its higher cost, its versatility and technological superiority, it determined its development without compromising other systems. The most common types of installations are two: natural circulation systems and forced circulation systems. Let's see what the main features of each of them are.
It consists of a series of panel collectors connected to a special insulated tank that collects hot water. Usually the accumulated water is then consumed in a direct way, by applying a plant tank and mixing it, if necessary, with cold water.
Maintaining stable characteristics of the coolant in heating systems is necessary for their long-term trouble-free operation.
For this purpose, various devices are used in such systems, one of which is a membrane expansion tank.
Membrane tank design
Externally, the membrane tank looks like a sealed barrel with a flange for connection to the pipeline.
A membrane tank is a sealed vessel in which there are two compartments separated by a flexible membrane:
- the air compartment contains air under a certain constant pressure
- the water compartment is connected to the water supply or heating system; water flows into it at different pressures
The compartments are separated by an elastic membrane that can compress and stretch, thereby changing the ratio between the volumes of one and the second compartments. The air compartment has a valve with a nipple, through which you can change the air pressure, thereby regulating the operation of the membrane tank. It is the air pressure that will determine what volume of water and under what pressure can enter the water compartment.
Diagram of a membrane expansion tank
Why is it needed?
Practically, all coolants for heating systems are weakly compressible liquids.
Equipment of this type can be used in homes, sports facilities, small workshops, bathing establishments and in all situations where the main requirement is the production of hot water. Anodized aluminum frame that is not susceptible to weathering. Anti-reflection selective solar crystal improves efficiency by 15%. Titanium coated inserts increase yield by 16%. High density polyurethane foam insulation to keep water hot for long periods of time. Anodized aluminum exterior.
Accordingly, there is a need to use stabilizing devices - membrane expansion tanks for the heating system (), capable of receiving part of the liquid when volume and pressure increase, and returning it to the circulation circuit when these indicators decrease.
To compensate for the coolant volume
Expansion tanks are used in the system when the temperature changes.
Magnesium anode for preserving the kettle from stray currents. Forced circulation systems are more complex systems that, in addition to hot water for sanitary use, can be coupled to building system heating. In this way, higher energy efficiency is achieved and solar energy is exploited to its fullest extent.
The ideal solution combines solar collectors, condensing boilers and a highly efficient heat distribution system, all in a highly insulated building. Most often, a solar collector system is integrated into an existing heating system, providing great savings on fuel consumption and the emission of harmful elements into the atmosphere.
Among them there are 2 types of devices:
- open;
- closed (sealed);
Open expansion tanks
have become widespread, but are gradually giving way to sealed heating systems, since they have a number of disadvantages:
- additional installation costs, since they are installed at the top point of the system to create the required level of excess pressure;
- loss of coolant due to natural evaporation, and, as a result, the need to constantly monitor the liquid level and top it up;
- the danger of the development of corrosion processes in the system due to constant contact of the heated coolant with oxygen in the air.
Sealed expansion tanks do not have such disadvantages
.
Expansion tank calculation
How to choose an expansion tank? To correctly calculate the pressure in the expansion tank of the heating system, you must first establish the total volume of coolant. To do this, it is necessary to add up the volume of the heating boiler, the volume of the entire pipeline, which consists of pipes connected to the heating network, and the volume of radiators or radiators.
Method for calculating the volume of the expansion tank
- V = (Vsys xk) / q, in which:
- Vsys – coolant volume;
- k is the liquid expansion coefficient;
- q is the efficiency coefficient of the membrane tank.
For proper operation of the system, the volume of the expansion tank is calculated with an acceptable approximation. Usually calculate 15 liters for every 1 kW of boiler power. The average power value for a private home is about 50 kW.
Substituting the values into the formula, we get:
The expansion coefficient of the coolant fluid is about 5% if ordinary water with a heating temperature of no higher than +93 degrees Celsius is used. Sometimes, not water, but ethylene glycol with different percentages is used as a coolant for the heating system.
In this case, the expansion coefficient is determined as follows (for 10% and 20% content):
As a rule, the manufacturer indicates the efficiency coefficient of the membrane tank, but this indicator can be calculated by yourself using the formula:
- q = (Pmax - Pn) / (Pmax + 1) where:
- Pmax is the maximum permissible pressure in the network... For conventional systems it does not exceed 2.6 bar.
- Pn is the initial pressure of the membrane tank during charging. Calculated based on 1.0 bar for every 10 meters of system.
So, to determine how to select equipment for a room with a total area of 400 m2 with a maximum network height of 6 m and an estimated equipment power of 50 kW, the volume of the tank will be calculated as follows:
- Vsys = 15 x 50 = 750 l;
- Pmax = 2.6 bar;
- Pn = 0.6 bar;
- q = (2.6 – 0.6)/(2.6+1) = 0.56
- V = 750 x 0.04/0.57 = 53.6 m3.
Thus, the calculated volume of the expansion tank is 53.6 m3.
To simplify calculations, there is a list of standard approximate values:
- Radiators or radiators - 11 l;
- Warm floor system - 15 l;
- Convector - 8 l.
The video shows how to make such a selection.
Design and principle of operation
The design and principle of operation of the device become clear from the name “membrane tank”.
It represents a hermetically sealed metal container, which is divided into 2 chambers by an elastic membrane.
One of them, the pneumatic chamber, contains air or gas under pressure. The coolant enters another hydraulic chamber (it is written about plastic water tanks).
The device works as follows
:
When the coolant pressure decreases in the heating system lines, reverse processes occur.
The air (gas) compressed in the pneumatic chamber expands, displacing liquid from the hydraulic chamber into the system until the pressure difference is compensated.
This sealed design eliminates
contact of the coolant with air, which significantly reduces the likelihood of the development of corrosion processes not only in the tank itself, but also in other elements of the heating system - boilers, pipelines, etc.
In addition, expansion machines
(sealed expansion tanks) in accordance with SP 41-101-95 “Design of Heating Points” are equipped with safety valves (safety valves), which allow limiting the maximum pressure in the system to a level acceptable under operating conditions.
Due to this, the expansion tank acts as a protection device for the elements of the heating system.
The advantages of balloon membranes include:
- wide range of operating pressures
at which the use of a sealed expansion tank is allowed;- the ability to replace the membrane
, thanks to which repairing the device (it is written about a manual pipe cutter for plastic pipes) becomes faster and cheaper;- ease of setting the minimum (set) pressure for any system.
Model ranges of tanks produced by manufacturers
with replaceable membranes cover a wide range of not only pressures, but also volumes.
At the same time, devices are available in various designs, for horizontal and vertical installation, with mounting on building structures or installation on legs, which significantly increases the flexibility of designing heating systems.
Pressure in the membrane tank and checking it
For a closed heating system to work properly, the pressure in the expansion tank must be 0.2-0.5 Bar lower than in the system. The larger the system, the greater the pressure difference. But, as already said, at the factory they are pumped up to 1.5 Bar, so before installing the expander, it is better to check it and adjust it to your heating system.
The spool is often hidden under a plastic cover
We check the pressure with a pressure gauge by connecting it to the outlet with the spool. If the pressure is higher than you need, bleed off a little. This is not difficult to do - press the petal in the nipple with something thin. You will hear the hiss of escaping air. When the pressure reaches the desired level, release the petal.
If the membrane tank is inflated too weakly (this also happens), it can be inflated with a conventional pump. But it’s more convenient to use a car one, with a pressure gauge - you can immediately control the pressure. After verification, you can install it on the system.
How to choose correctly
The correct choice of an expansion tank is one of the tasks, the solution of which will ensure the safe operation of the heating system as a whole.
When choosing a membrane expansion tank
You should pay attention to the following characteristics:
The main characteristic by which a tank is selected is its volume.
Calculation of optimal volume
Some sources provide advice on choosing the volume of the expansion tank within 10% of the total volume of coolant in the heating system.
This method of determining the capacity of the expansion tank () is based on the fact that the coefficients of thermal expansion of the coolant, even with a glycol content of up to 90% and heating up to 100 degrees, do not exceed 0.08.
However, this calculation option does not take into account pressure
in the system and can cause significant errors.
A more accurate method for calculating the required volume of a membrane tank uses the ratio:
- V = C * Bt / (1 - (Pmin / Pmax)).
In this expression:
The volume of coolant in the system is determined
taking into account all its nodes. This parameter can be obtained from the heating design documentation.
If it is not available, and it is difficult to determine the exact value of the indicator, you can resort to an approximate calculation.
Its essence is that the volume of coolant in heating systems is directly related to the heating power - for every kW there is about 15 liters of liquid.
Thermal expansion coefficient
The liquid is determined by its composition - most often, water is used in heating systems of private houses and apartments, but it is possible that glycols are added to it to improve characteristics.
In addition, this coefficient depends on the temperature of the coolant.
You can find the necessary values in, which are given in specialized literature or on relevant Internet resources.
Maximum system pressure
is determined by the minimum of the values permissible for various nodes. It is to this that the safety valve is adjusted.
The setting (minimum) pressure of the tank corresponds to the initial pressure in the heating system with cold coolant.
For most devices, it is possible to finely adjust it using standard means (bleeding air from the tank or pumping it with a conventional pump).
Tank pressure
can be controlled by installing a pressure gauge on it.
The values obtained as a result of the calculation give an increase in the volume of coolant in the system when it is heated.
The tank is selected according to the calculated value, taking into account the fill factor, rounding it up.
The tank filling coefficient depends on the initial and maximum pressure and can be found from tables provided by device manufacturers or from tables in reference literature.
Tanks for heating systems
In a situation where the documentation for the tank does not prescribe how to correctly orient it in space, we advise you to always place the tank with the inlet pipe down. This will allow it to work in the heating system for some time if a crack appears in the diaphragm. Then the air at the top will not rush to penetrate the coolant. But when the tank is turned upside down, the lighter gas will quickly flow through the crack and enter the system.
It doesn’t matter where to connect the tank supply – to the supply or return, especially if the heat source is a gas or diesel boiler. For solid fuel heaters, installing a compensating vessel on the supply side is undesirable; it is better to connect it to the return line. Well, at the end, adjustment is required, for which the device of the expansion membrane tank provides a special spool on top.
The fully assembled system must be filled with water and the air vented. Then measure the pressure near the boiler and compare it with the pressure in the air chamber of the tank. In the latter it should be 0.2 bar less than in the network. If this is not the case, it must be ensured by bleeding or pumping air into the membrane water tank through the spool.