The main reasons for increased pressure
Most often, the reason why the pressure in the heating circuit increases in a closed heating system is equipment failure due to which the indicators either jump up or drop sharply down. But apart from this, the reasons also include the following:
- A sharp increase in coolant pressure due to blocked shut-off valves. An increase in pressure is observed in the system, after which the boiler is blocked and the system stops. To fix the problem, you need to check the fittings for leaks, open valves and taps to relieve pressure.
- The reason for the increase in pressure in the heating system may be contamination of the dirt filter. Rust particles, debris, sand and slag accumulate on the surface of such a filter. As a result, the pressure increases greatly in the area between the boiler and the filter. To eliminate the cause, it is necessary to regularly clean the filters, at least 3-4 times a year. Also, a good solution would be to replace conventional mud filters with magnetic or flush filters. They cost more, but their maintenance is much easier.
- The operating pressure of the system may increase due to a malfunction of the heating boiler automation. This is a manufacturing defect, incorrect system settings, or a breakdown of the control board. All these problems require boiler repair, which can only be carried out by a master.
- There are leaks in the make-up tap, that is, water will constantly penetrate into the general circuit, which causes a pressure surge. The repair is usually quite simple, you just need to replace the rubber gaskets. But if there is a defect, the crane or equipment should be completely replaced.
Why does the pressure drop in a double-circuit or conventional boiler? This situation most often occurs when the expansion tank breaks down or the air valve leaks. To fix the problem, you may need to repair or completely replace the tank.
Heating system
Why do you need an expansion tank?
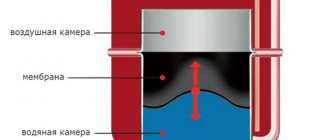
The heating expansion tank stores excess expanded coolant when it is heated. Without an expansion tank, the pressure may exceed the tensile strength of the pipe. The tank consists of a steel barrel and a rubber membrane that separates air from water.
Air, unlike liquids, is highly compressible; with an increase in coolant volume by 5%, the pressure in the circuit due to the air tank will increase slightly.
The volume of the tank is usually taken approximately equal to 10% of the total volume of the heating system. The price of this device is low, so the purchase will not be ruinous.
The correct installation of the tank is with the hose facing up. Then excess air will not get into it.
Why does pressure decrease in a closed circuit?
Why does pressure drop in a closed heating system?
After all, the water has nowhere to go!
- If there are automatic air vents in the system, the air dissolved in the water at the time of filling will escape through them. Yes, it makes up a small part of the coolant volume; but a large change in volume is not necessary for the pressure gauge to register the change.
- Plastic and metal-plastic pipes may be slightly deformed under the influence of pressure. Combined with high water temperature, this process will speed up.
- The pressure in the heating system drops when the temperature of the coolant decreases. Thermal expansion, remember?
- Finally, minor leaks are easy to see only in centralized heating through rust marks. Water in a closed circuit is not so rich in iron, and the pipes in a private house are most often not made of steel; therefore, it is almost impossible to see traces of small leaks if the water has time to evaporate.
Why is a pressure drop in a closed circuit dangerous?
Boiler failure. In older models without thermal control - up to an explosion. Modern older models often have automatic control of not only temperature, but also pressure: when it falls below a threshold value, the boiler reports a problem.
In any case, it is better to maintain the pressure in the circuit at a level of approximately one and a half atmospheres.
Consequences of a heating boiler explosion.
How to slow down the pressure drop
In order not to recharge the heating system over and over again every day, a simple measure will help: install a second expansion tank of a larger volume.
The internal volumes of several tanks are summed up; the greater the total amount of air in them, the smaller the pressure drop will cause a decrease in the volume of coolant by, say, 10 milliliters per day.
Several expansion tanks can be connected in parallel.
Where to put the expansion tank
In general, there is no big difference for a membrane tank: it can be connected in any part of the circuit. Manufacturers, however, recommend connecting it where the water flow is as close to laminar as possible. If there is a heating circulation pump in the system, the tank can be mounted on a straight section of pipe in front of it.
Air lock as a cause of pressure increase in closed systems
When operating a closed system, it is not uncommon for the pressure to increase, which may be accompanied by a decrease in the overall coolant temperature and blocking of the boiler. All this leads to imbalance in the operation of the circuit and failure of its individual elements.
Why does the pressure increase in the system or is there a sharp increase in it? Typically, in closed heating circuits using gas equipment or other types of boilers, such changes occur due to airing. Air locks are a fairly common cause of pressure drop. Typically, the presence of such problems is determined in the following cases:
- equipment breakdown;
- incorrect system startup;
- automation malfunctions;
- presence of cracks in the boiler heat exchanger.
There are several reasons for such system failures:
- the contour is filled from the top point;
- upon startup, there is a very rapid filling of water in the system;
- Mayevsky valves or air vents are faulty;
- the heating radiators were not vented after their repair;
- The impeller of the circulation pump is loose, that is, air pumping occurs with disturbances.
Relieving pressure in the heating system and filling it with water from the bottom with the taps open to bleed air will help solve the problem. The filling itself should be slow, the work ends when water begins to flow from the top point of the circuit. In addition, after installing the heating system and before starting its operation, it is recommended to treat the air drain valves with ordinary soap foam. This allows you to detect air leaks and prevent the formation of air jams in time.
Reason 3. Leak in the heating system
And, of course, the most unpleasant case of loss of pressure in a heating system is a leak. It can be either in a visible place or appear somewhere where it is difficult to visually detect. Regardless of its location, it will sooner or later make itself felt.
For example, if a leak occurred inside a water-heated floor. This happens when someone accidentally drills into his branch, either from above or below. This is easy to detect, because a stain immediately appears or even water gushes out like a fountain. To eliminate this problem, it is necessary, of course, to carefully disassemble the floor at the leak site, install the necessary coupling, and, upon completion of the installation, re-cement this area.
Optimal value for a private house or cottage
Any boiler operates at certain system settings, in particular, it is necessary to correctly calculate the water pressure. This value is influenced by the number of floors of the building, the type of system, the number of radiators and the total length of the pipes. Usually for a private house the pressure level is 1.5-2 atm, but for a five-story apartment building this value is 2-4 atm, and for a ten-story building it is 5-7 atm. For higher buildings, the pressure level is 7-10 atm, the maximum value is achieved in heating mains, here it is 12 atm.
For radiators that operate at different heights and at quite a decent distance from the boiler, constant pressure adjustment is required. In this case, special regulators are used to reduce it, and pumps to increase it. But the regulator must always be in good working order, otherwise sharp fluctuations and drops in coolant temperature will be observed in certain areas. The system must be adjusted so that the shut-off valves are never completely closed.
Pressure drop
An increase in pressure in closed heating systems is not the only problem; in some cases there is a sharp drop in operating pressure, and among the reasons why the pressure level drops, the following should be highlighted:
- hidden system leaks, corrosion, loose connections, leaking fittings;
- rupture of the tank membrane, which requires replacement or repair of equipment;
- pressure drops in the system are observed, if the nipple poisons, such an air leak leads to deflation of the tank, and this causes damage to the membrane;
- there are cracks on the boiler heat exchanger, which leads to coolant leakage;
- pressure drops associated with the appearance of air bubbles lead to a decrease in the overall temperature in the system and its shutdown;
- One of the reasons for the decrease in pressure may be a soured or slightly open tap used to discharge water into the sewer system.
Pressure drop and its importance for the functioning of the heating system
For optimal functioning of any heating circuit, a stable and defined pressure drop is required, i.e. the difference between its values at the coolant supply and return. As a rule, it should be 0.1-0.2 MPa.
If this indicator is less, this indicates a disruption in the movement of the coolant through the pipelines, as a result of which water passes through the radiators without heating them to the required degree.
If the difference exceeds the above value, we can talk about “stagnation” of the system, one of the reasons for which is airing.
It should be noted that sudden changes in pressure negatively affect the performance of individual elements of the heating circuit, often disabling them.
Methods for regulating operating pressure and ensuring the stability of its differential on the supply and return
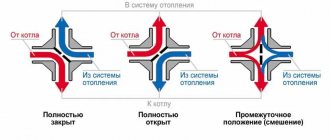
- First of all, it is necessary to remember that optimal operation of the heating system, incl. the creation of the required pressure in it depends on the correctness of the design, in particular, hydraulic calculations, and installation of lines and pipelines, namely: - the supply line in most schemes should be located at the top, the return line, respectively, at the bottom; — for the production of bottlings, pipes with a diameter of 50-80 mm should be used, for risers - 20-25 mm; — connections to heating devices can be made from the same pipes from which the risers are made, or one step less.
It is allowed to underestimate the cross-section of radiator piping only if there is a jumper in front of them.
Figure 3 – Jumper in front of the heating radiator
Figure 4 – Diaphragm expansion tank
The expansion tank, the volume of which is usually taken to be about 10% of the total volume of the system, can be installed in any part of the circuit. However, experts recommend installing it on a straight section of the return pipeline in front of the circulation pump (if available).
To prevent a situation where the device’s capacity is insufficient with a continued increase in pressure, the circuits provide for the use of a safety valve that removes excess coolant from the system.
Figure 5 – Pressure regulator
Finding the reasons for the drop and increase in pressure drop
Deviation of pressure more or less from the norm requires establishing the cause of this phenomenon and its elimination.
Pressure drop in the heating circuit
If the pressure in the heating system drops, then with a greater degree of probability we can talk about a coolant leak. The most vulnerable are the existing seams, joints and connections.
To check this, turn off the pump and monitor changes in static pressure. If the pressure continues to decrease, it is necessary to find the damaged area. To do this, it is recommended to sequentially disconnect different sections of the circuit, and after determining the exact location, repair or replace worn elements.
If the static pressure remains stable, the reason for the decrease in pressure is due to a malfunction of either the pump or the heating equipment.
It should be borne in mind that a short-term drop in pressure may be due to the peculiarity of the operation of the regulator, which at certain intervals transfers part of the water from the supply to the return. In the case when the heating radiators warm up evenly and to the required temperature, we can say that the difference was associated with the above cycle.
Other possible reasons include:
- removing air through vents, resulting in a decrease in the volume of coolant in the system;
- decrease in water temperature.
Increasing system pressure
A similar situation occurs when the movement of coolant in the heating circuit slows down or stops. The most likely reasons for this are:
- the occurrence of an air lock;
- contamination of filters and mud traps;
- features of the functioning of the pressure regulator or incorrect settings of its operation;
- constant replenishment of coolant due to automatic failure or incorrectly adjusted supply and return valves.
It should be noted that pressure instability is most often observed in newly launched systems and is associated with the gradual removal of air. This can be considered the norm if, after bringing the coolant volume and pressure to operating values, which lasts from several days to several weeks, no deviations are recorded. Otherwise, we should talk about an incorrect hydraulic calculation, in particular, the accepted volume of the expansion tank.
Source