We know that geothermy is the heat of the Earth, and the concept “geothermal” is often associated with volcanoes and geysers. In Russia, geothermal energy is used primarily on an industrial scale; for example, there are Far Eastern power plants that operate using the heat of our planet.
Many people are sure that making geothermal heating at home with their own hands is something out of science fiction. Is not it? But this is absolutely not true! With the development of modern technologies, the domestic use of “green energy” has become quite possible.
We will talk about the operating principles of alternative heating, its advantages and disadvantages, and compare it with traditional heating systems. You will also learn about how to position the heat exchanger and how to install geothermal heating with your own hands.
A few historical facts
When the oil crisis broke out in the 70s of the last century, a burning need for alternative energy sources arose in the West. It was at this time that the first geothermal heating systems began to be created.
Today they are widespread in the United States, Canada and Western European countries.
Image gallery
Photo from
Prospects for geothermal heating
Dimensions of the indoor unit of the geothermal system
Cost of installation and operation of a heat pump
Environmental priorities of heat pumps
For example, in Sweden they actively use water from the Baltic Sea, whose temperature is +4°C. In Germany, the introduction of geothermal heating systems is even sponsored at the state level.
When we mention geothermal energy sources, we always imagine a valley of geysers or volcanoes, but the sources we need are much closer. And they will help us stay warm in winter and cool in summer.
In Russia there are Pauzhetskaya, Verkhne-Mutnovskaya, Okeanskaya and other geothermal power plants. But there is very little evidence of the use of Earth's energy in our private sector.
Benefits of Geothermal Heating
This type of system is an excellent way to supply heat to buildings. This is an opportunity to save money and energy. The main advantages of geothermal heating include:
A geothermal heating system generates 5 units of energy from 1 unit. The efficiency of such a system is 530%. The efficiency indicator of a modern gas boiler is 98%.
Due to the large difference in energy efficiency of such a system, on average, investments in it pay off in several years.
Geothermal energy sources are recognized as the most environmentally friendly. They minimize the threat of air pollution. Installing one geothermal pump is the environmental equivalent of planting 750 trees.
Since the heat pump does not use natural gas to operate, there is no source of flame or carbon monoxide.
The equipment can be installed anywhere. The main condition is the availability of electricity in the house.
The geothermal circuit is located underground at a constant temperature. It is not exposed to thermal loads during fuel combustion. The declared service life of heat pumps is 25-30 years.
About geothermal heating sources
The following sources of terrestrial thermal energy can be used for geothermal heating:
- high temperature;
- low temperature.
High-temperature ones include, for example, thermal springs. They can be used, but their scope is limited by the actual location of such sources.
While in Iceland this type of energy is actively used, in Russia thermal waters are located far from populated areas. They are concentrated to the maximum in Kamchatka, where underground water is used as a coolant and supplied to hot water systems.
To effectively use the earth's thermal energy, you do not need a volcano. It is enough to use those resources that are located just 200 meters from the earth’s surface
But we have all the necessary prerequisites for the use of low-temperature sources. The surrounding air masses, earth or water are suitable for this purpose.
A heat pump is used to extract the required energy. With its help, the procedure is carried out to convert the ambient temperature into thermal energy not only for heating, but also for hot water supply to a private household.
Image gallery
Photo from
Absorption of free heat from groundwater and rocks
External heat exchanger of the earth-water system
External heat exchanger in a natural reservoir
Geothermal Well Heat Pump
Geothermal heating equipment
The implementation of a system of this type is only possible with special equipment. It accumulates heat from soil or water and transfers it to the coolant of the building’s heating system. It includes:
- Heat pump;
- compressor;
- buffer tank;
- heat exchanger
The compressor helps bring the antifreeze to the required temperature. The buffer tank accumulates it after heating and transfers its heat to the coolant. The composition includes an internal tank, coolant water and a coil through which antifreeze circulates. This element is also necessary for the reason that the temperature of the antifreeze can vary from -5 to +20 degrees. At the same time, it expands and a container is needed to accommodate the increased volume.
The operating principle of such heating
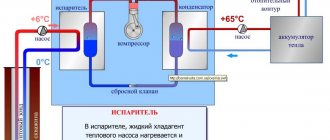
If you are familiar with how an air conditioner or refrigerator works, then the similarity of these processes with the principle of operation of geothermal heating is obvious. The basis of the system is a heat pump, which is connected to two circuits - external and internal.
To organize a traditional heating system in any house, it is necessary to install pipes for transporting coolant and radiators, when heated, heat will flow into the premises. In our case, pipes and radiators are also needed. They form the internal contour of the system. Warm floors can be added to the scheme.
The external contour looks much larger than the internal one, although its dimensions can only be assessed during planning and installation. During operation, it is invisible because it is underground or underwater. Plain water or ethylene glycol-based antifreeze circulates inside this circuit, which is much preferable.
The geothermal heating system includes two circuits - internal and external, as well as the heart of the heating system - a heat pump, which, by compressing the coolant, increases its temperature (+)
The coolant in the external circuit is heated to the state of the environment in which it is immersed and is sent in a “heated” form into a heat pump.
Through it, concentrated heat is transferred to the internal circuit, as a result of which the water in pipes, radiators and heated floors is heated. Thus, the key element that animates the entire system is the heat pump. If your home has an ordinary washing machine, then know: this pump will take up approximately the same area.
To operate, it needs electricity, but, consuming only 1 kW, it produces 4-5 kW of heat. And this is not a miracle, since the source of “additional” energy is known - this is the environment.
What is geothermal heating
A type of heating called geothermal is a system that uses heat from the subsoil. The history of its introduction into practice began in the first half of the 20th century. During this period there was an urgent need for alternative heat sources. Currently, geothermal heating is not uncommon in the USA, Canada, and European countries.
Design and types of system layout
The design of a geothermal heating system includes a pump and two circuits: external and internal. Heat transfer can occur through radiators or an installed heated floor, which is part of the internal circuit. The external part of a geothermal heating system is located in the ground or water. Its scale is greater compared to the internal pipeline. But this fact only matters during installation. During operation, the external contour is hidden from view.
A coolant circulates inside the pipes, the role of which is played by ordinary water or antifreeze. Experts recommend using ethylene glycol antifreeze. The “heart” of geothermal heating is the heat pump. It runs on electricity, but its needs are small. At a cost of 1 kW, the pump produces 4-5 kW of thermal energy. This heat is used to heat the house.
The heat exchanger of a geothermal heating system, operating from a low-temperature source, can have different locations. Two components (pump and internal circuit) remain unchanged in any case. The differences lie in the location of the external pipeline. She may be:
- Vertical
- Horizontal
With a vertical arrangement, the heat exchanger is located in a shaft extended from top to bottom, crossing or not crossing the aquifer. To preserve landscape conditions in the drilling area, several wells are made from one place, going at an angle. An external circuit is mounted in them. The exact depth of the wells depends on geological conditions, but on average it is 50-100 meters. The vertical arrangement is considered more effective than the horizontal one.
The horizontal arrangement assumes the presence of a pipeline coil in a pit or open reservoir. To install such a system, you need to know the depth of soil freezing in the region. The pit is located below this mark. Its dimensions should allow for laying pipes of considerable length.
It is advisable to lay a horizontal heat exchanger if the site for a house is just being developed and the location allows for large-scale excavation work.
External circuit for horizontal geothermal heating of a private house with an area of 250 sq. meters occupies six acres
What sources are used
Geothermal heating uses high- and low-temperature energy sources from the earth. The first type includes, for example, geysers. The efficiency in this case is high, but the application is limited by the geographical location of geothermal sources.
Low-temperature springs are more widely used, especially in those regions where there is no hot underground water. The temperature of the internal layers of the soil at a depth of 50-100 meters ranges from +10 to +15 degrees, depending on the climate. This level is stable regardless of the time of year. This is why the earth can be a source of heat. Water resources are in demand in areas located near the sea. Thus, in Sweden, many private houses are heated using the waters of the Baltic Sea, the temperature of which is maintained at +4 degrees.
How Geothermal Heating Works
The geothermal system is based on the principle of converting heat into cold or, conversely, cold into thermal energy. This is how an air conditioner or refrigeration unit works. The coolant located in the external pipes of the system acquires ambient temperature. In this slightly “warmed up” state, it reaches the pump, where final heating or cooling occurs.
A decrease in pressure in the throttle causes a corresponding decrease in the temperature of the water or antifreeze. An increase in pressure in the compressor entails compression of the coolant and an increase in its temperature. Thus, the heat of the earth enters the house through heating pipes.
Pros and cons of the heating system
Heating a house using heat concentrated deep in the soil of the earth is considered effective, low-cost, and safe. If you break down all the advantages in detail, you get a significant list:
- Easy equipment installation. Affordable installation is supported by a long service life.
- Absolute fire safety. During operation of the equipment, fuel combustion is excluded, so there is no reason for a fire.
- Budget after launch. Financial costs for long-term operation of the heat pump are minimal.
- Environmentally friendly. The system does not emit toxic substances, so there is no burden on nature.
- Functionality. Geothermal heating can not only produce heat, but also create a cooling effect in hot weather.
The disadvantages of the heating system include the high initial costs of installing the equipment and putting it into operation. This minus could be considered conditional, since in the future the investment will pay off in savings on current expenses. But this period averages 5-15 years.
When choosing geothermal heating, you should also consider its dependence on electrical power. In case of electrical problems, the pump stops performing its functions.
Negative aspects also include the limited use of geothermal heating. In densely built areas, obtaining permission for the necessary excavation work is problematic. In addition, due to the low heat transfer rate, generating heat in a large household will require a significant amount of underground piping.
Immersion of a horizontal heat exchanger in a reservoir
This method requires a special location of the household - at a distance of about 100 m from a reservoir of sufficient depth. In addition, the specified reservoir should not freeze to the very bottom, where the external contour of the system will be located. And for this, the area of the reservoir cannot be less than 200 square meters. m.
This option for placing a heat exchanger is considered the least expensive, but such an arrangement of households is still not common. In addition, difficulties may arise if the reservoir is a public property.
The obvious advantage of this method is the absence of mandatory labor-intensive excavation work, although you still have to tinker with the underwater location of the collector. And special permission to carry out such work will also be required.
However, a geothermal installation using water energy is still the most economical.
Do it yourself: what and how
If you are going to install geothermal heating yourself, then it is better to buy the external circuit ready-made. Of course, we are only considering ways to horizontally position the external heat exchanger: under the surface of the soil or under water.
It is much more difficult to install a vertical well collector yourself if you do not have the equipment and drilling skills.
A heat pump is not a very large piece of equipment. It will not take up much space in your home. After all, in size it is comparable, for example, to a conventional solid fuel boiler. Connecting the internal circuit of your home to it is not a difficult task.
In fact, everything is done in exactly the same way as when organizing and distributing heating using traditional heat sources. The main difficulty is the design of the external circuit.
This arrangement of the house relative to the pond is more common. The main thing is that the reservoir is no further than 100 meters from the cottage
The best option would be to use a reservoir if one is found at a distance of no more than 100 m. It is necessary that its area exceed 200 sq. m. m, and the depth is 3 m (average freezing parameter). If this body of water does not belong to you, then obtaining permission to use it may become a problem.
If the reservoir is a pond that is on your property, then the matter becomes simpler. The water from the pond can be temporarily pumped out. Then work on its bottom can be done easily: you will need to lay the pipes in a spiral, securing them in this position.
Excavation work will only be needed to dig a trench, which will be needed to connect the external circuit to the heat pump.
After all work has been completed, the pond can be filled with water again. In the next hundred years, the external heat exchanger should work properly and not cause trouble to its owner.
If you have at your disposal a plot of land on which you just have to build housing and grow a garden, it makes sense to plan a horizontal ground-type heat exchanger.
To do this, you should make a preliminary calculation of the area of the future collector, based on the parameters already indicated above: 250-300 sq. m of collector per 100 sq. m of heated area of the house.
If you have a plot without buildings or vegetation that you would like to preserve, the soil can simply be removed when constructing an external horizontal soil contour: this is easier than digging trenches
The trenches in which the circuit pipes are to be laid must be dug below the soil freezing level.
Better yet, simply remove the soil to the depth of its freezing, lay the pipes, and then return the soil to its place. The work is labor-intensive and complex, but with great desire and determination, you can complete it.
Costs and payback prospects
The costs of equipment and its installation during the construction of geothermal heating depend on the power of the unit and the manufacturer.
Everyone chooses a manufacturer based on their own considerations and information about the reputation and reliability of a particular brand. But the power depends on the area of the room to be served.
This figure summarizes the benefits of using a geothermal heating system. It is precisely this ratio of incoming and outgoing energy that allows the system to first quickly pay for itself and then save its owner’s money (+)
If we take power into account, the cost of heat pumps varies in the following ranges:
- for 4-5 kW – 3000-7000 conventional units;
- for 5-10 kW – 4000-8000 conventional units;
- for 10-15 kW – 5000-10000 conventional units.
If we add to this amount the costs that are needed to carry out installation work (20-40%), then we will get an amount that for many will seem absolutely unrealistic.
But all these costs will be recouped in a very reasonable time frame. In the future, you will only have to pay minor expenses for the electricity needed to operate the pump. And it's all!
Due to the insufficient efficiency of geothermal systems for heating residential buildings, they are used as an addition to the main heating networks or built in complex with two or more heat exchangers
As practice shows, geothermal heating is especially beneficial for houses with a total heated area of 150 square meters. m. Within five to eight years, all costs for installing heating systems in these houses are fully recouped.
If geothermal heating is not particularly in demand among owners of private houses, then the effectiveness of solar systems has already been appreciated by residents of the southern regions. The technology for constructing solar heating is quite simple, and its efficiency and practicality are confirmed by many years of experience in use by Western countries and our compatriots.
More information about alternative energy sources is provided in this article.
Horizontal collectors for heating a house with earth's heat
They are used in regions with a relatively warm climate, where the depth of soil freezing does not exceed 1-1.5 meters. In this case, organizing heating of the house from the ground is much simpler, because you can dig trenches yourself, and the cost of the work will be significantly reduced.
But this scheme also has its drawbacks. First of all, heating from the ground with your own hands is not so easy: for example, for a house with an area of 275 square meters, you will need to lay 1200 meters of pipes in trenches. In addition to the fact that you will have to spend a lot of time digging trenches, the pipes will also take up a large area. This area cannot be used, for example, for a garden or vegetable garden: the roots of the plants will freeze due to the way the collector operates.
Thus, heating with earth's energy is a good idea, but very difficult to implement. The situation is similar with solar heating. It is for this reason that alternative energy sources are not widespread today.
Conclusions and useful video on the topic
If it’s easier for you to perceive visual information, then this video will allow you to see with your own eyes exactly how a geothermal system functions, as well as learn more about who benefits from this type of heating and why.
We invite you to watch a short video in which the owner of a horizontal subsoil collector will talk about his impressions of its operation. Additionally, by watching this video, you will learn about the ongoing costs associated with operating a geothermal heating system.
Each owner of a private home chooses for himself whether to buy the services of resource supply organizations or rely only on himself. In doing so, he is guided by a whole list of considerations.
The goal we have set for ourselves is not to push you to a ready-made conclusion, but to share information about options for solving the problem facing you.
Do you have anything to add or have questions about geothermal heating of a private home? You can leave comments on the publication. The contact form is located in the lower block.