Insulation is one of the types of building materials designed to protect a building from the negative effects of natural factors and maintain warmth and comfort inside. The main property of such thermal insulation is the minimum thermal conductivity.
- Ceiling insulation from above
Types of insulation
Currently, any construction supermarket will offer a large selection of insulation materials, differing in material of manufacture, characteristics, quality, cost and manufacturer. But in all this variety, it is necessary to choose the one that is most suitable for insulating a specific surface. Let's look at the main ones.
| Name | Characteristics | Photo |
| Insulation with an organic base | It is in great demand, made from woodworking and agricultural waste (natural raw materials) with the addition of cement and some types of plastic. It has high fire safety, is not afraid of moisture, and can withstand temperatures up to 150 degrees. | |
| Arbolite | In its production, small sawdust, shavings, chopped straw or reeds are used. Chemical additives or cement are used. The manufacturing process ends with treatment with a mineralizer. | |
| PPVC (polyvinyl chloride foam) | It contains polyvinyl chloride resins, which acquire a foamy structure during the production process. It can be either hard or soft. Used for insulation of facades, walls, roofs and other surfaces. | |
| Chipboard | It is based on small shavings (90% of the total volume) and 10% - synthetic resins and antiseptic substances. | |
| DVIP | Identical to chipboard, but straw trimmings, wood waste, and corn stalks are used in production. Synthetic resins with additives of fire retardants, antiseptics, and water-repellent substances are used as a binder. | |
| PPU (polyurethane foam) | The composition includes polyester, water, diisocyanate, emulsifier. It has excellent heat-insulating, sound-proofing and moisture-repellent properties. | |
| EPP/foam | The composition includes air (98%) and polystyrene (2%). Small amounts of flame retardants are expected. | |
| Foamed polyethylene | The porous structure, with good vapor barrier properties, does not conduct noise well. | |
| Fibryolite | The composition includes wood shavings, cement or magnesium components. It looks like slabs. Resistant to chemical and biological aggressive influences, moisture resistant, does not allow noise to pass through. | |
| Mineral wool | There are two types: stone and slag. Main composition: diabase, dolomite, basalt, limestone, bound by components containing phenol or urea. | |
| Glass wool | Glass industry waste is used in production. It has sufficient elasticity and strength, sound insulation, is not afraid of open flames, and does not emit harmful substances at high temperatures. | |
| Ceramic wool | The basis is zirconium, aluminum, silicon. Not afraid of high temperatures. |
Density of insulation
All thermal insulation materials differ from each other not only in composition and production method, but also in the main indicator - density.
| Name | Density indicator (kg/m3) |
| Cellulose wool | 30 — 70 |
| Wood-fibre board | 150 230 |
| Foam glass | 100 — 150 |
| Linen mats | 30 |
| Cotton wool | 25 — 30 |
| Mineral wool | 50 — 200 |
| Styrofoam | 25 — 35 |
| Extruded polystyrene foam | 35 — 40 |
| Expanded clay | 450 — 1200 |
| Polyurethane foam | 30 — 80 |
The type of insulation depends on the density. He can be:
- especially light;
- light;
- average;
- hard (dense).
The density of the material has a direct impact on indicators such as:
- load-bearing capacity;
- noise absorption;
- thermal conductivity;
- method of fastening.
Consequences of choosing the wrong size of thermal insulation
All types of wall insulation prevent energy loss to varying degrees. One of the negative consequences of choosing the wrong thickness of the insulating material is a shift in the dew point not outward of the coating, but inward. The walls will freeze and mold and mildew will appear on them. Excessive layer thickness does not harm the structure, but living conditions will not change. Excessive thermal insulation is a waste of material and labor costs.
Everyone decides independently which insulation to choose for insulating a house; the main thing is not to forget about a competent approach to the density and thickness of the layer.
Comparative characteristics of insulation materials
In order to make the right choice, you need to understand the difference between one insulation and another.
| Name | Moisture absorption(%) | Flammability | Vapor permeability Mg/m*h*Pa | Thermal conductivity W/m*K |
| Mineral wool | 1,5 | does not burn | 0,49 – 0,6 | 0,037 – 0,048 |
| PPU | 2,0 | burns moderately | 0,02 | 0,023 – 0,035 |
| Styrofoam | 3,0 | burns intensely | 0,03 | 0,036 – 0,041 |
| Ecowool | 1,0 | burns moderately | 0,3 | 0,032 – 0,041 |
| Penoizol | 18,0 | burns low | 0,21 – 0,24 | 0,028 – 0,034 |
To purchase the thermal insulation material you need, you need to pay attention to the following factors:
- where it will be used (for external or internal work);
- it will be laid vertically or horizontally;
- preload on the material;
- the need for sound insulation;
- weather conditions in a particular region.
The functionality of the insulated structure is also of great importance. For example, for commercial buildings, preference should be given to material with significant density and the impossibility of damage by small rodents or other pests.
Which insulation is better for walls?
The most suitable material for this type of work is considered to be mineral wool. It has good properties and a long service life. But in order for it to meet your expectations, it is necessary not only to purchase a high-quality product, but also to follow the installation technology, prepare the walls properly, and determine the dimensions and physical characteristics (density and thickness).
The size of mineral wool is determined taking into account the following data:
- humidity indicator;
- climatic features of the area;
- insulated surface;
- minimum and maximum temperatures throughout the calendar year.
If you purchase mineral wool with low thermal conductivity, it will not be able to perform its main functions. There is also no need to opt for cheap options packaged in rolls. In their production, as a rule, low-quality components are used. Moreover, the material in rolls is 50mm thick, which is unacceptable for work outside the building. It is advisable to purchase mineral wool slabs of significant size.
The higher the density of the insulation, the heavier it is, and, therefore, more expensive. The density of mineral wool varies from 20 kg/m3 to 250 kg/m3, and therefore there will be a significant difference between the materials. To understand which insulation is best for you, you need to understand what depends on the density:
- can the building withstand such a load;
- how much deformation is possible;
- how much the material can be compressed.
But the density indicator has no effect on:
- thickness of the slabs;
- insulating qualities;
- vapor permeability;
- soundproofing protection.
Which mineral wool is best for walls
In order not to make a mistake with insulation, it is necessary, first of all, to take into account the climate characteristics in the place of residence. In temperate climates, the recommended insulation thickness should be 80 – 100mm. For continental, sharply continental, sea, monsoon, arctic, subarctic climates, the range of mineral wool can be from 110mm to 150mm.
Insulation with a low density of 40 kg/m3. can only be used on horizontal surfaces that may not withstand significant loads. The minimum density for walls is 50-75 kg/m3. If the facade is supposed to be ventilated, then the density of the insulation should be 110 kg/m3, subject to subsequent finishing with siding. With further plastering of the walls, the density indicator can reach 140 kg/m3.
Manufacturers and types
However, modern materials, thanks to the latest technologies, can have different densities despite the fact that they are made from exactly the same raw materials.
Fiber raw materials
Basalt wool has an average value of 50-200 kg/m3 - the range is wide. The maximum value belongs to options intended for floors and roofs.
Thus, TechnoNikol Galatel basalt slabs have a specific gravity of 195 kg/m3. Dahrok basalt wool from Rockwool, 190 kg/m3, is intended for insulation under roll roofing. Knauf Insulation HTB basalt fiber with a low density of 35 kg/m3 is intended for frame structures and prefabricated buildings. TechnoNikol Rocklight mineral wool in 30-40 kg/m3 is a lightweight insulation option, and the same Knauff company produces Knauff NTV in a density variation of 150 kg/m3.
Foam materials
The density of foam plastic is about 100-150 kg/m3 - the densest slabs are needed for finishing the roof or floors. Manufacturers clearly divide foam boards by area of application, when the specific gravity changes accordingly. Extruded polystyrene foam at 28-35 kg/m3 is one of the lightest materials and the most heat-insulating.
For example, TechnoNikol Carbon Sand with a rating of 28 kg/m3 is used for sandwich panels, and TechnoNikol Carbon Prof with a rating of 30-35 kg/m3 is applicable for insulating walls and load-bearing structures. Plates from the same manufacturer with a density of 50-60 kg/m3 are used for road construction. Penoplex Wall has a differentiated density: 25 kg/m3 - for insulating vertical structures, 47 kg/m3 - for road construction.
Which roof insulation is best?
Manufacturers produce a wide variety of this material. They all differ in their characteristics, quality and cost. Let's focus on the main ones:
- Styrene materials, which include polyurethane foam, polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam. They are lightweight, easy to install, convenient in size, moisture-resistant, and durable.
- Glass wool or mineral wool. The main advantages are low cost and fire safety. But the disadvantages include excessive absorbency of cotton wool, which negatively affects its density and service life. Its negative effect on the human body has been established.
- Expanded clay, slag, sand, sawdust. They belong to the category of environmentally friendly materials. But they are used only for flat roofs and are mounted exclusively on top. The insulation capabilities of such material are insufficient. Negative aspects include their friability and moisture absorption.
Roof insulation with expanded clay - Polyurethane liquid insulation. Currently very popular. They have many advantages, including significant density.
Polyurethane - Cellulose. A new trend in construction. Its density is good. Thanks to fire retardant additives, it is considered fire resistant. But such insulation can negatively affect the health of residents, so it is not recommended to insulate the roof of residential premises with it.
To select the right material, you need to consider the following points:
- its weight should be insignificant so as not to additionally load the roof;
- mandatory environmental cleanliness, since under constant exposure to the sun, volatile chemicals enter the premises, causing harm to people;
- the optimal service life of the insulation is about 50 years, with maximum preservation of all its qualities;
- the presence of such qualities as heat resistance, moisture resistance, noise absorption.
The design of roofs is of great importance. For flat ones, styrene and environmentally friendly materials are suitable, for pitched ones - cotton wool. For such work, combined options can be used. Such insulation is fastened using a stapler or construction tape.
Attention! Roofs on residential buildings are insulated in one or two layers, and baths and saunas in three or four. Metal roofs require higher density insulation than tile roofs.
Mineral wool for frame house
Frame structures are erected quickly and easily, and mineral wool can be used as a thermal insulation layer. Mineral wool slabs are laid between wooden beams and covered with finishing materials on both sides. The density for the walls of a frame house must be at least 55 kg/m3. During construction, two layers of mineral wool are required. The first is laid directly between the frame beams, the second - from the outside.
For thermal insulation of horizontal surfaces that will not be subject to any load, mineral wool with a density of 35 kg/m3 is sufficient. There is no point in buying denser and heavier varieties; they will only increase the load on the supporting structures.
Mineral wool remains one of the most common insulation materials in construction due to its excellent technical characteristics and attractive cost.
In the video you can see how to insulate a frame house with your own hands using mineral wool. The video clearly demonstrates this method of thermal insulation.
Which insulation is better for the ceiling
There are several ways of ceiling insulation: from above (from the attic) or from below (from the room). There are five main types of insulation for such work:
| Mineral wool | It has a thickness of 20mm to 200mm, is sold in bales or rolls, and may have one foil side to improve thermal insulation properties. |
| Foiled polyethylene foam | Thickness from 1mm to 20mm, rolls 1m wide. Effective, can be used as a second layer to mineral wool to increase the power of the thermal barrier. |
| Styrofoam | Sold in squares with sides of 1m and thickness from 20mm to 100mm. Density ranges from 15kg/sq.m. up to 25kg/sq.m. They are used as intermediate insulation before installing suspended and suspended frames or as a rough base before filling the ceiling. |
| Polyplex | Presented in the form of sheets 120cm x 60cm, thickness from 10mm to 200mm, in a variety of colors and with special bevels for installation. Products with a density of 35 kg/m2 are in great demand. or 45kg/sq.m. Used as a rough coat before puttying. |
| Expanded clay | It has a porous structure, light weight, and oval shape. The attic floor is covered with it to create a thermal cushion under the screed. |
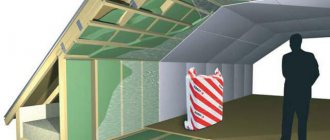
Ceiling insulation from above
Any insulation is suitable for the attic, especially since there is no need to attach them. They are laid tightly on the surface so that there are no gaps or cracks through which heat will escape. Products that are not too expensive are suitable for these purposes, as long as the thermal insulation properties are at their best. The main insulation materials are mineral wool and expanded clay.
Insulation of the ceiling from below
You definitely need to take care of the hanging frame or special fastenings, since fastening work is carried out on weight. The easiest way is to fill the voids between the base and the suspended ceiling with thermal insulation material. You can also use U-shaped hangers. In this case, the insulation is threaded inside the devices, and then profiles made of wood or metal are installed. But this method is only suitable if the height of the ceiling allows them to be reduced by lowering the frame.
Classification of insulation by density level
Usually everyone remembers school physics and associates the density of insulation with weight and mass.
The heavier the better, but this does not always follow true, depending on what factors and what operating conditions.
The choice of insulation directly depends on the budget, as paradoxical as it may sound, and of course the load on the structure as a whole or on a specific element.
Based on the density of the material, the following classification is distinguished:
Extra light
These include polystyrene foam (expanded polystyrene), which has a porous structure.
Designed for insulation in the cavities of walls, partitions, and for unloaded elements of the house.
Lungs
These are insulation materials based on mineral wool. They have a low thermal conductivity coefficient. Widely used in the construction of private houses and cottages.
Average
These types usually include foam glass. It is in the form of blocks and slabs, with high thermal insulation and sound insulation properties. It is not widespread in Russia.
Dense or hard
They also contain mineral wool, tightly pressed under high pressure. This type of insulation is used for outdoor work and is resistant to moisture and mechanical stress.
Density of floor insulation
If you choose the right floor insulation, you can save a third of your heat payment. You can use heated floors, or you can use insulation. The main thing is to make the right choice. It is not recommended to use materials that are too thin, as their benefits are minimal. Too much thickness will also not be acceptable. We need to settle on the “golden mean”.
The climatic conditions of a particular area play a big role. But in any case, the main insulation materials are:
| Styrofoam | If the floor is above the ground, then the thickness of the insulation should be 300mm, if there is a wooden floor - 200mm, for interfloor floors 150mm is enough |
| Ecowool | The thickness of the layers is the same as glass wool |
| Glass wool | For the first floor, the insulation layer should not be less than 400mm, if there is a basement, the thickness can be reduced to 300mm, wooden floors - 200mm, floors in an apartment building - 100mm |
| Penoizol | It is identical in thickness to foam plastic for different floors |
| Expanded clay | If the floor borders the ground, then the thickness of the insulation should not be less than 400mm, if there are wooden floors - 300mm, between floors the insulation layer should be 200mm. In apartment buildings, the layer thickness is from 50mm to 80mm. |
| Cork material | The thickness of the insulation in a private house is 100mm, between floors - 50mm, if there are wooden floors, the thickness can be increased by 20mm. Floors in a multi-storey residential building require insulation thickness from 10mm to 30mm. |
| Polystyrene concrete | The floor in individual residential buildings requires a thickness of insulation of 200 mm; between floors, 100 mm is sufficient. In residential high-rise buildings, the layer should be 50mm. |
What density should insulation be for the walls of a frame house and which insulation is better
Before you start selecting insulation, you need to decide on the thickness of the walls; it should be sufficient to lay the appropriate layer of thermal insulation material. In a frame structure, the dimensions of the wall can be adjusted by selecting a frame base of greater or less thickness.
Important! The space between the outer and inner walls must coincide with the thickness of the insulation in order to avoid the formation of air voids that can disrupt the thermal insulation properties of the entire structure.
Installation of insulation between frame posts.
In particular, you can read about insulating a frame house here.
Several types of thermal insulating materials are widely used as insulation, which have different properties, their own advantages and disadvantages. In particular, these are:
- Styrofoam. The advantages of polystyrene foam are its lightness and ease of installation, and its immunity to moisture. Polystyrene foam is produced in thicknesses from 20 to 100 mm. With a density of 15, 25, 35, 50 kg/m3. For insulation of a residential building from the outside, a density of 25 kg/m3 is recommended. With a small thickness, this material perfectly retains heat inside the house, and is not afraid of moisture, which is very important. If the hydro- and vapor barrier is installed incorrectly, then a dew point appears inside the walls on the thermal insulation layer. A type of foam material is polystyrene foam. You can learn how to properly insulate a frame house with polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene from the corresponding article.
- Glass wool. Available both in rolls and in the form of small slabs, this facilitates installation on various surfaces. Unlike most other materials, it is highly fire-resistant and can withstand temperatures up to 450 degrees. Depending on the purpose and the manufacturer, glass wool is produced with a density of 30–220 kg/m3. Moreover, regardless of the compaction of the fibers, the sound insulation and vapor barrier indicators do not change. The only thing that changes is strength and moisture absorption.
- Stone - basalt wool. Just like glass wool, it is produced in slabs and rolls with a density of 30–220 kg/m3, but since it is made from molten fibers of volcanic rocks, it can withstand temperatures of up to 1000 degrees, both direct fire and indirect heating.
- Expanded polystyrene. Unlike polystyrene foam, polystyrene for home insulation has a higher density of 35 kg/m3 or 45 kg/m3. This not only makes it a more durable material, with good heat retention properties, but also increases sound insulation properties. A significant disadvantage of the material is its low fire-resistant properties. Already at a temperature of 75 degrees, polystyrene foam begins to deform and release a large amount of toxins into the atmosphere. For this reason, it is recommended to use it mainly for external insulation.
Higher density insulation is usually more expensive than low density insulation. At the same time, for high-quality insulation it is better to choose a denser material. The correspondence between price and density must be chosen for each specific case individually.
According to standards
It is clear that many people violate standards during the construction of a house: they install insulation of greater or lesser density and size, especially if the construction is carried out independently. To build a frame house with your own hands and fulfill all the necessary requirements, you must carefully study the issue of insulating the house. If all requirements for the construction of a frame structure are met and all standards are met, it is quite possible to obtain buildings with good thermal performance indicators.
Thus, for residential premises, according to the latest SNIP data, for regions with low temperatures in winter, for example, the Urals and Siberia, the thickness of the thermal insulating layer should be at least 200 mm and the density at least 25–35 kg/m3.
The minimum thickness and density for walls in warmer regions is 150 mm and 25 kg/m3, respectively.
Experienced builders recommend using insulation with a density of at least 50 kg/m3.
At the joints of walls and ceilings, floors and ceilings, the thickness of the thermal insulation layer must be increased by at least 50 mm. Only in this case can you count on building housing with good thermal insulation properties, which will ensure not only the preservation of heat, but also minimal costs for the energy consumed to heat it.
In addition to density, the following standards must be met:
- Fire safety. As a rule, it is marked with the letter G and numbers from 1 to 4, which indicate the degree of immunity to open fire. The highest quality is marked NG - non-combustible materials.
- Shrinkage. To insulate a frame structure, materials with minimal shrinkage are needed.
- Moisture absorption. Moisture absorption should be minimal, otherwise the material increases in mass and becomes deformed, or fungal growths may form in its structure and on the surface.
Stone wool - density
In order to choose the right density of stone wool, you first need to decide on the thickness of the thermal insulation layer. You can find out what thickness of insulation is needed in a frame house from the corresponding article. For example, for stone wool with a thickness of 150 mm, the density should be in the range from 30 to 50 kg/m3.
With a greater thickness of the thermal insulation layer, the density can be reduced to 25 kg/m3.
Basalt insulation - density
Basalt wool, like stone wool, is produced in rolls or slabs, with a recommended density for thermal insulation work in a frame house from 30 to 50 kg/m3. The main difference between basalt wool and other types of mineral thermal insulating material is its high fire resistance.
Basalt fibers can withstand up to 1000 degrees of both direct fire and indirect heat.
Insulation density for facade
The main insulation used for building facades is mineral wool. Its main advantages include the ability to restore its original shape and a long service life. If the facade assumes the presence of ventilated suspension systems, then the density of the insulation should range from 45 kg/cub.m. up to 100kg/cub.m. Such insulation can be attached using elements of the entire system, but for greater strength special dowels can be used.
If finishing with decorative plaster is planned, then the thickness of the insulation increases to 145-165 kg/cub.m. To attach such heat-insulating material, you need to use dowels or a special mixture for gluing mineral wool. As a rule, both types of fasteners are used, which increases the level of reliability significantly.
Properties of foam plastic
Foam plastic is also offered on the construction market in a wide variety.
The following main types are produced, differing in their density and other characteristics:
- PSB-S-15, insulation density up to 15 kg/cub.m.
- PSB-S-25, from 15 kg/cub.m to 25 kg/cub.m.
- PSB-S-35, from 25 kg/cub.m to 35 kg/cub.m.
- PSB-S-50, from 35 kg/cub.m to 50 kg/cub.m.
Each of these types is used to insulate certain parts of the house. Polystyrene foam is a cohesion of polystyrene balls with air inside. The abundance of air determines its thermal insulation properties. The more air there is, the warmer the house will essentially be.
Properties of foam plastic
However, a material with such a reduced density is more fragile; it loses its properties when used in places where there is a possibility of mechanical damage. Therefore, various types of foam plastic are often used when building a frame house. Foam plastic from 15 kg/cub.m to 25 kg/cub.m is suitable for the ceiling, and for floors that are constantly walked on - from 35 kg/cub.m to 50 kg/cub.m. For walls, something in between is suitable - from 25 kg/cub.m to 35 kg/cub.m.
Detailed information about floor insulation is here.
Due to lower thermal conductivity, a high degree of energy saving in frame houses is ensured. Therefore, if you compare polystyrene foam with other materials, for example brick, their energy-saving ability will have significant differences. For example, 12 cm of foam insulation corresponds in its thermal characteristics to 210 cm of brick walls. And to compare the material with wood, you will have to imagine side by side the 10 cm thickness of the insulation and the 45 cm thickness of the wooden wall. The stages of foam insulation are described here.
Average thickness of insulation
Foam plastic with a density of 25 is considered the most universal. It can be used to insulate the facade of a frame or other house or wall. The standard is most often taken to be polystyrene foam, which is 5 cm thick, but if this is the only type of insulation you want to use, use 10 cm polystyrene foam or a double layer of 5 cm polystyrene foam. This method of insulation is used for most purposes.
Foam plastic with a density of 35 can also be used for building facades, insulating slopes of windows and doors, basements, walls and foundations.
Which insulation is best for the attic?
For the most part, mineral wool, glass wool, sandwich panels, organic materials and foam glass are used to insulate the attic. All of them must have fire-fighting properties, high acoustic protection, and significant vapor permeability. As a rule, two layers of material are used for insulation, but experts recommend making the thickness of the insulating layer 250 - 300 mm. These criteria apply to both roll and slab materials.
What density should I use mineral basalt wool in interfloor wooden floors?
Hello, my Readers and Viewers of the construction Blog “The Way Home”! Today I will answer a fairly extensive question. But, in fact, the answer to this is very short. I want to look at this issue a little more broadly. Using the example of some manufacturers, I will try to give an answer and explain why this is so. It would seem that everything should be simple, but in fact there are some nuances.
Full question: What density should I use mineral basalt slab when laying in the interfloor ceiling over wooden beams (insulation thickness 150 mm) and when laying on the attic floor over wooden beams (planned insulation thickness 200-250 mm)?
In order to get the correct answer, you must ask the correct question. There is some kind of paradox in this question: if these are interfloor ceilings on wooden beams, why are we talking about the insulation thickness being 150 mm? Why is he needed there? After all, it’s +20° above, and below too, why insulate yourself? But for some reason they use mineral wool there. Why? But because there is a false ceiling below, some light boards and floor covering above. And if you leave a void between the membranes, a drum effect appears, that is, the sound is reflected repeatedly and creates this effect when walking. Plus the sound insulation of this ceiling is poor. If you lay a porous material between two membranes, which has sound-absorbing properties, the soundproofing parameters of the floor will improve. Therefore, it is more correct to talk about sound-absorbing material with a thickness of 150 mm in the interfloor wooden ceiling.
If the task is to improve the sound insulation of the ceiling, and not just perform insulation, which makes no sense, then the question arises of what density of material to use? And then I immediately want to go to the manufacturers’ websites and show you examples. In the post-Soviet space there are such monster producers of basalt wool as Rockwool and Paroc.
Mentioned in the video
Topic 2014 “Wooden floors. Soundproofing." Topic 2021 “Soundproofing wooden floors.” V. Blasi “Designer’s Handbook. Construction physics."
2:16 Analysis of the issue 3:53 Improving the sound insulation of the floor 7:49 Density of mineral wool 11:12 Features of the attic floor 15:15 Insulation
User Questions
20:35 Wouldn’t it be cheaper to fill the interfloor space with sand? 21:20 What do you think about the “environmental friendliness” of such a decision? 24:41 What glass wool can you recommend? Which manufacturer? 26:08 What if you use expanded clay? 26:47 Why is the negative effect of small particles of mineral wool and glass wool not taken into account?
Sincerely, Alexander Terekhov