How to insulate a house and why - insulation for a house without consequences
Why do our clients order ecofoam insulation? What exactly motivates them not to use traditional insulation? The picture, as always, is very simple. An example from one of our clients (we filmed a whole video story under this post): the house was initially insulated with mineral wool. After insulation, it was discovered that the cotton wool was getting wet. This became especially noticeable when the walls were plastered. The customer decided to dismantle the mineral…
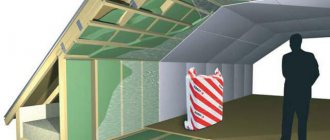
What is the best way to insulate an attic roof?
Roof insulation Ecopen, PPU, Polyurethane foam There is a huge selection of polyurethane foams on the market and the question often arises: which insulation for a home is better. There are two types of foams: hard foam and soft foam. Their density differs: one foam has a density from 10 to 20 kg/m3, the other has a density from 30 to 60 kg/m3. Solid foam (high-density polyurethane foam) has ...
Possibility of using foam fillers
Then manufacturers began to produce sprayed insulation in compact-sized cylinders, which led to a reduction in the cost of the method. To spray such a mixture of steel, complex installations and specialists in thermal insulation finishing are not needed, since the material itself is filled into small containers and the possibility of manual spraying is provided. Each cylinder is designed to cover one square meter of base (layer up to 60 mm thick). One person can process up to one hundred square meters per day.
As a result, calculations showed that working with insulation such as Polynor is much more profitable in terms of labor costs, costs for the materials themselves and surface preparation. If a professional team of workers charges up to one and a half thousand rubles for insulating one square of wall, then using Polinor insulation with the same amount of material, you need to spend only about 500 rubles. You can work independently, which eliminates the need to look for experienced workers, reduces finishing time, and saves money.
The choice of thermal insulation of this type remains the only optimal option that is available to people without special training. Foam can be used to create insulation for foundations, basements, walls inside and outside buildings made of brick, stone, concrete, and blocks. This option is also suitable for thermal insulation of non-load-bearing coatings, including floors on joists, as well as pitched roofs and attic floors.
Since Polinor is suitable for application to bases made of almost any material, it can be used as thermal insulation for plumbing fixtures and sewer pipes or fittings. In such cases, foam insulation in cylinders can be used indoors or in open areas. There is only one limitation on the use of balloon thermal insulation, which is that the material cannot be used to foam voids. It can only be applied to a dense base.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=HzNxMCfzjrE
How to insulate the attic roof of your house during construction?
When you are building a house and at the same time thinking about how to insulate the attic, many additional questions arise: 1. Is a ventilated gap under the roof space necessary? 2. How to properly lay a hydrobarrier (diffusion membrane) 3. Which insulation should I choose? 4. Which vapor barrier should I choose to isolate the insulation from water vapor that tries to escape from the room during the operation of the house? Need...
Spraying polymers for thermal insulation
Polymer foam: 2 main types
One of the most effective methods of thermal insulation is spraying self-expanding polymers with high porosity on surfaces (vertical and horizontal). In this case, two-component foam is almost always used for work: initially the components are stored separately, and only when applied are mixed and polymerized.
Foamed polyurethane between the sheathing beams
The most common material for the production of such foam is polyurethane (PPU). It is produced by mixing a polyol and a polyisocyanate, and the pores are formed by carbon dioxide under high pressure.
Comparison of microphotographs of two types of insulation
Polyurethane foam comes in different varieties, and the main differences are in the type of cell:
- Open cell insulation (density from 8 to 20 kg/m3) is soft and elastic. The pores in the thermal insulation layer communicate with each other so that air can circulate inside. Due to fairly active heat transfer, thermal conductivity increases somewhat, so open-cell foam is usually applied in a thick layer.
It is advisable to spray loose materials in a thick layer or combine them with other types of thermal insulation
The low price of this material is due to its ease of production: ordinary water is used for foaming.
- Closed cell foam (30-60 kg/m3 core) is denser and stiffer. Insulated cavities in the thickness of the material minimize heat transfer, so high density does not reduce thermal insulation. The material is practically impervious to moisture, therefore it is suitable for insulating plinths and basements, for concreting, etc.
Where there is a possibility of contact with moisture, closed cell material is used
Relatively recently, another material has appeared on the market, which is used for sprayed thermal insulation. This is ICYNENE (Aisinin), better known to us as Ekopena. The manufacturer positions the insulation as the most environmentally friendly (foaming occurs only under the influence of water), while being vapor-permeable, airtight and very effective.
Ecofoam spraying: the material is applied similarly to conventional polyurethane foam
In practice, the declared characteristics of Ecopen are confirmed, and the release of volatile substances during polymerization of this material is quite low. But the cost of ICYNENE is significantly higher than its analogues, so it should be used where environmental friendliness will really be a priority.
Advantages of the technique
Insulation with polyurethane foam provides us with a number of advantages:
Pressure spraying allows large areas to be treated
- Convenience of applying foam with your own hands. Thermal insulation material is stored in separate containers: foaming is carried out immediately before spraying. For spraying, dispensing guns are used, with which it is convenient to fill voids.
- Good adhesion. Liquid foam adheres perfectly to almost any surface, so there are no problems either with spraying on walls or with filling large cavities.
The material adheres perfectly to almost any surface
- Expansion and rapid polymerization. Once sprayed, the foam insulation continues to expand, increasing in volume and filling the available space. Contact with air ensures fairly rapid hardening of the outer layer of foam, which provides good time savings.
When using polyurethane foam to insulate windows, its expansion is slowed down by moistening the surface with a spray bottle. Thanks to this, a more dense and uniform structure is formed, which reduces the risk of blowing along the slope to a minimum.
When thermally insulating a mounting seam, it is important that the mounting foam is as uniform as possible
- Good insulation. The thermal conductivity of polyurethane foam is very low: in terms of energy conservation efficiency, 25 mm of material is equivalent to 600–650 mm of solid brick masonry.
Even deliberately setting fire to polyurethane foam is not easy!
Insulating walls with foam allows you to get other advantages:
- vapor permeability (varies for different modifications and brands);
- increased sound insulation;
- reduction in flammability;
- reduction of weight loads on supporting structures;
- insulation of metal frame elements and mortgages.
Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, the material is destroyed, so the exposed thermal insulation layer must be protected.
Good sound insulation will also help with insulation under the bathroom!
When in contact with metal, polyurethane and its analogues do not provoke corrosion
What is penoizol scientifically and where did it come from?
The Germans are considered the creators of penoizol. It was they who, in the thirties of the last (XX) century, synthesized urea with formaldehyde and obtained liquid foam. Today it is made and used differently than ninety years ago. The technology of its production at that time was so serious, complex and problematic that thermal insulation of houses and cottages with it was out of the question. Too expensive! Two decades later, the Germans conducted a series of studies and found that it could be obtained much easier. Reducing the cost of foam insulation has made it accessible to private homeowners.
In the mid-twentieth century, more precisely in the 50s, penoizol was already widely used in the thermal insulation of private houses and cottages in France, Austria, Germany, and even Japan. For residents of the Commonwealth of Soviet Socialist Republics or simply the USSR, it was inaccessible for a number of reasons. The price tag, cosmic for an ordinary person at that time, automatically endowed it with magical, miraculous characteristics. In addition, in the post-war country, penoizol was used in the aviation and rocket industries. It was impossible to get it even for those who lived, as they say, in abundance.
At the end of the era of Secretary General Brezhnev, the military began to use liquid foam. There is a version according to which penoizol was poured between the walls of strategically important objects for conspiracy. It was used to insulate cold armored weapons depots, metal hangars for fighter aircraft, workshops, factories, and service stations for special equipment. A factor in the rapidly growing popularity of penoizol was and remains the list of technical characteristics. One of the priority properties is unsurpassed fire resistance of class “G2”, as well as compliance with the interstate Russian standard “GOST 30244-94”.
How to make urea liquid polystyrene foam penoizol with your own hands.
Description of liquid foam - penoizol.
Urea insulation is a foamed plastic consisting of 98% air and 2% urea-formaldehyde resin with approximately the same number of both open and closed pores. The structure of liquid foam is similar to the well-known soufflé type “Merringue”, and from a distance many people confuse it with expanded polystyrene (foam), but upon closer examination they recognize a completely different material from foam. Other names for insulation are mipore, liquid foam - penoizol, liquid insulation, urea foam, bipor and mettemplast.
Video: Appearance of liquid foam - penoizol and its mechanical properties.
Insulation with liquid foam plastic - penoizol.
— insulation of hollow walls: wooden frame houses, houses made of timber with insulation under the siding, hollow pockets in brickwork;
Video: Insulating the wall of a frame house with liquid foam - penoizol.
— insulation of floors, for example, if the house is on stilts with a ventilated underground;
— insulation of attics;
Video: Filling the floor and attic with liquid foam - penoizol.
- insulation of the attic roof;
— insulation of industrial refrigeration chambers and containers;
— insulation of industrial premises.
Production of urea liquid foam - penoizol.
It is quite simple to obtain liquid polystyrene foam - penoizol - it is a process consisting of several stages:
— Preparation of components: pouring resin and water into working containers, mixing the foaming agent and hardener with water, heating the water to 40 C;
— Filling the hydraulic system of the installation with resin and solution;
— Test pouring into a test container to control the quality of the insulation;
— Direct pouring of insulation into a building structure or mold.
Price for liquid polystyrene foam - penoizol.
The cost of raw materials for producing liquid foam - with 10th density at 2021 prices does not exceed 1000 rubles, even taking into account delivery.
Per cubic meter of 10-density
required:
15 l. resins*45 ruble liter = 675 rubles;
0.085 l. phosphoric acid * 120 rub/l = 10.2 rub;
0.170 l. foam concentrate ABSC * 160 rub/l = 27.2 rub.
Total: 712.4 rub/m3
Per cubic meter of 20-density liquid foam
required:
30 l. resins * 45 ruble liter = 1350 rubles;
0.085 l. phosphoric acid * 120 rub/l. = 10.2 rub;
0.170 l. ABSC foam concentrate * 160 rub/l. = 27.2 rub.
Total: 1387.4 rub/m3
One liter of resin contains 1.3 kg. The usual packaging is 200 liter barrels, approximately 260 kg per barrel.
One liter of phosphoric acid contains 1.75 kg. The usual packaging is 20 liter canisters, 35 kg each.
One liter of foaming agent ABSA contains 1.25 kg. The usual packaging is 20 liter canisters, 25 kg each.
For Siberia and the Far East:
LLC "Sibtem" Dealer, Nizhny Tagil
Novosibirsk, Prigranichnaya str. 3 (Pervomaisky district, Matveevka),
tel.8-913-923-30-72 Yuri Gennadievich
Supplies: Resin: Criterm, phosphoric acid, foaming agent ABSA
OJSC "UralKhimPlast"
Nizhny Tagil Northern Highway, 21. Supplied by: Criterm resin
Technical characteristics of penoizol - list
- thermal conductivity coefficient according to “MCE” – from 0.028 to 0.044 W/m*Kelvin;
- compressive density at relatively weak (no more than 10%) deformation – 0.003 MPa;
- resistance to temperature changes in degrees ℃ – from +70 to 55 with a minus sign;
- the volume of suspended particles of liquid and volatile ingredients is not higher than 12%;
- tolerance to aggressive environments – mold and fungal growths;
- acoustic barrier and noise reduction potential – from 20 to 60 decibels;
- the average density of a thermal insulation cushion is from 10 to 30 kg/m3;
- compression level providing support for the initial shape - 0.07-0.55 kg.cm2;
- repels small insects, voles, rats, and other pests;
- sorption humidification during the day (24 hours) – no more than 20% (twenty);
- resource guaranteed by the manufacturer – from 75 (min.) to 120 (max.) years.
Comparisons of POLYNOR with other insulation materials
POLYNOR (polynor) - can be compared with many materials and insulation materials, but we will focus on the most basic ones.
We consider the economics or the true cost of insulation
When choosing any product or building material, the question always arises regarding the price/quality ratio. I would like to do everything efficiently, relatively inexpensively and not return to this issue for a long time. When insulating, it is not enough to choose the insulation you like based only on the cost and its physical and chemical properties, but you also need to understand what additional costs will arise during the work. Let's consider this using the example of traditional insulation materials: polynor, mineral wool, expanded polystyrene and polystyrene foam for an insulation area of 100 m2.
The thermal conductivity coefficient of Polynor thermal insulation is 0.023 W/(m*deg.). This is the minimum indicator among the insulation listed above! The number of closed cells is 70%. Based on this and similar parameters for other insulation materials, the thicknesses required for insulation, all other things being equal, were determined:
Mineral wool -15cm.
Accordingly, the required volume and cost of the material itself (at Leroy Merlin prices as of December 5, 2014):
Polynor - 5m3 (or 100 cylinders) X 325 rub. = 32500 rub.
Mineral wool (Ursa Terra 34PN, 50mm.) - 15m3./70rub. per m2. RUR 21,000. Expanded polystyrene (URSA XPS, 50mm) - 13m3. /224 rub. per m2. 58240 RUB. Polystyrene foam (PSB-S15U, 1x0.6x0.03) - 15 m3/36.3 RUB. per m2. 18150 rub.
Now let's move on to the second part of the question - additional costs for installing thermal insulation, the cost of work and delivery of insulation materials to the construction site.
Transportation. Polynor is produced in cylinders with a capacity of 1 liter, the covered area is 5 cm thick. is 1m2. For 100 m2 you will need 100 cylinders or 9 boxes. Transportation costs are insignificant, unlike other compared insulation materials. Their transportation requires special transport.
Cost of work. Polynor is a high-tech material, there are no requirements for the preparation of the insulated surface, it does not require lathing or vapor barrier, any person without special skills can apply PPU insulation. As a rule, construction company prices for work are 90-100% of the cost of the material itself, but this does not apply to the Polynor brand. You can apply it yourself or negotiate at your own discretion (maximum 30% of the cost of the material).
At Leroy Merlin prices as of 12/05/2014:
Vapor barrier Izospan, roll 70m2-950rub/piece.
Hydro-windproof membrane Izospan AM, roll 35m2-30 RUR/m2.
Mounting adhesive Tytan Prof Classic Fix - 139 RUR/pc.
Cost of thermal insulation materials per 100m2
hydro windproof membrane
The cost of the required materials was calculated based on the amount of materials used:
- Edged board: distance between logs 1 m. Board section: 0.02X0.08m. Cubic capacity: 100X0.02X0.08=0.16m3. Cost: 0.16m3X7000rub.=1120rub. 1a. This section of the board when insulating Polynor is necessary and sufficient to ensure the solidity of the entire insulated structure as a whole, eliminates the temperature gradient, cold bridges and moves the dew point outside the insulated plane.
- Lathing + counter-lattice: Cell format - 0.6X1.2. With this format, the amount of timber per 100m2 is 25 pieces with a length of 10m. Section of timber: 0.05X0.15m. Cubic capacity: 250X0.05X0.15=1.875m3. Cost: 1.875m3X7000rub.=13125rub.
- Vapor barrier: Cost: 100m2-1360rub.
- Hydro-windproof membrane: Cost: 105m2-3150rub.
- Assembly adhesive: 17 pcs x 139 rubles = 2363 rubles.
Mineral wool: 5-7 years (further absorbs moisture and becomes deformed)
Expanded polystyrene: PPS_JSC JV Tigi Knauf _ GOST 15588-70_13 years EPPS_NPP "Expol"_TU 2244-001-17953000-97_34 years EPPS_ZAO "Khimich. Plant"_TU 2244-002-17953000-95_16 years Eps Flomate_ "Dow Chemical"_DIN 4108_37 years Eps Roofmate_ "Dow Chemical"_DIN 4108_40 years Foam plastic: at least 30 years Polynor: 45 years
Thus, to summarize: we see that Polynor is in the middle price segment between mineral wool and expanded polystyrene, but in terms of the totality of all costs for arranging thermal insulation, durability and transportation, it is confidently in the lead.
Types of penoizol and use in thermal insulation
People who are poorly informed about it mistakenly believe that white foam, similar to a delicacy from distant childhood, is the only form of urea-formaldehyde foam. In fact, it comes in three variations. The most popular and objectively in demand is the liquid form of penoizol, which some craftsmen obtain using artisanal methods. Penoizol can indeed be prepared at home, but we categorically do not advise you to do this for reasons of basic safety. Mistakes when working with hazardous chemicals can cost you much more than you realize.
Harmfulness of penoizol and impact on human health
Get straight to the point! In the United States of America, as well as Canada, it was banned for use at the official state level for a long time. Later, researchers proved that during operation, liquid foam does not emit carcinogens and is therefore safe. As a result, the ban was lifted. Russian factories, which simultaneously act as suppliers, claim that this insulation is not inferior in safety to steak sawdust and ecowool. In England, the use of urea-formaldehyde insulator in the thermal insulation of residential buildings is permissible only with a special document in the form of permission from regulatory authorities.
Application Features
Before using POLINOR to insulate a particular area, it is necessary to prepare the surface by carefully removing dirt, dust, grease and oil stains from it. Before starting work, the PU foam cylinder should be left for some time in a room with an air temperature of +18 °C. This is done so that the substance does not harden - then the applied layer will be more uniform.
To prepare POLINOR for use, install a special nozzle on the cylinder, which is included in the kit. Having put it on until it clicks, you need to remove the cover from the cross and attach the mounting gun, which is purchased separately. All actions must be performed while holding the packaging in a vertical position. At the beginning of work and as it progresses, the container should be shaken well.
The insulation is applied to the surface by spraying by pressing the “trigger” of the mounting gun. The maximum layer thickness should be no more than 500 mm. At the end of the work, the gun must be disconnected from the cylinder and its parts must be cleaned with a liquid solvent. Each package includes instructions for using the material with clear recommendations and explanations.
Customer Reviews
Three years ago, when the composition first appeared on the domestic market, many experts treated it with some caution. Today, most buyers leave only positive reviews about this product:. “I was considering liquid insulation in cylinders as an option for insulating floors in the basement of my country house
I chose POLINOR and it turned out to be absolutely right. I decided to do the whole process myself and, to be honest, I didn’t even expect such a result. Imagine as much as 120 m2 of high-quality insulation in just four hours of work! I would especially note the good adhesion of the material to the concrete base"
“I was considering liquid insulation in cylinders as an option for insulating the floors in the basement of my country house. I chose POLINOR and it turned out to be absolutely right. I decided to do the whole process myself and, to be honest, I didn’t even expect such a result. Imagine as much as 120 m2 of high-quality insulation in just four hours of work! I would especially note the good adhesion of the material to the concrete base.”
Evgeniy, Samara.
“I insulated a standard 3.5 square meter balcony in just an hour, and spent three times less money than on the mineral wool that my neighbor suggested installing. POLINOR has only one drawback - certain conditions are required for its application. The air temperature should be at least +15 °C; if it’s colder outside, it foams worse and consumption increases.”
Fedor Fedorovich, Ufa.
“We planned to order a team of specialists with equipment, but we thought about it, did the math and decided to do everything ourselves. Believe it or not, you saved twice as much! We insulated the garage (the walls between it and the house), spent a long time choosing materials and, after reading reviews on the Internet, decided to buy sprayed POLYNOR. It turned out very well, and most importantly – quickly and inexpensively.”
Ekaterina, Moscow region.
Pros and cons of insulation
Concluding the review, we need to once again list all the advantages of the innovative insulation of the POLINOR brand:
1. Efficiency. The energy saving indicators of the material are higher than those of its analogues.
2. Ease of use. POLINOR does not require installation of a frame structure.
3. Cost-effective. The insulation is packaged in small cylinders - this allows you to purchase the exact amount needed for work.
4. Environmentally safe to use and harmless during operation.
5. High performance. The insulation can be sprayed over an area of 1 m2 in just 15 seconds.
6. Durability. The service life of the material is at least 50 years.
7. Affordable price. POLINOR in cylinders costs 2.5 times cheaper than visiting a team of craftsmen with special equipment for standard insulation.
Comparison of penoizol with other insulation materials
The fire resistance of penoizol is superior to foamed polyurethane. It does not ignite even with prolonged contact with open flame. This is facilitated by thermosetting resin, which, when interacting with flames, forms an infusible material. As for polyurethane foam, its flammability in classes “G1” and “G4” is determined by aluminum fire retardants. Upon contact with open areas, polyurethane foam is destroyed, loses its ability to withstand flames, melts and can ignite. In terms of service life, sprayed polyurethane foam is also inferior to liquid foam made from urea-formaldehyde ingredients.
The most serious competitors of penoizol, in our opinion, are ecowool (dry cellulose) and crumbly sawdust steak. These environmentally friendly insulation products are the best on the market. They are made from wood fibers. They do not contain chemicals, except for antiseptics and fire retardants - products that are harmless to health. Meet international quality standards. They work better than any insulator, as they penetrate hard-to-reach points, crevices and depressions with a diameter of up to 0.01 millimeters. For objective reasons, they are officially approved for use in all countries of the world without any restrictions.
According to international statistics, in Europe, from 0.5 to 1.5 million residential houses, cottages and townhouses are insulated with ecowool. Americans use ecowool and sawdust every quarter to insulate 150,000 buildings and structures. As sad as it is to state, the “stupid” inhabitants of the notorious America, as Mr. Zadornov called them, have long been superior to us Russians in their knowledge of ecology. It is ecowool in the West that is considered the number 1 insulation material. Neither penoizol, nor polyurethane foam, much less basalt insulator, can compete with it. If you, as a reader, do not agree with this statement, please write your view of the situation in the comments to this article. Thank you!
How to choose from all the varieties
The choice of type of insulation depends on the situation, as well as the area of application; let’s consider some common cases in which foam insulation is used:
- You can use polyurethane if you need to repair cracks or eliminate other defects on the walls. Do not expose it to direct sunlight.
- To fill large volumes, use penoizol. In this case, it is necessary to purchase a special high-pressure apparatus, since a regular cylinder will not be enough for this.
- To seal cracks and thermally insulate a small surface area, select mounting samples in cylinders. It does not ignite when interacting with fire, does not support combustion, has an environmental composition and hardness after hardening.
Remember! Polyurethane foam is categorically not suitable for insulating the entire building, since it does not have the appropriate characteristics.
To eliminate defects that have been detected externally, foam, which contains polyurethane, is applied using direct method technology, using a machine or a special cylinder. Errors within the layer that foam insulation creates require a long hose to push the material through. To fill the air gaps inside the insulation, holes are made in the wall.