Gasification has not yet touched many regions of our country. Heating of houses there is carried out using modern equipment that runs on other energy sources.
When choosing fuel for long-burning solid fuel boilers, its efficiency and economic benefits are taken into account. In addition, the cost of delivery and the ability to provide the necessary conditions for storing raw materials are important.
Solid fuel boiler as an alternative heating system.
Fuel Options: What to Look for When Choosing
Until recently, the main heat sources for heating a house using a solid fuel boiler were only wood, coal and peat. Modern technologies have made it possible to expand this range, and now, in addition to the listed types of raw materials, briquettes, wood chips, pellets, etc. are used.
Each of these options has its own calorie content, and in order to make the right choice, it is necessary to study in more detail the characteristics of all types of fuel intended for TKDG.
Firewood
This is a traditional raw material that has been used for many years to fire stoves, and is now also used for modern TT boilers.
It is difficult to prepare firewood on your own; it will require great physical effort, the presence of special equipment, as well as permission from local authorities, otherwise a fine cannot be avoided.
Not all wood is suitable for solid fuel boilers. The low density of soft rocks causes them to burn out quickly.
You often have to make new bookmarks, and this is not only inconvenient, but also takes a lot of time. In addition to density, the moisture content of the wood is also important, since under natural conditions it can dry well only after 2 years.
Firewood made from hardwood (oak, birch, etc.) is best suited for TKDG. The specific heat of the same wood at a moisture content of 50% is 2.2 kW/h, and at 20% it is 3.4 kW/h. Often, unscrupulous suppliers sell unseasoned firewood, which greatly reduces the efficiency of the purchased raw materials.
Firewood for solid fuel boilers is recommended from birch or oak.
Pellets
This type of fuel is in the form of cylinders with a diameter of 7-10 mm and a length of 2-4 cm, made by pressing waste from the wood processing industry (sawdust, shavings, chips, etc.) and agriculture (husks, straw, plant stems).
Some manufacturers add coal chips or peat to improve the heat transfer of such products. Before pressing the pellets, the raw materials are dried. When it is compressed, lignite is released, due to which all the particles are firmly connected to each other.
Main advantages of pellets:
- waste-free production;
- environmental cleanliness;
- high heat transfer (achieved due to low humidity of the finished product - up to 12%);
- low ash content (up to 3%), so the boiler will have to be cleaned less often;
- transportability;
- possibility of organizing automatic feeding.
Among the disadvantages, they note the higher cost compared to firewood and the fact that not all regions have the opportunity to buy such material.
Pellets have high heat transfer.
Fuel briquettes
These products are also made from wood waste crushed to a powder form, which is then compressed. Depending on the type, such fuel looks like a brick, cylinder or tablet.
After the combustion of briquettes, about 1% ash remains, and the heat transfer reaches 5.8 kW/h, which gives them the opportunity to compete with firewood. If bark is used instead of wood chips in the production of this type of fuel, the listed advantages are neutralized.
The disadvantage of briquettes is that under inappropriate storage conditions they quickly gain moisture, resulting in reduced heat transfer.
Fuel briquettes are also perfect for solid fuel boilers.
Coal
Of all types of solid fuel, it is the most efficient energy carrier.
Coal is:
- stone;
- brown;
- anthracite (it is rarely used for heating a house, because when burned it creates too high a temperature and is expensive).
When using a modern TT boiler to heat a small building, you will need 1 bucket of coal per day.
Disadvantages of this type of raw material:
- High price.
- When stored in large piles there is a risk of spontaneous combustion.
- When it burns, a lot of ash is formed, so the boiler will have to be cleaned more often.
The heat transfer of coal is 2 times higher than that of wood, so to maintain a given temperature in the house you will need less of it than even well-dried firewood.
Coal for solid fuel boilers requires a certain fraction.
Peat
This type of natural fuel was formed over many years as a result of the decay of plants. The process took place under conditions of high humidity and with minimal access to oxygen.
Thus, a special layer of soil was obtained, having a dense structure and good heat transfer. The more humus it contains, the darker the color of the fuel. After extraction, the peat is cut into briquettes, which are dried and sent to the consumer.
Advantages:
- low cost;
- simple storage conditions.
The disadvantage is that peat is mined in swampy areas, so purchasing it is beneficial for those who live nearby. Delivery to other regions increases the cost of such raw materials.
Peat for boilers cannot be found in all regions.
Helpful information
When choosing heating equipment, we often proceed from the price of the equipment itself, its power and installation costs. However, few people are focused on fuel efficiency, heat transfer characteristics during the combustion process, and the need to create conditions for maximum boiler efficiency.
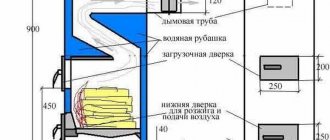
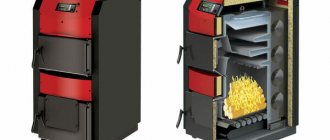
Most often they are connected to main natural gas, but in areas where it is impossible to connect to gas pipelines, it is more effective to use long-burning solid fuel boilers.
Fuel used in boilers for private homes
The amount of heat released during fuel combustion determines the effectiveness of use for the space heating process. Many people believe that dry firewood that burns quickly produces more heat than coal that takes a long time to burn. This is a wrong opinion, since quickly igniting fuels burn faster, which means they can emit significantly less heat compared to hard-to-ignite rocks.
For example, coal grades A, C, TT are low-flammable fuels, but after ignition they burn for a long period of time and produce more heat. Yes, to maintain the combustion process, air supply to the combustion chamber is needed, but the complexity of the design is more than compensated by the economic effect of arranging the blower.
To ensure a long-lasting combustion process, it is important to create an optimal blowing structure, which is what Polish engineers took care of when creating the PEREKO long-burning solid fuel boiler. In this case, difficult-to-burn rocks burn for the maximum time, since oxygen contained in the atmospheric air is constantly supplied to the combustion chamber.
Boilers from Poland are considered, perhaps, the best European boilers, because... In this country, heating from solid fuels (coal/wood/pellets) is the main source of heating in private homes. The Pereko brand is a leader in this country due to its quality and long history.
To determine the most efficient types of fuel, we provide a table of the calorific value of the most common types of fuel, including diesel fuel, gas and electricity for comparison. One of the most important characteristics of fuel is the specific heat of combustion. The higher this indicator, the lower the fuel consumption for heating under the same conditions, and therefore the lower the cost of heating the premises. It must also be remembered that in order to increase the efficiency of the heating process, the room must have good thermal insulation properties. They can be adjusted by installing an additional external and internal insulating layer.
| Type of fuel | Specific heat of combustion in kW (per 1 kg, cubic meter or kW) | Equivalent to 1 cubic meter. natural gas |
| Anthracite coal (cannot be used in boilers due to its high calorie content) | 7,8 | 0,8 |
| Coal | 7,5 | 0,8 |
| Charcoal | 7,5 | 0,8 |
| Wood pellets | 5,2 | 0,5 |
| Brown coal | 4,7 | 0,5 |
| Freshly cut wood | 2,2 | 0,3 |
| Dry firewood | 3,9 | 0,4 |
| Wood chips | 3,0 | 0,3 |
| Sawdust | 2,3 | 0,3 |
The table shows that the most profitable types of solid fuel are charcoal and stone. Anthracite coal cannot be used to heat any boiler due to its high calorie content.
So, we are once again convinced that solid fuel is the most profitable. Moreover, in terms of cost, depending on the region, firewood will be cheaper. However, given the need for a dry room for storing firewood and heat transfer, coal is still the best option.
Choose the most profitable and affordable type of fuel for your area.
Heat transfer table of all types
The energy efficiency of the listed fuel types differs. Even the same type of raw material, under changed production and storage conditions, will have different heat transfer rates. For comparison, average values are taken (see table).
| Type of fuel | Humidity, % | Calorie content, kcal/kg |
| Firewood | 20-25 | 2800-3400 |
| Coal | 12-18 | 6500-7000 |
| Brown coal | 14-22 | 3100-3600 |
| Peat | 28-30 | 2600-2800 |
| Pellets and briquettes | 6-10 | 4300-4700 |
Main types of fuel for solid fuel heating
Solid fuel is one of the first used by humans.
Today, other, more technologically advantageous options have been added to traditional materials for combustion in modern boilers. Main types of fuel for combustion in boilers:
- traditional coal and firewood, which have been constant fuel for many centuries;
- fuel briquettes made from wood, peat and various combustible wastes;
- pellets, like small-sized fuel elements, produced from the remains of various organic combustible compounds.
The most calorific value and long-practiced material for industrial use and use in solid fuel boilers is coal. It is an organic rock containing carbon and other chemical elements. One of the harmful components that affects human health when burning coal is sulfur. For use, they try to reduce the percentage of its content, but the very fact of the presence of an unsafe element forces one to be careful when using this type of solid fuel.
There are three types of coal: anthracite, hard coal and brown coal. The most energy-rich is the anthracite group. This is a very ancient rock with a low moisture content, which affects the quality of combustion. Coal ranks second in terms of calorific value. The youngest is brown coal, with a lower calorific value and combustion quality indicator.
Firewood, as an ancient type of fuel, is used for combustion in solid fuel installations. They are:
- sawn;
- chopped.
Cut into 30 cm lengths, the wooden pieces are burned in the furnaces of modern boilers, generating heat energy. For efficient combustion, the wood is dried, and the equipment is set to slowly burn the wood, transforming each calorie released into heat. Modern multi-chamber boilers create conditions for the most efficient combustion.
Fuel briquettes are a relatively recent type, which is produced on the basis of wood processing waste, wood dust, combustible waste of agricultural products (husks of seeds, straw, tops, etc.), and other waste of various materials. Three main types of extruded fuel cells are common:
- rectangular in shape, which stack well and do not take up much space during transportation;
- in the form of cylinders, with an internal hole-space that contributes to the quality of combustion;
- multifaceted.
The advantages of this type of fuel include:
- possibility of long-term storage, convenient transportation and storage;
- briquettes do not rot, their composition is thermally treated;
- the high compression density of the material composition allows it to burn for a long time, producing an even and constant fire;
- the energy productivity of a fuel cell is almost twice that of firewood;
- minimal ash content remaining during combustion;
- economic benefits when heating with briquettes and environmental friendliness in use.
Fuel briquettes include peat briquettes, which are quite effective in use as solid fuel.
Pellets, like small granules, which are made from almost the same waste of wood and agricultural origin, are very popular for combustion in solid fuel boilers. Compared to briquettes, they are made using a slightly different technology. Before pressing, the raw materials for pellets are crushed and then held together with a binding plant polymer - lignin. In a special granulator, granules are pressed, which are subsequently used as a combustible material for many solid fuel units.
There are several types of raw materials for the production of pellets:
- wood processing waste;
- peat;
- waste from agricultural seed processing;
- straw.
Pellets are a high-calorie fuel that can burn evenly and for a long time in the boiler firebox. It is more expensive than fuel briquettes, since its production is more expensive, but it is very popular due to its convenient loading into the boiler, low slagging, and high environmental friendliness.
What are the dangers of using unsorted coal?
The use of this type of fuel in TKDG can lead to equipment failure. Unsorted coal contains a lot of dust, and its combustion efficiency is low.
In addition, large pieces are often found. When using automatic fuel supply, their entry into the mechanism leads to jamming and breakdown.
In our country, sorted coal is rarely sold, and it is expensive. Therefore, for boilers operating on solid fuel, it is better to buy “seeds” - the fraction of such a product is 6-13 mm.
Most often it is anthracite, but it has a high calorific value and combustion temperature, as a result of which equipment often fails.
The use of fine coal in TKDG will lead to the following results:
- the fuel is not burned out, it will have to be sifted and reused;
- the rated power is reduced (for example, in the technical characteristics of the equipment it is 25 kW, but the unit will be able to generate no more than 15 kW).
For efficient operation of a boiler with automatic feeding, it is recommended to use long-flame coal. In Russia, such raw materials are produced with a fraction of 13-50 mm, while for this equipment it is allowed that the size of individual pieces does not exceed 30 mm.
Types of fuel for long-burning boilers
Simultaneously with the advent of solid fuel heat generators, in addition to firewood and coal, alternative combustible materials appeared on the market. Currently in highest demand are:
Pellets
– waste from the woodworking and furniture industries, pressed into briquettes. You can not only buy pellets at a construction supermarket, but also make them yourself.
Sawdust and wood chips
. This type of fuel is the cheapest; moreover, there have been cases when sawmill owners even paid extra for waste removal. The amount of heat released during the combustion of the material is quite acceptable, and the air contained between the individual elements makes the combustion process more intense and uniform.
Briquettes
They are produced using the same technology as granulated pellets and differ only in shape. Most often, briquettes are in the form of natural logs with a through hole in the center. The heat transfer of the material is practically no different from granules.
Conditions and rules for fuel storage
Each type of raw material has its own characteristics. Coal and peat are placed in a warehouse only after a 2-week stay in the open air, with 2- or 3-fold mixing. Firewood is dried and stored in stacks, and is treated with antiseptics and insecticides.
Pellets and briquettes initially have low humidity, but can absorb it from the environment. They require a dry place to store them.
Such fuel is placed on pallets to provide air access from all sides. Most of these products come in sealed bags, but there is always a risk of damage.