Home » Central heating » Combined
As a result of many years of experience, operating short-distance passenger cars equipped with electric heating, experts came to the conclusion that this type of heating is the most favorable. It has advantages in terms of economy and equipment operation. But if you use this type on trains with long routes, you may experience difficulties with power supply. For example, at the exchange of cars. There may also be damage to the electrical main or breakdown of the electric locomotive.
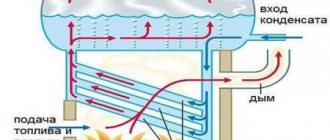
Car heating system
It is for this reason that combined types of heating were developed. Their production was carried out in three countries: the USSR, the GDR and Poland. Combined heating of the car is installed on both compartment and other types. Water acts as a heat conductor. On tracks supplied with electricity, carriage rooms are heated using electric heating. In the absence of electrical networks, they are transferred to solid fuel heating. In both cases, water flows through the heating system as a heat conductor. The combination of these two types of fuel is more suitable for car heating.
Combination heating device for carriages
The combined heating system provides heating using electric heaters located in the boiler equipment. Water is used as the coolant in this device. The boiler equipment is equipped with a coal firebox and a water jacket located below. High voltage heaters in the amount of 24 pieces are attached to the flange. The power of all heaters is 48 kilowatts. 3 insulating elements are installed on the flange. The wiring passes through the insulating elements and approaches the heaters of the boiler equipment. For safety reasons, all heaters are covered with protection elements, and the protection itself is grounded.
Considering any type of carriage, it can be noted that identical heaters, heating circuits and other devices operate everywhere. Boiler equipment heaters are divided into two parts. Each part is divided into two parallel branches. One branch has heating elements connected in series. The heater has five hundred volts of voltage.
Heating diagram for passenger cars
The heating elements of the boiler equipment are connected to the electrical mains, in which the voltage is 3000 volts. Under the carriage there is a box for high-voltage switching equipment. The box can only be opened using a special heating key. The relay located in the box performs the function of protecting the heaters from short circuits.
We recommend: Types of combined heating systems for a private home
The dimensions and weight of the combined heating system are impressive. If you compare water heating with air heating, you can find many disadvantages. But what makes combined water heating universal is the ability to generate heat using solid fuel. This is due to the increased demand and widespread use.
Heating system in a railway carriage
The invention relates to the field of transport engineering, more specifically to passenger car building, and is intended for heating systems for railway, mainly passenger, cars. The heating system of a railway car consists of interconnected coolant circulation circuits and contains a boiler with supply and return heating pipelines laid along the side walls of the car, an expansion tank, a water heater, a heater, a circulation pump and a jumper pipe connecting the ends of the return heating pipelines. The jumper pipe is made in the form of a pipeline that rises up near the side wall of the car, for example, in the toilet room of the boiler side of the car, passes over the ceiling of the corridor, goes down in the boiler room of the car and serves as an additional source of heating for the toilet room of the boiler side of the car. The technical result is to simplify the design, improve operating conditions and prevent freezing of water in the jumper pipe. 1 salary f-ly, 1 ill.
The invention relates to railway transport, namely to passenger cars for transporting passengers over short and long distances in conditions of low ambient temperature.
The heating system of cars built in the GDR is known (see “Guide to the conductor of passenger cars”, V.P. Shcherbakov, A.B. Rabinovich, Publishing House “Transport”, Moscow, 1971, Fig. 31 “Water heating system for computers of international traffic 1 -th and 2nd classes of size 03-T (RIC).”
When operating the car on railways, the car was heated using a water heating system. Solid fuel (anthracite) is burned in the boiler furnace.
As a rule, low air temperature in cars is the result of negligence or inability of conductors to properly use technical heating means.
The prototype of the invention is the “Heating system for a carriage” type 47k and a dining car SKk, described in the book “Air conditioning in passenger carriages”, Faershtein Yu.O., Kitaev B.N., Moscow, “Transport”, 1984, Fig. 42 . The system is made with combined (electric coal) heating of the coolant, has a boiler with a heating surface of 2.92 m, a grate area of 0.245 m and a heating capacity of 45 kW. The boiler holds about 171 liters of water.
The mass of the boiler without water and electric heating elements is about 450 kg.
The heating system consists of interconnected coolant circulation circuits, contains a boiler with supply and return heating pipelines laid along the side walls of the car, an expansion tank, a water heater, a heater, a circulation pump and a jumper pipe connecting the ends of the return heating pipelines.
The jumper pipe connecting the compartment and non-compartment parts of the heating system is laid in the floor of the corridor on the side of the conductor's compartment. To prevent irrational heat loss through its walls and the possibility of freezing in the event of severe frosts, the jumper pipe is wrapped in several layers of non-hygroscopic insulation and placed in a metal casing. Due to the necessary installation of this unit in the floor, while maintaining the flow area, the jumper pipe is given a flattened shape. Outside, the section of the floor above the casing with the jumper pipe is made in the form of a removable hatch with metal enclosing thresholds.
On all types of passenger cars of domestic and foreign construction, the jumper pipe remains a vulnerable point: at low temperatures, there are frequent cases of water freezing in it, especially when the intensity of the boiler fire is weakened and water circulation deteriorates. This is the disadvantage of the prototype.
The objective of the invention is, firstly, to prevent freezing of water in the jumper pipe, and secondly, to simplify the design of the heating system in a railway car.
The essence of the invention is that the heating pipes-jumpers from the compartment side of the car to the non-compartment (corridor) side of the car are laid in the under-roof space above the ceiling of the corridor, and in the boiler room they are brought to the lower part of the boiler body above the floor, without enclosing it in a recessed casing.
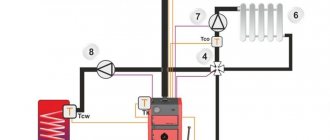
The drawing shows a diagram of the heating system in a railway car.
The system contains a hot water boiler 1, the upper part of which is connected to an expansion tank 5, a water heater 6, a heater 7 and heating supply pipelines 2. The lower part of the boiler 1 is connected to the heating return pipelines 3 and 4 by a circulation pump 8. A jumper pipe 9 connects the ends of the return pipelines heating 3 and 4, is made in the form of a pipeline that rises up near the side wall of the car, for example in the toilet room of the boiler side of the car, passes above the ceiling of the corridor and falls down in the boiler room. The jumper pipe 9 serves as an additional source of heating, for example, for the toilet room on the boiler side of the car.
The heating system works as follows. In the lower part of the boiler 1, the coolant (water) is heated from the combustion of solid fuel or electric heating elements, as a result of which warm layers of the coolant naturally move upward into the expansion tank 5, which serves to collect and store excess water formed as the volume increases as a result of heating. The heated water of the boiler 1, moving through the pipes of the water heater 6, gives up its heat to the water entering the water heater body from the water supply system and used for the needs of passengers and the conductor. The expansion tank 5 also supplies the heater 7 with heated water, which serves to heat fresh air in the winter. The expansion tank 5 is connected to the supply heating pipes 2, which pass into the return heating pipelines 3 and 4, laid along the side walls of the car, serve to heat the car and are connected by a jumper pipe. To enhance water circulation in the heating system, there is a circulation pump 8.
The technical result achieved by the invention is that heat loss is reduced and freezing of water in the jumper pipe is prevented.
The implementation of this invention is possible using existing manufacturing technologies and using materials widely used in car building. At OJSC Kryukov Carriage Works, technical documentation has been developed and prototypes of cars using this invention are being manufactured.
1. A heating system for a railway car, consisting of interconnected coolant circulation circuits, containing a boiler with supply and return heating pipelines laid along the side walls of the car, an expansion tank, a water heater, a heater, a circulation pump and a jumper pipe connecting the ends of the return heating pipelines, different in that the jumper pipe connecting the ends of the return heating pipelines is made in the form of a pipeline that rises up near the side wall of the car, for example, in the toilet room of the boiler side of the car, passes above the ceiling of the corridor and falls down in the boiler room of the car.
2. The heating system of a railway car according to claim 1, characterized in that the jumper pipe serves as an additional source of heating, for example, for the toilet room on the boiler side of the car.
Operating rules
With the onset of cold weather, the conductors check the serviceability of the combined heating in the car and its preparation for the winter period; the following types of work are carried out:
- boiler equipment is checked for malfunctions;
- attention is paid to the position of taps and valves;
- the presence of grates and their serviceability are examined in the firebox;
- the operation of pumps and measuring instruments is corrected;
- The water in the system is checked. Is there sufficient quantity? The reserve tank is also inspected for the presence of water;
- attention is paid to solid fuels. If there is a shortage, management must be notified;
- inspection of equipment for working with solid fuels;
- technical documentation on the rules for using mixed heating of cars is also being put in order.
The lower part of the boiler of a reserved seat carriage
For the normal and uninterrupted functioning of mixed heating, the serviceability of the equipment in each car must be checked, one hundred and ninety-eight heating heads that fit the water-filling pipes.
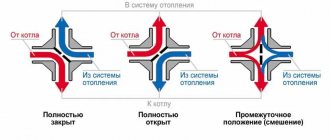
Before starting up the boiler equipment, it is necessary to check the serviceability of the ventilation system. To do this, you need to look at the position of the valve handle. It is located on the ceiling in the boiler room. When ventilation is running, the position of the handle will be turned to the word “Open”. Another important requirement is to look at the fire damper. By the position of the drive handle, you can guess that it is open.
Operation of water heating
At the stage of preparing the car for a trip during the heating period, if the car has water or combined heating, the conductor is obliged to check the condition of the boiler, the position of all valves and throttle valves, the presence of grates in the firebox, the serviceability of pumps and measuring instruments, the presence of water in the system and the absence of leaks, availability of technical documentation, as well as equipment.
Heating of the cars begins at an outside air temperature of 100 C or lower. The boiler is lit with paper and finely chopped wood. As the wood burns, the firebox is loaded with fuel evenly along the grate. In this case, the firebox door should be closed and the ash pan door should be open. The intensity of fuel combustion is regulated by the amount of air supplied to the firebox through the ash pan door. To increase draft and air flow, open the ash pan door, and close it to reduce it. The recommended thickness of the fuel layer for large pieces of coal is 100-200 mm, for small pieces 50-100 mm. For better fuel combustion, punctures of fuel and slag are periodically made with a lance. Ash and slag should not be allowed to accumulate along the perimeter of the grate at the point of contact with the fire box casing, as they create a significant obstacle to heat transfer. While firing the boiler, it is necessary to maintain constant combustion of the fuel and the required water temperature in the boiler. It is necessary to systematically monitor the water level in the heating system using a hydrometer or control tap, pumping up water if necessary.
To avoid steam formation and the associated loss of water and deterioration of its circulation, the conductor must monitor the thermometer to ensure that the water temperature in the system does not exceed 900 C. At higher temperatures, the ash pan lid should be closed.
At low outside temperatures, the heating of the car is accelerated using a manual circulation pump at a water temperature in the boiler of at least 500 C. Before passengers board the car, it must be warmed up to a temperature of 18 -200 C.
If dark spots form on the surface of the fuel, gradually covering the entire surface of the grate, the furnace boiler should be cleaned. It is recommended to clean the firebox in three stages: rake the entire hot layer of fuel to one side, lift the slag with a peak, after removing the flue gases, put it in a bucket, remove the ash through the holes of the grate into the ash pan; move the hot layer of fuel onto the cleaned surface of the grate and also clean its second part; level the hot layer of fuel and load the firebox with fresh coal, scrape the ash from the ash pan into a bucket. The boiler firebox should be cleaned quickly, without waiting for it to cool down.
At the point of formation and turnover, it is necessary to clean the firebox and ash pan from ash and slag and keep the boiler in working condition. After the heating season, for safety reasons, the heating system must be filled with water. During operation, periodically, but at least once a day, and when filling the heating system with water, it is necessary to release air through the air bleed valves.
In winter, when outside temperatures are above zero, the cars on all trains are supplied with fuel at the formation and turnover points up to the full capacity of the coal boxes.
Temperature
The maximum permissible water temperature of the heating system is no more than 95 degrees. If its level rises above permissible standards, then the dust that settles on the lower level of the pipes will burn.
The boiler has two devices installed that monitor the operation of the heaters and their temperature conditions. If the temperature in the boiler equipment rises above the permissible norm, the thermostat blocks the heaters and they turn off.
We recommend: How to choose a collector for a combined heating system?
YouTube responded with an error: The request cannot be completed because you have exceeded your quota.
- Related Posts
- Types of combined heating systems for a private house
- How to choose a collector for a combined heating system?