The new always makes its way with difficulty. It is in the human mentality to hold on to the well-known old rather than take advantage of something unusual that goes beyond the usual. This fully applies to a new type of insulation for Russians: rigid polyurethane foam, or PPU - they pay too little attention to it (by and large, many have not heard of it at all). To reverse the emerging trend, polyurethane foam manufacturers conduct an active advertising campaign, during which the advantages of polyurethane foam are sometimes exaggerated.
The editors of StroyGuru decided to look into the issue in more detail and, using the example of roof insulation with polyurethane foam, consider the advantages and disadvantages of the material, insulation features: technology and emerging nuances.
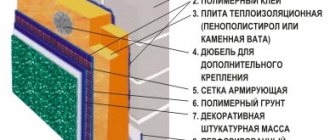
Characteristics, pros and cons of PPU
Polyurethane foam (PPU) is the result of a chemical reaction between a polyol (manufacturers designate it as component “A”) and polyisocyanate (component “B”), which results in the formation of a rigid, foamed plastic mass. It contains about 3% dense matter and 97% air. Having this structure, the material has excellent thermal insulation properties, low weight and low hygroscopicity.
Types of polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam has several types, differing from each other in their state of aggregation, elasticity and cell structure. Therefore, the existing classification distinguishes 4 types of polyurethane foam:
- elastic . Presented by well-known foam rubber. It has a density of 15-20 kg/m3, good vapor permeability, open cells, high elasticity. Completely restores its shape when deformed over 90%. It is not used for roof insulation. Although, rather as an exception, it can be found when insulating an attic;
Foam rubber.
- hard . It consists of two components, when mixed, a foam is formed. It has a closed cell structure and is therefore vapor proof. Density is 30-60 kg/m3, which allows it to withstand various types of deformations (that’s why it’s hard). Widely used for thermal insulation, both inside and outside the building;
Hard polyurethane foam.
- semi- rigid Single component open cell insulation. Vapor permeable. Density 20-30 kg/m3. Used only for thermal insulation of walls, roofs and ceilings. Requires a standard procedure for vapor and waterproofing of the insulated surface. Known to many as polyurethane foam;
Semi-rigid polyurethane foam with a non-uniform structure.
- liquid _ They are used to insulate a space that is closed on all sides or when installing soft roofing on flat roofs. Density - 20 kg/m3 or less.
Liquid polyurethane foam.
Types of polyurethane foam
Polyurethane foam is a type of plastic made from two main components. The reaction of these components creates a material whose properties can change with different ratios of the starting substances. There are soft varieties of polyurethane foam with a density of 5-40 kg/m3, and hard varieties - 35-80 kg/m3
The variety of types has led to the widespread use of the material, from furniture (the well-known foam rubber) to insulation in construction. One of the most useful properties actively used in industry is the ability to spray the material directly at the point of use, bypassing the stages of manufacturing, storage, transportation, installation, adjustment, etc.
This property distinguishes polyurethane foam very favorably as an insulation material, which is applied directly to the surface to be treated with virtually no preparatory operations, forming a highly effective heat-retaining layer that does not react to moisture, does not change its qualities over time, does not interact with biological organisms and is not subject to swelling.
Insulation characteristics
In polyurethane foam, the type of cells determines the main characteristics of the insulation. In tab. 1 shows the indicators of rigid polyurethane foam and polyurethane foam (single-component, with open-cell insulation).
Table 1. Main characteristics of polyurethane foam insulation.
| Types of cells / Indicators | Closed cell insulation | Open cell insulation |
| Thermal conductivity coefficient, W/(m×°K) | 0,022-0,035 | 0,025-0,045 |
| Number of closed cells, % | More than 90.0 | Less than 50.0 |
| Increase in foam volume compared to the beginning of polymerization | 1 in 40 | 1 to 70-90 |
| Vapor permeability, mg/(m*h*Pa) | 0,02-0,05 | 0,07-0,17 |
| Density, kg/m3 | 20,0-80,0 | 8,0-18,0 |
| Water absorption,% | 1,0-3,0 | 10,0-60,0 |
| Compressive strength, kgf/cm2 | 1,53-10,19 | About 1.02 |
| Bending strength, kgf/cm2 | 3,3-19,37 | About 17.0 |
Many positive properties are attributed to polyurethane foam insulation. However, not all advantages are such. Let’s look in more detail at where the advantages are real and where they are advertising gimmicks.
Advantages and disadvantages
Among the strengths that are beyond doubt:
- low level of thermal conductivity;
- long service life;
- good adhesion to all wall materials;
- absence of cold bridges entering through the seams;
- environmental friendliness of the applied spraying;
Polyurethane foam is an environmentally friendly product.
- fire safety (combustion class G1 - self-extinguishing);
- low density;
- the ability to insulate the most complex surfaces;
- low moisture absorption;
- inertness to all chemicals used in everyday life;
- does not provide a basis for the growth of mold and mildew;
- preservation of thermal insulation properties in a wide temperature range - from -160oC to +150oC;
- versatility.
Among the attributes attributed to them that are not:
- good level of noise absorption;
- resistance against rodents;
- a simple method of insulation;
- savings on vapor and waterproofing.
Among the disadvantages :
- intolerance to ultraviolet radiation;
- lack of vapor permeability;
- complex application technology;
- the need to use complex equipment, which makes it difficult to do the work yourself;
- high final cost of roof insulation with polyurethane;
- the slightest deviation from the instructions leads to a change in the spraying characteristics;
- a sharp increase in thermal conductivity during compression.
In addition to the above disadvantages, it is necessary to note such disadvantages as the inability to make an accurate calculation of the number of required components and the uneven surface of the hardened foam, reaching a difference between peak and valley of 8 cm.
You can read more about polyurethane foam in the article “PPU Insulation”.
Limitations when insulating polyurethane foam
The technology of polyurethane foam insulation is complex. Requires experience in mixing components and spraying skills. In addition, there are a number of restrictions when thermal insulation work cannot be carried out.
- The absence of any adhesion between polyurethane foam and polyethylene makes it impossible to insulate surfaces covered with polyethylene film.
- One-component insulation should be applied only to a moistened surface, two-component insulation should be applied to a completely dry surface.
- Before use, the cylinders must be heated to a temperature of +18 to + 20oC. Exceeding these limits reduces the quality of insulation.
- You cannot start insulating a PPU roof from the inside if it is not warm enough. Minimum temperature - +5oC.
Preparatory work
Preparing the roof for insulation is simple:
- the entire space between the rafters is covered with OSB (otherwise there will be nothing to spray the insulation onto). This is done either on top of the rafter system, or between the rafters, but so that the insulation layer does not extend beyond their plane;
Important: in all roof insulation work, theoretical authors advise installing sheathing instead of sheathing.
- the surface is cleaned of dirt, debris, mold;
- existing gaps more than 6 mm wide are sealed. If this is not done, the foam will actively expand on the other side of the skin;
- dormer windows are sealed with plastic film and tape - the foam that gets on them is unlikely to be completely removed;
- the sheathing and rafters are primed;
- equipment is assembled and then adjusted;
The gun is mounted on a spray can.
- its performance is checked, as well as the density of the insulating layer. If necessary, additional adjustments are made.
Important: when applying one-component polyurethane foam (in cans), the surface is wetted with water.
The surface under the semi-liquid polyurethane foam is wetted with water.
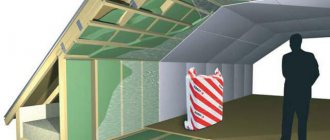
PPU roof insulation technology
Insulating a roof with polyurethane foam consists of several successive steps (we will look at the example of single-component polyurethane foam).
Step 1. Open the control valve on the gun to the maximum value. The can is shaken vigorously and then turned upside down. The first layer must be applied from bottom to top. The distance between the gun and the casing is 35-45 cm.
The first layer of foam is applied.
Step 2. After using the first can, the surface covered with foam is wetted with a spray bottle. The second canister is used.
Step 3. After 25-35 minutes, a second layer of polyurethane foam is applied to the layer of thermal insulation from the first can.
A second layer of insulation is applied.
Attention: at the very top of the roof it is impossible to hold the can vertically, head down. In this case, there are special attachments on the gun that change the movement of the foam jet at an angle of 45o.
Special attachment for the gun.
Step 4. To achieve the tightness of the insulation layer, it is necessary to cover the rafters themselves with foam.
Step 5. The tool is washed with water from a pressure cylinder, which is screwed onto the spray gun. After completely cleaning the insides of the gun from any remaining foam, the adjusting screw is tightened. The gun can be stored in this condition for a long time.
Step 6. Before the polymerization process is completed, which is about 40 minutes, the insulating layer is treated with a fire retardant, reducing the flammability class of the polyurethane foam. It is applied using a simple spray bottle, and the earlier, the higher the effectiveness.
Based on all that has been said, a simple conclusion follows: the roof needs to be insulated in sections, and not in one pass.
Step 7. The insulation is covered from the inside with a vapor barrier film (type B), and from the outside, along the skin, with a windproof membrane (type A). How to do the work correctly, and most importantly, which side to lay the vapor barrier material on, can be seen in the work “Laying a vapor barrier with your own hands.”
Attention: when using rigid polyurethane foam, vapor barrier work is not performed.
Step 8. In the attic room, the insulation layer is sheathed with sheets of plasterboard or OSB.
Insulation using semi- or professional equipment is a little easier.
Spraying of polyurethane foam with professional equipment.
After debugging the equipment, spraying is carried out in several layers from bottom to top. The process is similar to painting a surface using a spray gun. Layers are applied until the required thickness is achieved.
PPU roof insulation scheme.
At the end of work, the equipment is washed. Fire retardants are sprayed onto the surface. Excess sagging is cut off with a construction knife. The interior lining of the attic space is being carried out.
Advantages of roof insulation with rigid polyurethane foam
Can be applied to any surface
Rigid polyurethane foam has found wide application in the construction industry. This is the highest quality insulation used for thermal insulation of facades, internal walls, partitions, roofs or other elements. Thanks to the spraying function, the insulation is easily applied to any surface.
Increased adhesion of raw materials allows architects to design and thermally insulate elements of complex shapes: protrusions, columns and arches. It should be noted that polyurethane foam spraying is used to repair damaged roofs with different angles of inclination and to insulate old buildings. As practice shows, saving time when spraying is 80%, and saving money – 50%.
Nowadays, waterproofing and insulation of building roofs using this material is considered the most common.
Over the past few decades, thermal insulation of PU foam roofing structures has been actively used in America and Western European countries. It was these states that were the first to raise the issue of the need to save heat energy consumption for heating buildings. Experts have found that the level of heat loss and the power of heating systems can be reduced by insulating the roofs of residential buildings and other structures.
The roof, insulated with polyurethane foam, is airtight
A positive feature of insulating a roof structure using polyurethane foam is that applying one layer of material guarantees complete tightness of the roof.
It is believed that this material provides the highest level of heat, moisture and vapor insulation. In addition, a lot of money is saved on the installation of insulation. Thermal insulation of the roof with polyurethane foam using polyurethane foam spraying allows you to permanently get rid of the problem of icicles arising due to the low level of thermal insulation of the building. To get rid of this negative phenomenon, it is enough to apply a layer of 30-50 mm. Wide range of applications Thanks to easy application and providing a high level of protection against heat loss, polyurethane foam is used for:
Insulation of a flat roof with liquid polyurethane foam
Applying liquid polyurethane foam to a flat roof is more likely not insulation, but the installation of a soft roof, because Liquid rubber is added to polyurethane. Operations are performed in warm (no more than +15oC), dry weather in the following sequence:
- the surface is cleaned of debris and dust;
- primed;
- insulation is applied, manually or using equipment.
Insulation is carried out using powerful pumps - after the first layer has dried, the second is applied. Usually 3 layers are enough.
Methods for spraying polyurethane foam: step-by-step instructions
Installation of thermal insulation of a roof structure can be carried out in two ways: spraying or pouring.
Spraying technology is performed as follows:
Liquid polyurethane foam is poured into special equipment; The first layer of insulation is applied to tightly seal the voids and cracks. Work is done from bottom to top
When spraying, special attention should be paid to the joints and corners of the roof structure; Applying the next layer of polyurethane foam. This will improve the heat and sound insulation characteristics of the roof.
For high-quality insulation, the recommended layer should be 5-8 cm.
After waiting for the material to completely harden, you should cut off the protruding parts of the insulation; The final stage is finishing. For additional protection, it is recommended to apply plaster or paint.
During installation work on thermal insulation of the roof, safety precautions must be observed. All work must be performed in a protective suit with a mask.
The spraying method differs from pouring in that polyurethane foam is applied to the surface in a foamed state using special equipment under high pressure.
It is important to know the main features of spraying technology and follow the instructions in order to eliminate possible errors during roof thermal insulation
Roof insulation by pouring method
In this way, the free cavities along the legs of the structure are filled. Liquid insulation is poured onto the slopes using pumping equipment. Thermal insulation of the roof with polyurethane foam is carried out in several layers. First, apply a thin first layer, then subsequent
It is important to take breaks for drying. This method of roof insulation has some advantages, namely: speed of implementation, simplicity, easy adjustment of the thickness of the thermal insulation layer
Material pouring process
Installation of roofing with polyurethane foam should be carried out at a positive temperature of no more than 15 degrees and in dry weather.
The technology of pouring polyurethane foam is usually used when restoring an old roof structure, if it is necessary to process a terrain of any complexity, and also if there are arches, protrusions, columns, etc.
Technology for installing soft roofing with liquid rubber
It is important not only inside, but also to apply polyurethane waterproofing material outside to protect the structure from various negative atmospheric influences. For this purpose, liquid rubber based on polyurethane is used. . Liquid rubber can be applied manually or using a special device.
Application of liquid rubber can be done manually or using a special device.
Manual application of liquid rubber
Before applying liquid rubber, the surface should be cleared of debris and dust. It should be remembered that the installation of waterproofing should be done in dry weather.
The main stages of installing a soft roof with liquid rubber:
- Prime the surface. The primer should be applied to the roof thoroughly, without leaving any gaps. This especially applies to joints and corners;
- Application of material. To apply liquid rubber evenly, it is necessary to maintain a right angle between the surface and the sprayer;
- Applying the next layer. The number of layers depends on the climatic characteristics of the area. Usually 2-3 layers are enough.
A feature of the spraying technology is the application of subsequent layers only after the first has completely dried.
While working, you can involve another person to help
Sprayed roofing not only protects the surface from moisture, but also from other negative natural phenomena. It is better to entrust the work to a qualified craftsman, but you can carry out the work yourself by strictly following the instructions.