To protect the foundation of a building from the destructive effects of groundwater during the construction process, certain measures are taken, resulting in complete waterproofing of the structure.
The gluing method of insulation has become widely popular, in which rolls of bitumen materials are attached to the surface by gluing them. Roll foundation waterproofing can also be carried out by applying melted bitumen to the base under the influence of high temperatures. This type of waterproofing is characterized by ease of use, excellent vapor and water resistance, and durability. Sometimes, before roll waterproofing, a coating of bitumen solution is additionally used, which helps to improve the adhesion of the material to the surface.
Return to content
Technology for laying adhesive and built-up waterproofing
To perform waterproofing with adhesive or weld-on waterproofing, you must adhere to the following steps:
- The surface must be treated with a special primer.
- Next, a layer of mastic or varnish is applied over the primer to obtain good adhesion between the surface and the material.
- Next, the insulating material is laid: the lining material is laid in several layers, and the joints are coated with mastic, and the surfaced one is fused in one layer with a gas torch.
- After the waterproofing material has been laid, it must be additionally coated with mastic or varnish.
- Upon completion of the work, a protective layer is installed, that is, they lay brick, concrete, or perform thermal insulation of the foundation.
- Next, you can install drainage and fill the foundation, or make a blind area.
Installation of membrane material
Membrane films for horizontal and vertical foundation surfaces differ in structure and functionality, as well as in installation technology.
The external walls of the foundation are protected using a profiled membrane with spikes, designed to withstand high mechanical loads. The configuration of its outer side allows the soil pressure to be evenly distributed on the foundation walls. The studded surface forms gaps, thanks to which moisture flows freely into the drainage system.
A smooth membrane material is used to protect the horizontal surface of the foundation. If it is necessary to exclude contact of moisture with the base of the foundation, before pouring it, a “pie” is laid: geotextile-waterproofing membrane-geotextile-polyethylene film.
The membrane for horizontal surfaces is laid in strips with an overlap of 10-15 cm and welded into a single sheet using a construction hair dryer. To mount the studded membrane on vertical walls, a frame of PVC-coated metal strips is first attached to them. During the hot air welding process, the PVC coating of the fastening element and the back side of the membrane melts, which allows the waterproofing layer to be securely fixed.
Rolled waterproofing for buried foundations, provided that they are installed correctly, makes it possible to build on difficult soils and build reliable, durable buildings.
The process of vertical waterproofing of a strip foundation
When building a new house, work is carried out before the trenches are backfilled with soil. If the foundation of an old house needs insulation, then a trench is dug along its entire perimeter to the depth of the foundation base. The width of the trench must be sufficient for people to work comfortably.
Preparing the base
The vertical surfaces of the foundation are cleaned of dirt and flaking old coatings. Cleaning is done with spatulas and metal brushes. Cracks, potholes and other voids are sealed with cement-sand mortar. In places of transition from the vertical to the horizontal part, for example, along the line where the wall adjoins the plane of the expanded base, a transition fillet is laid. It can be formed with a quick-setting mortar. It is needed only to form a smoother angular transition.
Next, a bitumen primer is applied.
Methods for gluing roll waterproofing
Most types of roll waterproofing are glued using the hot fusion method. The bitumen layer is heated with a burner flame until it melts, the material is applied to the surface to be treated and rolled with a pressure roller.
There are also self-adhesive versions of the material. Their lower surface is covered with a temporary protective film, which is removed immediately before pasting.
Fusing of rolled waterproofing material
- Insulation strips are cut to sizes convenient for installation.
- First, paste over the corner transitions with fillets. The material must cover the fillet itself and extend to the vertical sides by at least 100 mm. The pasted area is rolled with a pressure roller.
- The next step is to isolate the corners of the foundation walls.
- The main vertical planes are covered. Fusing can be done in the vertical and horizontal direction of the strips. The main thing is that the process goes from bottom to top. Adjacent strips are joined with an overlap of 100-150 mm.
- When backfilling trenches, the waterproofing material can be damaged by clods of soil, so it is covered with a layer of protective membrane or insulating boards from.
Which waterproofing to choose for heated floors
A member of our portal with the nickname Ution785 planned the following floor pie in the bathroom of her house:
- EPPS on a monolithic slab;
- water heated floor;
- CPS;
- 1K coating;
- tile.
But are 1K compounds suitable for application over a warm water floor in a bathroom? Are harmful fumes possible when the heating field is turned on?
The participants of our portal approved the planned pie (it is important to prevent water from getting into the screed), so the GI is applied immediately before the tile.
And one-component elastic compounds are not afraid of heat, and do not emit any harmful fumes during operation.
Work technology
Do-it-yourself waterproofing should begin with preparing the base. Required:
- Cut off the protruding ends of the reinforcement, clean the protrusions so that the waterproofing material is not damaged by contact with solid particles of moving soil;
- Remove all dirt and dust using a stiff brush;
- Remove rust, paint and other coatings with a solvent, as... they reduce adhesion;
- Fill all potholes, chips, and cracks with cement;
- Fill the seams with sealant;
- Treat the base surfaces with a primer - a special bitumen primer.
Regardless of the type of TechnoNIKOL waterproofing material used, the installation technology has no fundamental differences:
- The mastic is first thoroughly stirred until smooth. The surfaces are cleaned of dirt, dust and the insulator is applied with a spatula, brush, or any other spraying method.
- Some types of waterproofing agents are applied to wet surfaces, others only to dry ones. Detailed instructions are indicated on the can of material or on paper that is attached to the rolls.
- TechnoNIKOL roll materials are laid overlapping to cover the joints.
- The bitumen layer is heated using safe electric heating equipment. Carefully heat the end of the material to securely attach it to the previous layer.
- A less safe way is to heat using an open flame of a gas burner. The installation speed will increase.
- Bitumen emulsion primers are used as independent waterproofing or as a primer before installing roll insulators. The protective properties will be better.
- The drying speed of the primer is no more than 50-60 minutes. Apply with a roller or brush.
Technology of adhesive waterproofing
From the name itself it is clear that such materials must be glued to the protected surface of the foundation. This is done in several steps:
- They prepare the surface by cleaning it from contaminants, leveling irregularities and smoothing sharp corners.
- Application of primer mixtures, including special primers that increase adhesion to the concrete surface.
- Coating the foundation with mastics, which further increase adhesion to the foundation.
- Direct installation of the rolled material by gluing several layers according to the instructions included with it.
- Applying an additional layer of mastic to the surface of the material.
- The installation of a protective or decorative layer in the form of brickwork or sheet materials, under which thermal insulation is made.
- Carrying out drainage work with partial backfilling of the foundation with soil. To do this, at a distance of 1 meter from the wall, they dig a trench around the house, into which a drainage pipe is laid.
- Construction of the blind area. Its width should be 60 - 100 cm.
Recommendations for waterproofing
The reliability and durability of the coating, which extends the service life of the building structure, depends on the quality of the material and the correct execution of installation work. To properly protect surfaces from moisture, it is recommended to follow simple tips:
- When gluing a horizontal base more than 10 meters long, you can use special construction devices - rollers, rollers.
- To protect the insulation itself when gluing foundations and roofs, a coating must be applied to the last layer of coating.
- When laying the sheets overlapping, they should overlap each other by less than 10 cm.
- If sheet insulation is used, all seams and edges are carefully sealed by soldering or filled with hot mastic.
- When protecting the roof, attention should be paid to the places of communication outlets, chimneys, and ventilation pipes.
Pasted waterproofing of building structures is a reliable option for protection against moisture. The cost of roll materials and mastic is quite affordable, and the work process does not require special skills. Pasting is a universal waterproofing option that can be used for different buildings, structures and premises.
- ← Application of gabions in construction
- Technology of coating foundation waterproofing →
Materials used and methods of their application
For secondary waterproofing in accordance with GOST 32384-2008 or SNiP 2.03.11-85, different types of materials can be used:
- Paint and varnish – thin-layer and elastic thickened coatings, for example, based on bitumen or bitumen-plastic mastic.
- Insulating: pasted or welded - in the form of rolls or sheets;
- plastering or coating types of coatings;
- block or piece facing, for example, tile products;
- membrane
Impregnating-colmatating, i.e., water-repellent or pore-compacting chemical compositions:
- based on cement with additives;
on a polymer-cement basis.
Alternative names:
- penetrating, i.e. penetrating;
- clogging, i.e. expanding in the pores;
- impregnating, i.e. permeating.
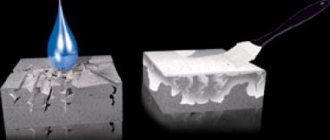
Colmatation is the filling of pores in a material with water-insoluble additives. When used, they increase the water resistance grade of concrete by 2 or more levels. Finely ground substances mixed with water penetrate the pores of concrete and after they are converted into crystals under the influence of water, they completely fill the capillary channels and pores and do not allow water to pass through.
Most often, two types of materials are used for “classical” horizontal waterproofing:
- coating mastics based on bitumen or polymer-bitumen;
- roll pasting materials.
All waterproofing materials are applied to prepared surfaces. To do this, all potholes, pits and other depressions are covered with cement-sand mortar, and protrusions are knocked down, especially linear ones from cracks in the formwork. The areas that are crumbling are treated either with a special bitumen primer, for example, from TechnoNIKOL No. 1, or with the same mastic diluted with a solvent.
Bitumen mastics come in cold and hot applications.
Cold ones are usually fully prepared or require additional dilution.
Hot ones should be heated to 130 - 180 degrees.
Mastics are applied with a brush or roller; on horizontal surfaces, a spatula or scraper is sometimes used.
When applying all mastics, the minimum air temperature should not be lower than + 5 degrees. When heating the mastic, you can work down to minus 20, and with sufficient heating of the concrete - at minus 30 degrees.
Polymer-bitumen is a mixture of bitumen and a polymer base: polyurethanes, acrylics, silicones.
Two forms are used for coatings:
- One-component, fully prepared mixtures in sealed packaging. After applying the mastic, water vapor from the air reacts with the polymer components, polymerization lasts from several tens of minutes to several hours.
- Two-component. They are sold in the form of two packages, the compositions of which are mixed and polymerization begins.
Polymer-mastic compositions usually do not have the main disadvantage of bitumen mastics - cracking when the temperature drops and due to low elasticity.
Waterproofing lining materials:
Rolled
Before use, they look like rolled rolls. One or both sides of the material are covered with hardened bitumen or polymer-bitumen mastic. One side may be coated with an adhesive material for bonding to concrete. The basis of the material is usually glassine, roofing felt, glass insulation, polyester.
Attached to concrete in one of the following ways:
- hot floating - use a burner to gradually heat the surface of the roll and roll it out onto the concrete;
- gluing onto freshly applied cold applied mastic;
- by gluing with an adhesive layer applied to one side of the roll.
Sheet form is the same materials, but in the form of flexible sheets of a certain size.
Usually two- or three-layer insulation is used with mandatory overlap of joints of at least 150 - 250 mm. After laying the first layer, the second layer is shifted by half the width of the first layer in order to compensate for defects in gluing the joints of the panels by gluing the panels of the first and second (third) layers.
Impregnating and clogging (impregnating) materials have the form of dry mixtures that are diluted with water at the construction site or ready-made aqueous solutions.
Apply by spray, brush or roller to a wet concrete surface in accordance with the instructions for use. The depth of penetration of the solution and subsequent blocking of water penetration is from 100 – 150 to 500 mm.
Classes and types of roll waterproofing
Manufactured roofing waterproofing, depending on the purpose, quality, components used and price category, is divided into several classes.
| Material class | Name | Price range | Characteristics | Purpose |
| Premium | Technoelast | 100-160 rubles/m2 For models with a noise-absorbing effect - price up to 250 rubles/sq.m. | Welded coating with application of bitumen and SBS modifier. Used at temperatures from -50 to +1000C. | Lower/upper layers of roofing, underground communications. |
| Technoelastmost | 235-250 rub./sq.m. | The canvas is 5-5.2 mm thick, heat resistance level is up to +1000C. Filler – bitumen with artificial rubber (SBS). High-strength coating, service life - up to 40 years. | Waterproofing of concrete slabs on the carriageway of roads or in the form of an adhesive layer on the spans of bridge structures. | |
| Business | Uniflex | 85-130 rub./sq. meter depending on the thickness and type of base. | Welded coating with SBS-modified bitumen filler. Damage resistance, durability. The expert period between repairs is at least 18 years. The flexibility of the material is maintained at temperatures down to -200C. | Laying the top and bottom layers of the roof, roofing repair work, waterproofing the foundation, basements, ground floors. |
| Standard | Bipole | 70-90 rub./sq. meter | Fused material, binder layer 1.5 mm thick. Withstands temperatures from -150C to +850C. The top layer of coating is shale chips. Service life – 5 years. | Used as the first layer of roofing or for the top part of the roof. Residential roof repair. |
| Bicroelast | 67-84 rub/sq. meter. | Fused material based on fiberglass, fiberglass or polyester. Protective coating - slate chips or film. Thickness 3-4 mm, remains flexible at -100C. | It is used as a lining material for roofing and waterproofing of various types of structures - buildings, tunnels, bridges. Variety “K” is used to cover the top layer of the roof. | |
| Economy | Bikrost | 55-85 rub./sq.m. | Welded coating with bitumen filler. Flexibility is maintained only at positive temperatures, heat resistance is up to +800C. Thickness 3-4 mm, service life - up to 10 years. | Waterproofing, installation of the lower/upper layer of the roof - depending on the coating. |
| Euroroofing material P | 13-16 rub./sq.m. | Fiberglass based coating with modified bitumen applied. The protective coating is applied to both sides of the insulating sheet. The thickness of the protective layer is 2-5 kg/sq.m. | Waterproofing of building structures, installation and repair of roofing carpet in buildings. |
The building materials market presents a wide range of models of rolled waterproofing coatings - both universal and intended for a specific type of work.
Advantages and disadvantages of waterproofing materials
Tekhnikol waterproofing products have the following advantages:
- Rolled waterproofing has a long service life. The foundation will last without repair for at least 35 years. Accordingly, the durability of the entire structure increases.
- Using multilayer polymer-bitumen sheets made of fiberglass, fiberglass, and polyester, it is easy to form a reliable protective barrier against dampness.
- Waterproofers are endowed with increased resistance to biological and chemical environments.
- The materials have good elasticity and can withstand increased tensile loads. Therefore, they often become the subject of choice as a floor insulator in basements.
- The process of installing foundation waterproofing using TechnoNIKOL high-tech products does not take much time and does not require much effort.
- TechnoNIKOL coating insulators are produced ready for use, even if they are intended for hot application. This greatly simplifies installation and ensures an excellent, uniform result.
- It takes a small amount of time for the insulators to dry; under the influence of negative factors, the waterproofing material does not deform or delaminate.
Compared to the advantages, the disadvantages of the insulator are not so significant:
- Inconvenient installation of rolled materials on surfaces with complex geometry.
- Relatively high cost compared to many other domestic and foreign insulators.
The high price is compensated by excellent workmanship, durability and reliability. Some types of TechnoNIKOL insulators, on the contrary, have a more attractive price.
Waterproofing containing bitumen
Waterproofing material containing bitumen has a low cost. Common materials include waterproofing; it is based on fiberglass impregnated with bitumen. The material is resistant to cracking because it contains a plasticizer that makes the product flexible.
Waterproofing does not rot and has a long service life. Hydroisol can be single-layer or two-layer. The double-sided material has a polymer film for a protective function; it melts if heated too much. This property is used to make multi-layer waterproofing of foundations. For single-sided material, mineral chips act as a protective coating.
Work technology
Protection with roll products varies depending on the application. Each case must be considered separately.
Vertical insulation
Required for house strip supports. Roofing felt on bitumen mastic, stekloizol, linokrom, waterproofing or membranes are suitable for the work. The work can be done both from inside the basement walls and from the outside. Rolled insulation is difficult to cope with the pressure of ground moisture, so it is used at low water levels. The work is performed in the following order:
Scheme of vertical and horizontal waterproofing of the foundation
- cleaning the surface from dust, dirt, grease, traces of old insulation or finishing;
- leveling the base; if there are large enough cracks or potholes, they are sealed with cement mortar;
- surface priming;
- cutting sheets, which takes into account the overlap of the material (10-15 cm);
- strengthening the corners of the foundation (installing fillets, securing reinforcing tape);
- installation of insulation depends on the chosen material (for adhesive, first apply a layer of mastic, and then apply roofing felt or glass insulation; to secure the welded insulation, its lower surface is heated with a torch or a hair dryer and attached to the foundation tape);
- roofing felt, stekloizol, linokrom and waterproofing are mounted in several layers to ensure greater reliability;
- The last step is to apply the finishing layer of mastic or varnish.
Horizontal insulation
Suitable for all types of bases when cutting foundations. Also needed for slab foundations. At the junction of the wall and the plinth, it is most often enough to lay two layers of welded or adhesive material (roofing felt, linochrome, waterproofing).
It is worth understanding the insulation of the slab in more detail. Here it is possible to use all the options discussed above, depending on the financial capabilities of the future owner of the house.
The work technology is as follows:
compaction of the foundation soil; backfill made from materials not subject to heaving (crushed stone, gravel, coarse-grained or medium-grained sand); production of concrete preparation from “lean” mortar (serves as insulation and leveling layer); time for concrete to gain strength; cleaning the surface from dirt, dust, grease; leveling and priming; laying waterproofing material (carried out in accordance with the chosen option, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations); installation of thermal insulation and vapor barrier; pouring the slab.
Proper use of rolled materials will reliably protect the main supporting structure of the house.
Types of insulation
Depending on the components that make up the waterproofing, flexible and rolled materials are divided into several types.
They differ in composition, characteristics and type of glue on which they are mounted.
Containing bitumen
This is the most common category of pasting, and also the most affordable. The most popular example of this type of material is waterproofing, the peculiarity of which is its roll form.
Fiberglass with double-sided impregnation of bitumen and plasticizer is not subject to rotting and is not destroyed by time and a constant humid environment.
Due to sufficient elasticity, the waterproofing material does not crack.
This material is universal and suitable for waterproofing work on any surface; it can be produced in two versions:
- unilateral;
- double-sided
In the first case, one side of the waterproofing layer is sprinkled with mineral or granite chips, thanks to which the bitumen does not melt when exposed to direct sunlight.
Double-sided waterproofing is equipped with a layer of polymer film on both sides, which melts when the material is heated. Most often it is used in the form of lower protection in the case when a two-layer waterproofing of the foundation, floor and basement walls is being installed.
Due to its versatility, both types of waterproofing can be used for the protective treatment of open areas (roofing, pipes, foundations) and complex structures (swimming pools, wells, tunnels, bridges).
Containing bitumen and polymers
The basis for isoplast and isoelast is polyester non-woven material impregnated with bitumen modified with polymer additives. Due to this technological feature, adhesive waterproofing has improved performance characteristics.
Isoplast has increased resistance to ultraviolet radiation and is highly heat resistant, so it is recommended for use in regions with hot climates. Isoelast, on the contrary, is suitable for northern latitudes, as it remains flexible in cold temperatures down to – 300°C.
Membrane (polymer)
When creating polymer membrane waterproofing, advanced production technologies are used. These types of material come in the following samples:
- thermoplastic membrane;
- vulcanized rubber membrane;
- polyethylene film, etc.
The main difference between the membrane and bitumen and bitumen-polymer insulation is its minimum thickness and, as a consequence, non-shrinkage at the moment of compression.
This modern and expensive material is durable and strong. The release form of polymer insulation is roll or in the form of soft sheets. It can be used to treat walls, basements, foundations, roofs and broken outdoor structures.
The installation of insulation with polymer materials requires preliminary application of primers to the base of the roof, floor, basement walls and other treated areas or the creation of an air ventilation layer. Otherwise, due to low vapor permeability due to water vapor pressure, the membrane may tear away from the base.
Carrying out work using the fusion method
Advice. When installing using the free-laying method on a foundation slab, it is recommended to first lay a layer of geotextile fabric with a surface density of 300 g/m². Geotextiles are laid with an overlap of 100 cm along all edges. On vertical surfaces, the top edge is mechanically secured.
For free lay installation you will need:
- Hot air welding machine or gas torch - for welding seams.
- Seaming machine - for processing longitudinal overlap seams.
- Stitching roller - for processing end overlap seams.
The procedure for carrying out work on horizontal surfaces:
- Lay the membrane with an overlap of 10 cm. Joints along the length should be offset by 1 m from adjacent rolls.
- Weld the seams with a gas torch or hot air welder, then roll them.
- To seal the seams on top, it is recommended to fuse IKOPAL bandage tape and also roll it.
The procedure for carrying out work on vertical surfaces:
- Lay the waterproofing in successive rows from bottom to top, rolling out the sheet vertically. The overlap along the edges of the canvases is 10 cm.
- At a distance of 5 cm from the top edge, mechanically secure the rolled bitumen-polymer membrane with a metal strip with dimensions 4 x 40 x 600 mm. Secure the strip with self-tapping screws or dowel nails in increments of up to 25 cm.
- Weld the seams with a gas torch or hot air welding machine, from bottom to top, rolling with a roller.
- Install the next highest row of waterproofing sheet with an overlap of 20 cm on the previous one. Move adjacent rows of fabric so that there are no cross-shaped joints.
- If the canvas is laid on a vertical surface higher than 3.5 m, then it must be additionally secured with metal strips and self-tapping screws (dowel nails) every 3–3.5 m.
- To eliminate leaks on the mounting metal strips, fuse a bandage tape with an overlap of 10 cm, rolling it with a roller.
- To seal the seams, also fuse bandage tape onto them, rolling it with a roller as necessary.
- Secure the material above ground level to the wall of the building with metal strips and self-tapping screws (dowel nails). Apply bandage tape to the metal strip that overlaps the wall to prevent moisture penetration. Roll it with a roller.
Advice. Before fusing the ULTRANAP roll material onto the insulated surface, it is recommended to apply a primer. Fusing should begin after it has completely dried.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to attach polystyrene foam to the foundation
When fusing rolled waterproofing for the foundation, you will need a gas burner.
Work order:
- Fuse the fabric with an overlap of 10 cm. The joints along the length of the rolled material should be staggered with an offset of adjacent rolls by 1 m.
- Lay the second layer similarly to the first, with offset overlaps relative to the seams of the first layer.
- When installing on vertical surfaces, fuse from bottom to top, excluding cross-shaped joints. If necessary, secure the waterproofing sheet with metal strips and self-tapping screws (dowel nails). To seal metal strips, fuse banding tape over them with an overlap of 10 cm.
- Secure the material above ground level to the wall of the building with edge strips or metal strips and self-tapping screws (dowel nails).
Note! When properly fusing rolled waterproofing (or when welding seams), bitumen mass should flow out evenly 5–10 mm along the edge of the sheet
Range of materials
Waterproofing is a necessary condition for protecting surfaces from moisture. It extends the service life of structures and structures. Moisture protection work is in demand at all stages of construction work. The installation of adhesive waterproofing involves applying moisture-resistant roll products to a base exposed to moisture. Previously, roofing felt was mainly used for these purposes as the cheapest option. But it contains a fragile cardboard base, so you should give preference to modern rolled products with high mechanical strength. Material classification:
- By the number of layers. Cloths can be single-basic or multi-basic, impregnated with organic substances of the coating-free and coating type. Protective layers are applied on both sides of the base, which ensures the durability of the products. Baseless materials are produced by rolling using a rubber-bitumen binder, additives and fillers (Izol, Brizol).
- According to the type of base. The cardboard version (roofing felt, glassine, rubemast) is made from roofing cardboard impregnated with low-viscosity bitumen. Products made of polyester and polyester (isoplast, isoelast) have increased elasticity, high strength, and are not subject to rotting. Fiberglass and fiberglass are treated with a bitumen-binding composition, obtaining hydroglass insulation, fiberglass.
- By type of binder. There are polymer waterproofing (self-adhesive films, carmizol on glue, bernizol and elastomer geomembranes), bitumen-polymer products (mostoplast, isoplast, bikroplast), bitumen-containing insulation (hydroizol, hydrostekloizol).
In addition, materials for adhesive waterproofing are distinguished by the type of finishing coating into foil, film, sprinkled and by installation method - glued to bitumen mastic, welded with a gas burner, fixed to mechanical fasteners.
On a note! All types of waterproofing materials are suitable for protection against moisture using adhesive technology. But when choosing a product, you need to take into account the angle of the surface and the nature of the work - internal or external.
Types of adhesive waterproofing for foundations
Builders distinguish three types of work for adhesive waterproofing.
- Rolled materials (roofing felt, glassine, glass insulation). They are glued in 2-3 layers using mastic or adhesive.
- Hot fusing method . The working part of the material is heated by a gas burner. When a certain temperature is reached, the bitumen polymer layer melts, which ensures reliable fastening of the waterproofing layer to the concrete base.
- Film membranes . These are diffuse-type materials with high vapor permeability, which prevents the formation and absorption of moisture in foundations. Helps remove steam from interior spaces.