Roof waterproofing is a necessary part of the work when installing a roofing pie. Its function is to protect interior spaces and structures from filtering water from the outside space, as well as from condensation from the lower surface of the enclosing material.
Stains and wet spots on the ceiling of the upper floor are not uncommon in the domestic housing stock. 80% of leaks occur as a result of gross errors in the installation of roof waterproofing, 20% - due to its improper operation.
The main purpose of roof waterproofing
The surrounding air is filled with water vapor, which, with daily fluctuations in temperature and humidity, precipitates in the form of condensate. In summer, the phenomenon is observed in the form of dew on the grass, and in autumn or winter - frost.
The roof is a barrier between street air and the attic. As a rule, it is made of materials with low water absorption. Water vapor condenses on the surface and forms droplets. In the absence of waterproofing, they freely fall into the under-roof space, penetrating into the insulation and elements of the rafter system.
This causes a deterioration in their properties, leads to rotting of the wood, corrosion of metal fasteners, and a decrease in the service life of the supporting frame.
Violation of the integrity of the coating occurs due to the negligence of builders. Failure to comply with the technology, in which the joints and interfaces of roofing elements become leaky, is the main reason for the appearance of leaks during rain or melting snow.
Utilities are installed on the roofs of houses - chimneys, ventilation ducts, antennas, and water intake funnels are installed. Improper execution of complex components leads to the appearance of gaps and cracks. If they are not tightly sealed, water very quickly penetrates into the attic and then further.
Under-roof waterproofing protects internal structures from leaks, which take time to eliminate.
Types of flat roofing
There are several main types of flat roofing; their differences come from the final purpose of the roof. Depending on the type of roof, the location of different roofing elements, such as thermal insulation, waterproofing, etc., is determined in different places.
Main types of flat roofing:
- Traditional non-exploited - It is assumed that such a roof will not be constantly in use and there will not be recreation areas or other areas where people will constantly be located. This design is not designed to withstand constant loads and mechanical stress; its main task is to protect the building from the penetration of water, moisture and other weather elements.
- Exploitable - This type of roofing is designed so that terraces or other exploitable areas can be built on it, where people and various objects (equipment, sofas, tables, etc.) will constantly be located.
- Inversion roofing – This type of construction is suitable exclusively for flat roofs. With this type of structure, some traditional layers are swapped, namely thermal insulation and waterproofing. Thermal insulation is laid not under, but on top of the waterproofing. Inversion technology is used to protect the finishing layer from temperature fluctuations.
Types of waterproofing materials for roofing
The construction industry produces a variety of materials for roofing waterproofing - rolls, pieces, films, mastics, pastes, emulsions. For their production, bitumen, tar, rubber, oils, tar and polymers are used. To seal seams, sealants, sealing gaskets, and cords are produced.
Waterproofing materials must meet the requirements of SNiP I-B.25-66. Properties are regulated:
- mechanical strength;
- waterproof;
- water absorption;
- temperature resistance;
- fire resistance;
- elasticity;
- crack resistance;
- frost resistance;
- weather resistance;
- biostability.
Painting or coating materials are subject to solubility and adhesion requirements.
Recommendations on the choice of material and method of roof waterproofing are contained in the construction project, which takes into account the design solution, type of coating, climatic zone, and economic feasibility.
The most common types of roofing waterproofing and sealing materials by method of application:
- Coating materials – bitumen, hot bitumen mastics and emulsions, asphalt mixtures, cold mastics, shotcrete mixtures. Application method: surface treatment with a semi-liquid composition in 2-4 layers. Each subsequent one is placed on a well-dried base. Used to insulate flat roofs.
- Rolled based on roofing cardboard, fiberglass, polyester, aluminum foil or baseless, fiber reinforced. These are roofing felt, Rubimast, Hydroizol, Bikrost, Isoplast, Folgoizol and others. The materials are laid on the surface of the ceiling treated with an adhesive composition, the joints are glued or welded. In pitched structures, the sheets are spread horizontally, starting from the bottom, with an overlap of 100-200 mm, depending on the angle of inclination, and secured with a construction stapler to the rafter legs.
- Piece materials – soft tiles made of bituminous polymers in the form of tiles or sheets. The basis is cardboard and fiberglass. Decorative effect is achieved by spraying mineral chips. The roofing material is laid over a continuous deck, secured with roofing nails, self-tapping screws, or fused.
- Film – sealed or vapor-permeable polymer materials. The former are used for waterproofing cold roofs that do not have thermal insulation. It is advisable to use vapor-permeable membranes for attic spaces insulated with fiber insulators. Cone-shaped pores prevent the passage of moisture in one direction and do not impede it in the other. The most popular are ordinary, perforated or reinforced polyethylene films, polypropylene, and glassine. They are produced under the names Ekoplast, Ondutis, Folder, Utahfon, Logicruf.
- Fused - roll materials based on pure or modified bitumen, on the inner surface of which a layer of polyethylene is applied. It is melted with a special burner and the panel is pressed tightly to the base. The result is a coating without joints and cracks. Domestic insulators - Technoelast, Uniflex, Bipol, Bikrost. Bicroelast.
Types of roofing waterproofing
Today, there are several roofing waterproofing materials that vary in application method and can be used with a variety of roof designs. These common types of waterproofing include:
- Rolled materials, including the well-known roofing felt and its modern varieties.
- Film roofing waterproofing is the cheapest type of material that is widely used in private housing construction. Coating materials are represented by various liquid mastics.
- Diffuse waterproofing is an innovative material that is distinguished by excellent workmanship, but at the same time has a high cost.
Roll waterproofing
Roll waterproofing combines an affordable cost, providing the roof of the house with the necessary protection from moisture, and is durable.
In addition to the roofing felt that we all know well, you can use glass roofing felt and euroroofing felt . The advantages of this type of waterproofing include the following: durability of the coating; high reliability; affordable price.
The disadvantages include the difficulty of installing roll waterproofing . It is necessary to lay ordinary roofing felt on bitumen mastic. In its technology, such work is vaguely reminiscent of wallpapering walls. When using euroroofing felt, there is no need to pre-treat the roof base with mastic, which makes repair and construction work somewhat easier. After laying, the material is heated with a gas burner, which allows the roll insulation to be glued together and subsequently eliminate the possibility of leaks.
Waterproofing roofing mastic
Various mastics can be used with flat roofs, which combine ease of use, effectiveness and affordable cost.
Currently, you can find on sale various types of liquid roof waterproofing , the materials of which differ in their composition, characteristics and cost.
The advantages of mastics include the following:
- Ecological cleanliness.
- No shrinkage.
- Resistant to aggressive environments.
- Solidity of the completed waterproofing.
Having a number of advantages, such liquid waterproofing still has one significant drawback, namely durability. Even the highest quality mastics last no more than 6 years , after which it is necessary to raise the roof and renew the waterproofing layer.
Film materials
Durable, inexpensive polyethylene films are often used today for roof waterproofing. The popularity of this insulator can be explained by its ease of installation and affordable cost.
The simplest type is polyethylene film , the use of which will require the installation of a double ventilation layer in the roof. The joints of the film floors can be sealed with tape or special equipment can be used for this work, which reliably solders the material, ensuring that there are no leaks along the seam.
On sale you can find the latest generation of film waterproofing, which is durable and has an adhesive layer that is attached to the base of the roof, which simplifies repair work. At the same time, we note that such modern film insulation has a high cost, which leads to a significant increase in the budget for repair work.
We can recommend that budget-conscious homeowners pay attention to waterproofing films with anti-condensation coating . This protective layer is located on the wrong side, allowing the material to accumulate moisture, preventing water from flowing down onto the insulation. The water droplets accumulated by the insulator gradually evaporate or roll down without getting inside the roof.
Diffuse waterproofers
Diffuse films and membranes are today considered the most high-tech and modern insulators.
They are able to allow moisture to pass through from inside the roof, but at the same time do not allow it to penetrate from the outside , which protects the thermal insulation used and the roof from possible leaks.
The following types of diffuse membranes can be found on sale:
- Pseudo-diffuse films that have a low degree of vapor permeability. Their advantages include affordable cost. This material is used primarily on cold roofs and attics.
- Diffuse membranes with normal vapor permeability. Membranes can be used to construct an attic and a warm roof. The only place where it is not recommended to use diffuse membranes is in dusty attics, where the porous coating can become clogged, which impairs the performance characteristics of the waterproofing.
- Superdiffuse three-layer membranes are designed specifically for use in harsh conditions; they are not afraid of significant temperature changes and retain their performance characteristics for a long time.
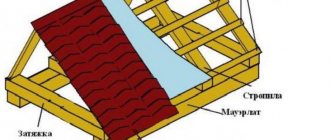
Waterproofing pitched and flat roofs - features and differences
Waterproofing inclined and flat surfaces is fundamentally different. In the first case, water rolls off the roof under the influence of gravity. The main task is to get rid of condensation that forms on the underside of the coating, as well as to protect joints and interfaces.
They use film or roll materials that are attached to the rafters. The roof sheathing is mounted on top, and roofing sheets or tiles are laid on it. This design allows condensation to flow over the surface of the waterproofing, and the gap serves to ventilate the under-roof space.
Flat roof waterproofing uses a different technology. To prevent rain or melt water from accumulating, a slight slope of 1.5-5% is created. It allows liquid to flow over the surface towards internal or external drainage funnels. The purpose of insulating such a roof is to ensure maximum integrity of the coating and sealing of junctions.
The base is carefully prepared, leveled, and treated with primers to improve the adhesion of the surface to protective coatings. Then pasting, coating or built-up waterproofing is performed.
The final stage is the laying of roofing material in pitched roofs or the installation of a ballast layer of gravel to protect the waterproofing on flat roofs (if necessary).
Waterproofing flat roofs
Separately, we note methods of waterproofing roofs that are almost flat - the angle of inclination does not exceed 5%. These are standard roofs of apartment buildings and private outbuildings. Waterproofing of such surfaces is usually carried out using self-leveling, coating, spraying and welding materials.
Welded waterproofing
The weld-on waterproofing is laid overlapping and then melted using burners. A fairly cheap way to completely protect the roof, but dealing with complex seam sealing and open flames is not the most pleasant.
Until recently, roofing felt and glassine were used as roofing insulation, the functionality and durability of which are questionable. But flammability is without a doubt. But today, roll roofing materials are used in two types: polymer and bituminous. Polymer coatings are characterized by a lower cost of coating and relative lightness.
Rolled waterproofing materials can be used on flat roofs or roofs with a slight slope. And a new modification of roofing felt, Euroroofing felt, is actively gaining popularity. This material is made from bitumen, polymer materials and synthetic rubbers. For comparison: in ordinary roofing felt the base is cardboard, but in euroroofing felt there are already synthetic fabrics, which, you must agree, is much stronger. And in order to make the euroroofing felt more durable, a multi-colored coating of mineral chips is additionally applied to it.
Spray waterproofing
Coating, pouring and spraying waterproofing materials create a complete, unbreakable membrane on the roof, with excellent qualities and practicality. But such waterproofing requires special equipment.
Powder insulation is also popular - these are mixtures based on synthetic resins, cement, plasticizers and hardeners. Such mixtures are sold in dry form, and you need to mix them at the work site.
More modern liquid waterproofing is water repellent. These are mixtures based on silicic acids, silicones and organic solvents. The main task of such waterproofing is to be absorbed into the concrete surface and thus provide complete protection against leaks. This material completely repels water, but at the same time – you will be surprised! - still breathing. The only disadvantage of such waterproofing is that after a couple of years the top layer washes away its important elements and begins to “fear” water. That is why such waterproofing is now more actively used for vertical roof surfaces of complex structure.
Coating waterproofing
Modern bitumen waterproofing of flat roofs is no less popular than more innovative solutions. Significant advantages play a role here: reliability, ductility, strength, softness and absolute resistance to temperature changes and any precipitation. Bitumen-polymer and bitumen materials for waterproofing roofs are good primarily because they create a multi-layer structure with a durable synthetic base - fiberglass or polyester fabric.
Basically, bituminous materials are divided into two main types:
- SBS-modified materials with Styrene-Butadiene-Styrene. This waterproofing perfectly withstands changing seasons and low temperatures.
- APP-modified materials with APP polymers. This waterproofing has high heat resistance.
For snowy Russia, of course, the first option is more preferable.
Special mastics - plastic waterproofing materials - are made from bitumen for waterproofing roofs. To do this, liquid bitumen is simply mixed with polymers and mineral fillers. This includes bitumen-rubber mastic, bitumen-polymer mastic, primer, and bitumen-emulsion. And these mastics are cold and hot. We recommend that you work with the first type, because... Hot materials require specialists. Not to mention the restrictions. For example, bitumen-based waterproofing materials cannot be used under metal tiles.
Mounted waterproofing
Sometimes, in special cases, even on a flat roof you have to try conventional film waterproofing:
Laying process
Installation of waterproofing film on a pitched roof is carried out according to the following scheme:
- vapor and heat insulation device;
- alternate laying of panels across the rafters, starting from the eaves of the slope;
- gluing seams, securing each layer with a stapler.
Installation of each upper waterproofing sheet is carried out with an overlap of at least 10 cm on the lower one. Carefully isolate joints, valleys and valleys.
The process of fusing or gluing waterproofing on a flat roof includes the following steps:
- surface preparation;
- sealing joints with ready-made fillets or made from mineral wool boards, cement-sand mortar;
- primer or mastic treatment;
- gluing or fusing the first panel using a torch, using material without sprinkling;
- installation of subsequent ones with an overlap of 80 mm in the longitudinal direction, 150 mm in the transverse direction, the joints should be spaced apart;
- laying the top layer, protected from external influences by sprinkling.
Particular attention is paid to the insulation of junctions, fastening of the roofing carpet to vertical structures, and complex assemblies of communication outlets to the roof.
Preparatory work
Before laying films on pitched surfaces, a rafter system must be installed, and steam and thermal insulation must be laid.
Preparation of flat roof surfaces is more complex and includes:
- leveling, creating the necessary slope using cement-sand screed;
- installation of fillets, water intake funnels with sealing of joints;
- drying the base, cleaning and removing dust;
- checking the moisture content of the screed - for cement-sand screed the indicator should not exceed 4%, for asphalt concrete - 2.5%;
- priming the horizontal base and vertical surfaces with a bitumen primer to the height of the material.
Recommendations from experts
When installing roof waterproofing with your own hands, you should listen to the recommendations of specialists:
- When laying films, be sure to leave a ventilation gap of 2.5-5 cm between the waterproofing and insulation, as well as in the ridge and cornice for the escape of water vapor. This does not apply to superdiffusion membranes, which are mounted directly on the thermal insulation.
- Superdiffusion films help remove moisture vapor from the insulation, while simultaneously preventing their penetration inside. And a reflective coating applied to some materials protects the attic from overheating. This is especially important for attics.
- In pitched roofs, when installing waterproofing, it is important to leave a slight sag of the anti-condensation film between the rafters. This additionally helps drain condensate and ventilate the insulation.
- Rolled materials based on modified bitumen are stronger, more elastic and durable than traditional roofing felt or roofing felt. Therefore, when choosing, you should give preference to more modern waterproofing materials.
Installing reliable roof waterproofing will protect the insulation, rafter system and ceiling from the destructive effects of water in the form of condensation or leaks. During construction, when the main covering has not yet been installed, a temporary roof is installed using insulation to protect structures and materials from getting wet.