Drafting
The positive aspects of aerated concrete do not in any way affect the success of the construction process.
In order for the idea to build a bathhouse from aerated concrete to be successful, it is necessary to think through each stage of the construction process. To do this, it is necessary to draw up a project. This is what you will have to focus on when carrying out activities at the construction site. Many experts note that creating a project for such a structure from scratch is quite a serious task. Not all architects can cope with its successful implementation. Therefore, a more reasonable solution would be to use a ready-made outline plan, to which changes are made in accordance with the customer’s preferences.
When drawing up a project for a bathhouse made of aerated concrete, the following important points must be present in this document:
- Dimensions of the object.
- Layout. It is also necessary to indicate the dimensions of individual rooms. In relation to a bathhouse, the design must include the dimensions of a steam room, a rest room, as well as a vestibule and a bathroom.
- Type of foundation used.
- Method of installation of furnace equipment, its main technical characteristics and location option.
- Features of communications supply. It is necessary to describe in detail how the ventilation system and chimney will be installed.
When the design work is completed, you can proceed to the preparation of the materials necessary for construction work. Naturally, you should also think about purchasing the necessary tools that will allow you to carry out the necessary activities efficiently and quickly. The main material for the construction of such a bathhouse, of course, is aerated concrete blocks. In addition to them, you will need:
- dry cement;
- adhesive for aerated concrete;
- ladle or carriage for adhesive composition;
- reinforcing bars;
- roofing felt;
- rubber hammer;
- hacksaw;
- sand;
- grater;
- level.
When choosing a material, you should not purchase cheap blocks. You need to understand that the lower their price, the less correct the shape will be. And this affects the quality of the work performed. Of course, aerated concrete should not have defects in the form of chips and cracks. Otherwise, you can immediately forget about the dream of building a reliable structure.
Stages of internal insulation
Taking into account the specifics of such a room as a bathhouse, experts recommend carrying out internal thermal insulation work when using any material, be it gas silicate or expanded clay concrete blocks.
It's best to start from the floor. To do this, the base must be covered with a layer of slag, preferably glass wool. The insulation must be at least 30 cm high. Next, a reinforced expanded clay concrete screed is laid, on which ceramic tiles can be laid. This type of flooring is ideal for a bathhouse and will help significantly reduce heat loss from the room.
After this, you can proceed to insulating the bathhouse from the blocks from the inside. Aerated concrete is considered a very warm material, so in most cases it does not require additional insulation. However, when it comes to a bathhouse, you should take care that moisture does not get on the walls. To do this, you need to carry out thermal insulation work.
Expanded clay concrete is porous and does not accumulate moisture. It retains heat well, but insulating a bathhouse made of expanded clay concrete blocks from the inside is still worth doing.
The first stage of the work is the sheathing, which should consist of wooden slats 5 cm thick. Then mineral wool, foam plastic or basalt insulation is laid. For additional waterproofing, you need to use foil film or aluminum foil. Particular attention should be paid to the tightness of the joints.
The last stage of insulating a bathhouse made of gas silicate blocks from the inside will be the installation of finishing materials. Often, wooden lining is used for this, which looks good in a bathhouse and creates an additional feeling of comfort. If this particular material is chosen, it is worth creating an air gap between the wooden slats and the heat-insulating material. Experts recommend mounting the lining in a horizontal position. This will make it easy to change the lower layers, which in any case will become unusable due to moisture.
As for the work on the ceiling, everything happens in the same way as insulating the walls. The same materials can be used, that is, polystyrene foam, mineral wool. First of all, it is necessary to make a wooden sheathing, which will hold the insulation.
Here it is necessary to take into account such a point as very high temperatures. As you know, the main heat is collected at the top. That is, in the bathhouse the temperature near the ceiling can be very high. For this reason, it is necessary to carefully select materials that will not deteriorate from overheating.
Insulation technology
Regardless of the type of material chosen as insulation, the following technology should be followed in the process. First of all, the floor is insulated, then the walls are equipped and at the final stage the ceiling is completed with materials.
The specifics of insulation presuppose the beginning of its use already at the construction stage, when builders use additional materials to protect the foundation and base.
Attention! It is important to use components that can easily withstand temperature changes, exposure to the environment, and are not subject to rotting and decay
Insulation of a bathhouse made of foam blocks from the inside
Useful video
In the video, pay attention to the explanation of why a bathhouse, unlike a residential building, is usually better insulated from the inside:
Internal insulation of walls made of foam blocks begins with filling the frame. Its function is perfectly performed by boards or slats with the indispensable condition of having enough indentation to accommodate the insulation. It is advisable to leave small holes at the top of the wall. They are called vents, promoting additional ventilation. Windows are equipped with shutters or plugs are used to plug them during bathing procedures. The rest of the time it is recommended to keep them open. As a result, moisture will not accumulate and the walls will remain dry.
After the frame is stuffed, the material chosen as insulation is attached to it. Depending on the choice and specifics, it can be fixed with nails, dowels, or simply inserted into the gaps. As already noted, it is desirable to use a component that has protective properties against rotting. Today, jute felt has the best performance on this point.
The most important step in insulating bath walls is vapor barrier. It must be used in two rooms, namely the washing room and the steam room. Without steam insulation, concrete and foam blocks will not be able to withstand increased exposure to moisture, not to mention maintaining the desired temperature, and will begin to deteriorate over time.
Along with the already mentioned foil and materials created on its basis, mirror film helps to isolate steam well. When laying the material, tension should be avoided by joining its elements to each other or by overlapping installation. Vapor barrier is relevant for the steam room and washing room; the dressing room and rest room can do without it.
After waterproofing the walls, they cover them with boards. This is the final stage of internal thermal insulation. It involves the use of antiseptics. Being applied to the boards they protect them from mold, mildew, bugs and other typical troubles.
External insulation
The outside of the baths is insulated using the ventilated façade technique with the necessary air gap. Foam plastic, jute felt and mineral wool have proven themselves well as materials here. The main selection criterion here is cost. In terms of its importance, external insulation in a bathhouse is significantly inferior to internal insulation, and it is left for later, and sometimes (if the climate and region allows) it is not used at all.
The floors and ceilings in the bathhouse are necessarily insulated, forming a single protective environment, without which the process cannot be considered complete.
Photo
So, if you master the technology, insulating a bathhouse from foam blocks is quite easy. The main factor here is the competent choice of material and its proper arrangement, and the emphasis is on internal work. If you have time and desire, you can do the whole process yourself. If for one reason or another this is not possible, it is enough to contact a specialist. In any case, the owner will have at his disposal a warm and comfortable bathhouse, always ready to welcome everyone into its arms.
Distinctive technology for insulating baths made of expanded clay concrete
Table of characteristics of block and foam concrete materials:
| Expanded clay block | Gas silicate block | Foam concrete |
| Strength kgssm 2 |
- No process of decomposition and rotting.
- Fire-resistant material (facilitates use for ceiling insulation).
- Good sound insulation.
- Frost resistance.
The advantage in the technology of insulating a bathhouse made of expanded clay concrete blocks is the strength of the material. The expanded clay block does not crumble and perfectly holds the entire structure in the wall. Heat absorption is less than that of gas silicate and foam concrete products, and the thickness of the expanded clay block allows you to avoid applying a plaster layer. The lack of moisture absorption also does not oblige bathhouse owners to carry out external finishing work.
A bathhouse can maintain vigor and strength in a person, giving spiritual and physical health and a boost of energy, and high-quality thermal insulation of the bathhouse will provide all the conditions for lovers and gourmets of the Russian steam room.
Visiting a bathhouse is a very pleasant and healthy pastime. In order for this lesson not to be overshadowed by anything, you should carefully think through all the stages of work even in the process of planning the bathhouse project. One of the most important stages of work is the insulation of the bathhouse. If everything is done correctly and efficiently, the bathhouse will heat up quickly, retain heat well, and fuel consumption will be significantly less than when heating an uninsulated bathhouse. You can read the instructions on how to insulate a brick bath here.
Proper insulation
The microclimate inside the bathhouse depends on what material the bathhouse itself is made of. Accordingly, the design and materials for insulating a bathhouse from the inside also differ depending on the original material of the bathhouse built.
The process of step-by-step insulation of a bathhouse from the inside depends, first of all, on the material from which the walls are made. In any case, there are basic standard insulation works that apply to any bathhouse:
- Waterproofing walls;
- Construction of the sheathing (depending on the type of insulation chosen);
- Vapor barrier;
- Finishing the walls with finishing material.
Types and methods of insulating a bathhouse from the inside
- Insulation of a bathhouse made of blocks from the inside. Block building materials, such as foam blocks and cinder blocks, have a porous surface, due to which they are endowed with excellent thermal insulation properties. And yet, in the cold season, a bathhouse made of blocks will freeze, so it should still be insulated. In this case, it is recommended to use mineral wool, fiberglass or foam, which are then covered with a vapor barrier if we are talking about a steam room. Read the instructions on how to insulate a bathhouse with foam on this page.
- Insulation of aerated concrete baths from the inside. When constructing a frame for thermal insulation, a gap must be provided between the wall and the frame and good ventilation must be ensured. To do this, special openings are left at the top and bottom of the building, which must be closed during bath procedures, and open during drying of the room. Next, the selected thermal insulation material is attached to the frame, a board is placed on top, then a vapor barrier and a finishing board on top of it, preferably made of aspen or cedar. If you follow this design, then the problem of wall freezing simply will not arise.
- Insulation of a frame bath from the inside. The very structure of a frame bath involves laying thermal insulation into its “skeleton”, and the insulating technology of this type is called “Canadian”. In this case, mineral wool is used, which will make the frame bath energy-saving, unlike foam plastic. Thus, insulation boards are placed in each compartment of the frame and are necessarily covered with hydro- and vapor barrier. Afterwards, all that remains is to cover the walls with finishing material, such as wooden lining. Experts also recommend using a mixture of sawdust and wood chips with lime as insulation for a frame bath.
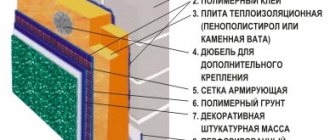
Numbers 1 and 3 indicate hydro- and vapor barrier materials. Number 2 is the thermal insulation material, number 4 is the finishing material of the walls.
The brick bathhouse is insulated with mineral wool slabs, on top of which foil-foamed polyethylene foam is attached, which enhances the thermal insulation properties of the main insulation and protects it from moisture.
It is recommended to insulate a bathhouse made of blocks with mineral wool or fiberglass, which are fixed to a pre-prepared wooden frame.
Insulation from the inside
Mineral wool is very popular among insulation materials; it is produced by processing mineral stones. This material has excellent thermal insulation characteristics, has a high thermal conductivity coefficient, is fire resistant, environmentally friendly and durable.
Features of different materials for insulation
Bathhouse premises are divided into types depending on the internal microclimate. The washing room, steam room and combustion chamber have high humidity and temperature, and the rest room and dressing room have normal conditions.
The following insulation is used for bathhouse premises:
- jute felt;
- mineral wool;
- expanded clay;
- Styrofoam.
The materials are intended for different rooms, because... differ in properties and characteristics. When choosing, the hydrophobicity of the insulation and the ability to release harmful substances when heated are important.
Jute felt
Jute felt
Natural fiber from the plant of the same name is used in production. Natural resins protect the threads from rotting; the material is durable, environmentally friendly, and has a uniform density throughout the mass. Polyester fibers are used for bonding, which impart elasticity.
Mineral wool
Mineral wool
For production, rocks, glass, and blast furnace waste are used, which are melted in high-temperature chambers and form fibers.
There are different types of mineral wool:
- glass wool;
- stone wool;
- slag.
Glass wool absorbs moisture less than the other two types, but is also used in bath rooms in combination with steam protection. Mineral wool reacts steadfastly to the action of chemicals and, in the event of a fire, forms a barrier to the spread of flame. Getting wet reduces the heat-shielding properties.
Expanded clay
Expanded clay
Porous insulation is made from clay shale as a result of firing. Subsequent processing results in material with different bulk densities. Expanded clay can weigh from 150 to 850 kg/m3.
Environmentally friendly insulation is divided depending on shape and size:
- crushed stone;
- gravel;
- sand.
The first two varieties have a large, medium and small fraction. Sand and small-sized elements are not used to insulate a cinder block bathhouse from the inside, because... Due to the high density in the mass, it conducts internal energy faster. Large and medium granules are used, which require the construction of a special frame into which the material is poured.
Styrofoam
The material belongs to the group of foamed polymers. Gas occupies a large volume in the mass, so the structure contains isolated balls glued together during the production process. Thermal insulating properties are due to the low conductivity of the internal elements.
Glass wool
Glass wool is inferior to basalt wool in thermal conductivity. Internal insulation of bathhouse walls is impossible with it, because... glass wool cannot withstand heating above 400 degrees. In addition, when this material wears out, it begins to emit an unpleasant odor, which is completely unacceptable for a bathhouse.
Materials for wall insulation
Let's take a closer look at insulating materials.
Minvata
Mineral (basalt) wool is very popular and is most often used for external and internal insulation of bathhouse walls. Excellent heat retention, very durable and noise-reducing properties. This absolutely non-flammable material can withstand heating up to 1000 degrees Celsius.
Mineral wool is harmless and biologically neutral, i.e. resistant to the formation of mold and fungi.
Glass wool
Glass wool is inferior to basalt wool in thermal conductivity. Internal insulation of bathhouse walls is impossible with it, because... glass wool cannot withstand heating above 400 degrees. In addition, when this material wears out, it begins to emit an unpleasant odor, which is completely unacceptable for a bathhouse.
Felt
Jute felt is of organic origin and is very good for insulating walls both inside and outside. It retains heat perfectly, is durable, resistant to mold, and has the ability to remove excess moisture from the room.
Expanded clay
Expanded clay is a dry heat-insulating substance consisting of light, tiny balls of baked fusible clay. Used for filling horizontal elements of a bath structure - for example, a ceiling or floor.
Styrofoam
Expanded polystyrene (foam plastic) - ideal for external insulation of bathhouse walls made of foam blocks. Typically, external walls are covered with polystyrene foam, fixed with glue and fasteners, and then plastered (or other decorative material is used).
Do-it-yourself bathhouse made from blocks - material features
The standard layout of a bathhouse includes a dressing room, a steam room and a washing room. The structure is erected on a permanent foundation and is reliably thermally insulated.
Various building materials are used to build walls:
- frame panels. Despite their visual appeal, insulated sandwich panels do not allow steam to pass through well. Condensation concentrates in the room, causing accelerated decay;
- wooden beams or logs. This is a traditional material that provides comfortable conditions. However, it is expensive and susceptible to destruction under high humidity;
- brick. It is characterized by strength and durability. The costs of building a brick bathhouse are quite high, since brick walls need a massive foundation;
- concrete blocks. They have a cellular structure. They are distinguished by their low weight, increased volume, vapor permeability, increased thermal insulation characteristics, as well as an affordable price.
Drawing of a bathhouse made of blocks Let's consider the construction of a bathhouse made of blocks in more detail.
Step-by-step instructions for thermal insulation of a block bath
The insulation of a bathhouse made of blocks begins with the work on thermal insulation of the floor, which will help to significantly reduce heat losses. First, an insulating waterproof layer, in the form of slag or expanded clay, about 35 cm high is poured onto the ground. A layer of reinforced concrete screed is laid on top, on top of which, after drying, ceramic tiles are laid.
To insulate the walls of a steam room from the inside, you need to prepare the following materials:
- wooden slats;
- foil material;
- mineral wool slabs;
- dowels;
- bars for counter-lattice;
- construction tape.
To do the job well, you also need to prepare tools such as a drill, a hammer, a building level and a stapler.
Below is a detailed plan on how to properly insulate a bathhouse:
- Installation of vertical wooden sheathing on previously cleaned walls. The frame cells are filled with heat-insulating material.
- A vapor barrier is installed overlapping the insulating material, which is secured with a stapler and the joints are sealed with tape.
- Next, the counter-lattice is installed, which serves as a ventilating layer.
- At the last stage, finishing is carried out, usually using natural wood.
Polymer materials such as polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam are suitable for the dressing room and washing area. A frame is installed on the walls, followed by laying a layer of insulation. Next, the vapor barrier and finishing material are installed.
Insulating a bathhouse from foam blocks from the inside - video with detailed instructions.
Materials for insulating a bath made of foam blocks must meet a number of characteristics, including fire resistance, thermal conductivity, strength, environmental friendliness and sound insulation.
Advantages and disadvantages of buildings
Positive aspects of aerated concrete:
- Good heat retention. Since aerated blocks are covered with decorative panels and a facing composition on top, this figure increases further.
- Fast construction of the building.
- Low price of material.
- Lightness of blocks.
- Resistant to fire. Aerated concrete does not burn, which is important for baths.
- Immunity to chemicals.
Flaws:
- To improve the appearance of the building, interior and exterior decoration is needed.
- The internal microclimate is not as comfortable as in wooden buildings.
- Aerated blocks quickly absorb moisture, which leads to rapid destruction of the material. To prevent this, it is necessary to perform high-quality waterproofing.
It is important to prevent the blocks from coming into contact with the ground, as they will quickly become saturated with moisture.
Features of aerated concrete blocks
Often, aerated blocks are made from the following components: concrete, sand, water and gas, which is why the blocks take on a cellular appearance. For the construction of a bathhouse, rectangular blocks of autoclaved concrete are suitable (there are both autoclaved and non-autoclaved types of aerated concrete). U-shaped blocks are usually used for laying gaps in windows, doors or fixing ceiling slabs.
For internal partitions where masonry is required, blocks up to one and a half cm wide are used, but if these are external walls, blocks are taken with a width of two cm. The height of the blocks varies depending on the height of the desired building. The standard dimensions of gas blocks for the construction of a bathhouse are 600:300:250 mm. At the same time, moving huge blocks on your own will be difficult and difficult, so choose them of the optimal size for your construction. The thickness of the blocks is selected depending on the need to build a bathhouse: how often it will be visited, in the area with what climate it is being built, how many rooms are planned to be placed in it
It is especially important to take into account the climate, since the required thickness will be selected based on the typical air temperature. For example, in countries with an average climate, a wall thickness of 60-70 cm is suitable
But if this is an area with a northern climate, then the thickness should be at least 250 mm, and it is better to take 300 mm in order to fully ensure a comfortable stay in the future bathhouse.
In addition to the size of the blocks, do not forget to check their frost resistance when purchasing
This will be especially important for buildings where exterior finishing will not be carried out. The standard indicator is marked F35
After checking the specified parameters, pay attention to the following factors: Are the edges of the blocks neat and even? And also compare their color - it should be uniform. Both their structure and density should be homogeneous
It is also important that each block is the same size and matches the weight of other objects
How to insulate a foam block bathhouse from the inside – Construction and repair
A building made of foam blocks has many advantages: light weight and high thermal insulation properties.
But a structure made of this material requires mandatory cladding, both external and internal.
This is due not only to increased visual appeal, but also to the high porosity of the foam block.
That is why walls built from porous material need reliable waterproofing.
This issue is especially acute when finishing the inside of a bathhouse.
Today we’ll look at how to properly carry out waterproofing work and at the same time insulate a foam block bathhouse.
How to insulate the walls of a bathhouse made of foam blocks?
Previously, we already wrote about the construction of a bathhouse from foam blocks, where we examined several layout options and looked at how blocks are laid from this modern material, which has recently been gaining popularity in the construction of bathhouses. Foam blocks, unlike logs, beams or frame-panel structures, do not burn , do not support the spread of rot and mold, are not susceptible to woodworms and have high thermal characteristics.
In this publication, let's look at how to insulate walls made of foam concrete, what materials for insulation are best to choose, and how to make insulation in different rooms of a bathhouse.
Design features of bath walls
A special feature of the design of bath walls is the requirement for their thermal characteristics in combination with resistance to moisture, and in a steam room also resistance to elevated temperatures.
Moreover, unlike a country house, where at different times of the year a comfortable air temperature must be ensured with the least energy consumption, in a bathhouse the walls should retain heat only for the duration of its use, that is, periodically from time to time.
This allows you to reduce the amount of construction work by reducing the thickness of the wall and installing a stove of sufficient power that quickly warms up the room. It is believed that in a steam room the walls should be especially carefully waterproofed so that moisture from the room is not absorbed into the porous foam blocks.
This is partly true; the porous structure of foam blocks reduces their frost resistance, and if they get wet and subsequently freeze, such blocks can crack quite quickly.
A properly selected stove provides good draft, quickly “pumping” moist air outside the bathhouse.
And in order to expel humid air from the interior of the bathhouse to the street, after the bath procedures it is enough not to immediately put out the stove, but leave it to burn for another 15-20 minutes, throwing in 2-3 logs.
Insulation of a steam room made of foam blocks
You should take the most responsible approach to the choice of materials and insulation design in the steam room.
The insulation material should not emit toxic substances and withstand high temperatures well. Mineral wool can be an excellent choice.
Its advantages as insulation for a steam room include the following qualities:
- high value of heat transfer resistance;
- mineral wool does not burn;
- does not emit odor or harmful substances;
- does not support the spread of mold and mildew;
- not susceptible to being eaten by rodents and woodworms.
Mineral wool materials are perfect for insulating walls and ceilings in a steam room.
To lay heat-insulating material on the walls, wooden blocks with a thickness equal to the thickness of the insulation layer are hammered at intervals equal to its width.
Thermal insulation is rolled out between the bars, covered on top with a layer of vapor-waterproofing material (foil) and sewn up with clapboard.
To ensure air circulation between the insulation layer and the interior finishing, the lining is nailed onto an additional sheathing placed on top of the vapor barrier layer.
In general, the layers of the thermal insulation “pie” of foam block walls look like this:
Interior decoration of steam room walls
On top of the insulation, the walls of the steam room can be finished with any environmentally friendly material that does not emit any harmful substances when heated, and has good resistance to moisture and elevated temperatures. The most popular finishing is made from hardwood lining - linden, cedar, larch.
You can also use tile finishing, which is laid on GVLV sheets (for example, Knauf supersheet with a straight (PC) or folded (FC) edge). To glue tiles in a steam room, it is recommended to use:
- Plitonite “super fireplace” is heat-resistant, reinforced, for tiling walls in the area where the stove is installed and the chimney is laid.
- Knauf tile standard for gluing tiles to the shelf level.
- Knauf reinforced fixation “elastic” (“Flex”) for all other areas.
Comparison of baths made of aerated concrete and other materials
The main requirement for a bathhouse material should be the ability to retain thermal energy. A traditional Russian bathhouse is built from wood - timber or logs. There are also brick baths, which are considered less preferable due to the high thermal conductivity of the material and the high fuel consumption for heating the premises. Recently, there has been a fashion for baths made of aerated concrete, which has a successful set of working qualities:
- low thermal conductivity allows you to save and accumulate thermal energy;
- Gas silicate is lightweight and easy to work with. The construction of the bathhouse is quick and does not require the use of lifting equipment;
- unlike wood, aerated concrete does not rot (although contact with water is no less destructive for it);
- The cost of a bathhouse made of aerated concrete is low and allows you to save significant amounts.
It is not advisable to compare aerated concrete with brick or other piece elements - all dense building materials have high thermal conductivity and are uneconomical in terms of heating. Therefore, the main competitor for gas silicate is wood. It has a lot of advantages:
- is an excellent heat insulator and does not require insulation;
- has a considerable service life - there are baths that are 100 years old or more;
- the frost resistance of wood is practically unlimited, which fundamentally distinguishes it from other materials;
- environmentally friendly material, has a pleasant smell, creates a comfortable and attractive microclimate in the room;
- wood is a traditional material for building a bathhouse and is psychologically more preferable than other options.
However, wood has many disadvantages:
- tendency to rot;
- ability to burn;
- logs or beams are heavy, it is difficult to build from them without lifting devices.
In a number of indicators, aerated concrete and wood are almost identical. For example, density (500 kg/m3 for wood and D500 gas blocks), thermal conductivity (both have an indicator of 0.14 W/m·C), almost the same water absorption. At the same time, wood does not allow water vapor to pass through, and aerated concrete is able to “breathe,” which allows you to remove excess water vapor and protect the interior from the appearance of fungus and mold.
The only indicator by which wood is many times superior to aerated concrete is its ability to withstand pressure (439 kgf/cm2 versus 50 kgf/m2). However, the bathhouse is a low, most often one-story building. The weight of the walls cannot create excess pressure that is dangerous for the lower elements. Therefore, in terms of technical and physical indicators, aerated concrete and wood are approximately equal. The choice of material is made based on personal preferences and capabilities. Many owners of bathhouses made of aerated silicate blocks explain their decision simply - lifting one block weighing 25-30 kg is much easier than lifting a heavy log to a height of 2-3 m. Working with aerated concrete is easier and faster, and also cheaper. These considerations largely determine the choice of wall material. There is one more reason - the shrinkage of a wooden bathhouse takes much longer and occurs more intensively than the shrinkage of walls made of aerated blocks. The ability to quickly complete the finishing process and get a finished bathhouse attracts users and forces them to choose a cheaper and more practical material - aerated concrete.
Main stages of construction
The process of constructing a bathhouse from aerated concrete includes the following main stages:
Construction of bath walls
Laying the foundation. The optimal solution is a shallow strip base. Dig a trench 50-60 cm deep along the perimeter of the work site, lay a sand cushion made of crushed stone on its bottom, install formwork on top, pour cement mortar into the trench, install a reinforcement cage and leave the foundation to harden for 2-3 weeks. Then lay roofing material on the base.
Advice. The recommended thickness of aerated concrete bath walls is 0.3-0.5 m.
Roof installation. Mount a rafter system from edged boards on the upper stiffening belt. Cover it with a sheathing of beams, on top of which lay waterproofing. Then mount the roofing material on the equipped frame - any options are allowed here that meet your requirements in terms of aesthetics and functionality.
Insulation technology by type of block
Differences in the insulation technology of baths built from different types of blocks are directly related to the method of production of the blocks. The spread of block baths is caused by the reasons already stated, as well as the high speed of construction of baths from building blocks.
Insulation of a bathhouse made of foam blocks from the inside
The specificity is related to the porous (foamy) structure of the blocks, because they are produced by foaming cement or concrete with the addition of sand and a special protein agent. Porosity makes the blocks more susceptible to moisture penetration, thereby reducing the thermal insulation of the structure and its service life.
Useful video
Watch the video about insulating a bathhouse, there are useful explanations about the difference between insulation from the inside and outside:
Find out more: How to insulate a bathhouse from foam blocks: inside and out. Don't let the walls collapse.
Insulation of a bathhouse made of expanded clay concrete blocks from the inside
Expanded clay concrete blocks also have a porous structure, despite their production on a vibropress. They are among the high-quality and environmentally friendly materials. When a bathhouse is built from expanded clay concrete blocks, the insulation of the walls is similar to the thermal insulation of foam block walls.
Similar to foam blocks, they have a tendency to absorb moisture. Foil (including aluminum foil) and kraft paper work well as waterproofing. Foil is excellent as an additional shielding material.
Interior decoration and insulation of a cinder block bathhouse
Cinder blocks are distinguished by a very low price, which can hide various “fillings” of the block : from residues of the metallurgical industry to slag from coal combustion. They are most often made in a handicraft way. Therefore, blocks may differ in weight, thermal conductivity and other characteristics .
The popularity is also due to the fact that the blocks can be produced in different sizes. The insulation is similar to the insulation of a bath made of expanded clay concrete.
Interior finishing must be carried out while maintaining a ventilated gap. Wooden finishing materials are best suited: lining, block house, etc. Cover them with bath oil, and they will last a long time (they will protect against moisture, and as a result, prevent the appearance and development of rot). In addition, oil impregnation will emphasize the natural grain of the wood.
Insulation of a bathhouse made of gas silicate blocks from the inside
Gas silicate blocks have several gradations:
- category D800 and higher (high strength, but low thermal insulation);
- category in the range D500-D800 (average of both indicators);
- category D500 and below (characterized by low strength and high thermal insulation).
In addition, aerated concrete is a type of cellular block, that is, its structure contains air cells. But they are all hygroscopic. You can’t do without high-quality and reliable waterproofing. In addition, it is necessary to protect the blocks themselves from exposure to high temperatures, which can negatively affect their strength and durability.
Wall decoration
Aerated concrete is very good for building a bathhouse - it is the best thermal insulation material. But one of its drawbacks - absorbing moisture - can be eliminated by interior decoration. Waterproofing walls must be done correctly so that there is no obstruction to natural air circulation, and the walls do not crack after freezing.
The plaster finishing of a bathhouse made of aerated concrete should serve as a barrier and allow evaporation only to the outside.
Stages of finishing work:
When developing a bathhouse project made from aerated concrete blocks, it is necessary to take into account all the technical characteristics of this building material. By following all the rules of hydro- and vapor barrier, you can build a high-quality bathhouse from aerated concrete with your own hands, especially since experts recommend using this material, which retains heat well.
Pros and cons of aerated concrete baths
Let's start with the characteristics of aerated concrete structures. This information is extremely important, since its use during construction determines not only the service life, but also the indoor microclimate, which should be healthy in the bathhouse.
Aerated concrete is a non-flammable material, so if force majeure occurs, people will always be able to evacuate in time, and the structure will withstand the influence of extremely high temperatures.
The material is resistant to microorganisms, rot-resistant, and not attractive to insects and rodents.
With good protection from moisture, aerated concrete buildings can last indefinitely. This caveat is very important - the process of hydro and vapor barrier during the construction of a bathhouse is complex and technologically advanced.
The thermal conductivity of aerated concrete is on par with wood. With additional insulation, the room turns out to be especially energy efficient - the bathhouse will heat up quickly and cool down slowly.
Aerated blocks have high geometric accuracy and large dimensions, which allows the construction of buildings from it at high speed. Mastering masonry technology does not take much time; you can get down to work after good theoretical preparation. Particular attention should be paid to the foundation installation technology.
Aerated concrete is an environmentally friendly material; when heated, it does not release toxins, which is also important for a structure such as a bathhouse.
The low strength of the material means that masonry can only be done on a solid foundation. It is important to select the foundation correctly according to the type of soil on the building site in order to minimize shrinkage processes, which the gas block does not tolerate well even with mandatory reinforcement of the masonry rows.
A high level of water absorption (25%) indicates the need for high-quality hydro and vapor barrier in combination with insulation. When a gas block gets wet, it loses its thermal insulation properties; if it also freezes, then the ice formed in the pores of the material destroys its structure, reducing its strength.
The gas block can withstand up to 50 freeze/thaw cycles. The indicator is at a high level, but compared to a tree it is small. The use of insulation outside the room significantly increases the service life of the material.
You can also note the low cost of gas blocks, however, when drawing up an estimate, you need to take into account the costs of insulation, external and internal cladding of the material.
Bathhouse made of aerated concrete: photo
Let's look at the most common bathhouse designs. In most cases, land owners have to save space. Therefore, a bathhouse is often combined with a summer kitchen. You can also combine a bathhouse with a terrace or outdoor barbecue area.
If space allows, the relaxation room is made as spacious as possible. Here you can not only relax after the steam room, but also receive guests. It would be great if the design of an aerated concrete bathhouse (see photo) includes a bathroom and a small utility room.
To protect against precipitation, it is also advisable to immediately prepare the roof and install windows.
Bathhouse premises and requirements for their insulation
As a rule, a bathhouse consists of the following premises:
- dressing room (acts as a vestibule for cutting off cold air and a locker room);
- washing compartment;
- steam room
Some baths also have relaxation rooms with a pool or plunge pool for cooling after the steam room. However, this is not typical for small private baths, where they are limited to functional rooms.
The main and most important room of the bathhouse is the steam room. It should be insulated as much as possible, since this is where the highest temperatures are created. The next level of thermal insulation is considered to be the washing compartment, where it is necessary to ensure comfortable temperature conditions. The most moderate requirements are placed on the dressing room - in traditional Russian baths it is not insulated at all, although in winter the heat from the stove may not be enough. If we consider a bathhouse made of aerated concrete, insulating the dressing room becomes a necessity - humid internal air hitting the cold walls will cause abundant condensation, which is unacceptable. Therefore, internal insulation of a bathhouse made of gas silicate blocks should be carried out in all rooms, regardless of purpose and size.
It is necessary to insulate not only aerated concrete walls, but also floors and ceilings. This is done at different times - for example, insulation of the floors of a bathhouse should be done during the construction process, with the laying of thermal insulation material on the subfloor, under the screed and floor covering. Bathhouse ceilings are insulated after laying (or laying) the ceiling; this procedure can be performed during finishing work.
Object cost
Those who have decided to acquire their own bathhouse made of aerated concrete are, of course, concerned about the issue of cost. Here everything largely depends on how complex the project was chosen for implementation. The simplest bathhouse made of this material will cost 10,000 rubles per 1 sq. m. m.
It is possible to arrange a more complex structure on the site. However, in this case you need to be prepared for serious financial costs. After all, the cost of constructing a large facility with a complex layout increases significantly.
You can do the construction of a bathhouse on your own site yourself. This will significantly reduce the budget for the construction of the facility. In this case, the main expense item will be the purchase of building materials.
The construction of a bathhouse made of aerated concrete is a cheaper measure compared to the construction of a building for steam procedures made of wood. An object for rest and relaxation can be obtained subject to the correct choice of aerated concrete blocks. The building material from has proven itself well. The blocks of this manufacturer are characterized by a homogeneous composition, have the same geometric dimensions, and their surface is absolutely flat.
Aerated concrete is an excellent material for building a bathhouse. It has many advantages and very few disadvantages. This structure can be easily erected with your own hands. When performing work, you must act in accordance with the developed project. In this case, many mistakes that novice builders often make can be eliminated.
If the main points of construction technology from aerated concrete blocks are observed, it becomes possible to construct a reliable bathhouse.
For its long-term operation, it is necessary to correctly approach the issue of interior decoration. In this case, the procedures in it will bring joy, and the need for repairs will not arise soon.
Calculation of aerated concrete blocks and glue
| ROOM PARAMETERS: | |
| Wall height (m): | |
| External walls: | |
| Density class: | D350D450D500D600D700 |
| Wall length (perimeter) (m): | |
| Thickness of walls (block)*: | 100 mm.150 mm.200 mm.250 mm.300 mm.375 mm.400 mm.500 mm. |
| Area of door and window openings (m2): | |
| PARTITIONS: | |
| Density class: | D600D700 |
| Length of partition walls (perimeter): | |
| Thickness of partition walls: | 50 mm.75 mm.100 mm.150 mm.200 mm. |
| Area of door and window openings (m2): | |
| Total per room: | |
| APPROXIMATE VOLUME OF BLOCKS: m3 | |
| VOLUME OF PARTITIONS: m3 | |
| NUMBER OF GLUE BAGS**: pcs. | |
| * - wall thickness according to the project ** - glue consumption: 25 kg per 1 m3 of aerated concrete blocks with an adhesive layer thickness of no more than 3 mm and block size 600x375x250. |
Third stage: erection of walls
Aerated concrete blocks begin to be laid in the corners of the building, and a thread is pulled between them - this is a kind of guideline that will prevent uneven laying of the walls.
Professionals recommend that at the stage of laying the first row of blocks, using a building level, get rid of all the shortcomings that arose during the construction of the foundation itself
The first row is laid on the mortar and manually leveled so that the blocks do not move to the side in the future. Once the cement has completely dried, all dust is blown off, the blocks are cleaned and floated. The second, like all other rows, is laid on a special construction adhesive. The layer thickness should not exceed 7 mm.
Use the solution to secure the first row. For others, an adhesive solution is better
*If the bath area is up to 20 square meters, then the thickness of the walls is half a block; in other cases, the thickness of one block is sufficient.
The blocks are laid edgewise, try to make the joints as small as possible, because the thermal conductivity of the bath directly depends on this. Constantly check the evenness of the walls horizontally and vertically, if necessary, level the blocks using a rubber hammer.
A reinforced belt is laid on every fourth row. Using a hand cutter, a small trench is cut out in the blocks around the perimeter, the depth of which corresponds to the diameter of the metal rods. They must be completely immersed in the recess and filled with solution.
Laying is carried out with bandaging on the floor of the block using a glue carriage or ladle. And the installation itself must be done in such a way that the vertical seams of the previous row do not coincide with the next one. To arrange window and door openings I use a concrete belt made of U-shaped blocks. First, temporary support structures are installed under the openings, and then reinforcement is installed in the product tray and poured with concrete.
A wall chaser will help you easily cut grooves in blocks to create a reinforced belt
The last row of aerated concrete blocks is reinforced with a monolithic stiffening belt, which helps to more reliably fix the Mauerlat and other components of the rafter system.
Bathhouse project
At the first stage of work, it is necessary to choose a layout that is ideal for the owner. In this case, not only the quadrature is calculated, but the need to construct an attic is also taken into account. As a rule, the building will consist of two parts - a dressing room and a steam room. It is also convenient to combine a bathhouse with a common house.
The project with an attic can be expanded by adding an entrance to the second floor. If there is free space, a billiard room or guest room can be placed on it.
Laying aerated concrete blocks can only be done by experienced builders. It is prohibited to implement the project on soft ground. The structure cannot be heavy. In a bathhouse made of aerated concrete, a strip-type foundation should be used. Thanks to this, you can save up to 20% of the total amount.
At the first stage of creating a project, you should choose a location for the stove. It can be located on a common foundation or located separately. Only the brick version is placed separately due to its heavy weight. Any floor can withstand a metal stove.
Waterproofing a bathhouse made of aerated concrete will be expensive. You can reduce the cost if you use gas silicate or plaster. However, the finishing of the steam room can be made of lining. It is allowed to use linden or aspen.
At the first stage of creating a project, you should choose a location for the stove.
Main characteristics of the material
Aerated concrete blocks produced for sale, intended specifically for the construction of baths, are determined by the following indicators:
- frost resistance marking not lower than F 35;
- elements in the form of a P symbol (U-shaped) or rectangular. The first type is used to form door and window openings and ceilings;
- porous structure. It is typical for foam concrete, since when it is created, gas is added to the mixture of cement, water and sand;
- wall blocks have a heat-insulating layer applied;
- standard dimensions of elements are 60x30x25 cm or 62.5x24x25 cm. For laying external walls, blocks with a thickness of 20 cm are used, and partitions - up to 15 cm.
Appearance of aerated blocks A bathhouse built from aerated block in the middle zone should have walls with a width of 25-40 cm. For the northern regions, this value increases to 60 cm.
Do-it-yourself bathhouse made of aerated block
Before the start of construction, it is imperative to prepare all the necessary documentation. In order to find out the necessary documents, contact the registration chamber, where you will be given a detailed list of documents. Remember that if the bathhouse is built next to the house, then a new registration certificate for the house will be needed.
After collecting the necessary documents, determine the place where you will build your bathhouse.
Where is it advisable to build a bathhouse:
- At any elevation, this will help organize a simplified sewage system.
- So that the paths that lead to and from the bathhouse are surrounded by vegetation: bushes, trees with a dense crown.
- So that the building is no further than 20-30 m from the nearest body of water.
- It is advisable that the doors face the south side and the windows face the west.
Materials for insulating baths made of expanded clay concrete
Functionally, the bathhouse is intended for healing procedures, therefore all materials used for its construction must be of high quality and environmentally friendly. This also applies to insulation materials, whose action is aimed at maintaining a comfortable temperature in the premises. The negative impact of samples that are not resistant to its changes and emit harmful substances is greatly enhanced by the extreme “climatic” conditions of the bathhouse. Such materials are prohibited for use in such structures. Today, several excellent “candidates” claim to be insulation for bathhouses made of expanded clay concrete; we will list the most popular of them.
Mineral basalt wool for thermal insulation of baths
This fibrous insulation is obtained by processing basalt rocks. The natural composition of the insulation guarantees its absolute harmlessness. Sometimes the reputation of basalt wool is spoiled by some manufacturers who add slag impurities to it, trying to reduce the cost of their products. The insulation does not rot and is not edible by insects and rodents. This guarantees trouble-free service of the material for at least half a century. Regardless of its fibrous structure, the material is quite strong and has a “strength” indicator of 80 kPa. Basalt wool is a type of non-combustible material. It can easily withstand temperatures up to one thousand degrees Celsius. This material is used for external and internal insulation of baths, as it is produced in the form of rigid slabs, semi-rigid mats and soft rolls with varying densities of their structure.
Glass wool for insulating baths made of expanded clay concrete
The insulation has a fibrous structure, but is inferior to basalt wool in its technical characteristics. The material is made from broken glass with the addition of sand, dolomite, soda, etc. Having a thermal conductivity coefficient of 0.052 W/K*m, it has good insulating properties, but is completely unsuitable for internal insulation of a steam bath for the only reason: glass wool does not withstand the temperature regime over +450 degrees. Therefore, it is not recommended to insulate the area that is located in close proximity to the stove. Glass wool is used for thermal insulation of the attic and bathhouse roof, reducing the cost of this process by 20-30% compared to the use of basalt insulation.
Expanded clay for thermal insulation of baths
“Airy” expanded clay granules are obtained by quickly firing low-melting clay. This material is used in the form of backfilling the horizontal elements of the bath structure - the ceiling and floor. Various calibers of insulation in the form of gravel, crushed stone and sand are used in construction. The insulation effect is obtained from expanded clay when it is poured onto the surface in a layer of over 25 cm.
Polystyrene foam for a bath made of expanded clay concrete blocks
Bathroom insulation with this material is ideal for external wall surfaces. The facades of buildings are covered with polystyrene foam, and then they are plastered or covered with decorative finishes. It cannot be used inside bathhouses due to the harmful phenol fumes emitted by the foam and its flammability.
Jute felt
Jute felt
Natural fiber from the plant of the same name is used in production. Natural resins protect the threads from rotting; the material is durable, environmentally friendly, and has a uniform density throughout the mass. Polyester fibers are used for bonding, which impart elasticity.
The peculiarity of jute is that when it is hot, it does not release toxic substances into the surrounding space. Requires film vapor and waterproofing, since the fibers get wet when in contact with moisture.