Is ventilation needed in the attic?
It is impossible to use the attic as housing without ventilation. It is necessary to ensure normal air exchange. A person produces heat and produces moisture. Condensation forms on the surface of the walls. As a result, the insulation and roof suffer.
Expert opinion
Nikonorov Vladimir Alekseevich
Our expert. Specialist in the field of air conditioning and ventilation with 10 years of experience.
Ask a Question
If the attic is considered as a non-residential premises, it is also impossible to do without ventilation. People store things and the air stagnates. If you do not ventilate the attic space, favorable conditions for the proliferation of microbes are created on the walls, floor and ceiling.
Is ventilation of the attic floor necessary, and why?
It is imperative to install a ventilation system in the attic space, since it allows you to solve several very serious problems with the microclimate at once. At the same time, you can equip it yourself with a relatively small budget for work.
Consequences of lack of ventilation in the attic
Proper attic ventilation solves the following problems:
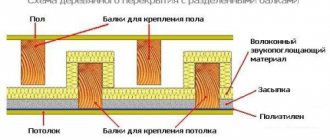
- Elimination of excess moisture and prevention of the appearance of dampness in thermal insulation (insulation) materials. That is, ventilation protects thermal insulation materials from wear and functional damage.
- A significant reduction in the likelihood of the appearance and accumulation of colonies of fungi and mold, which creates additional protection for wooden roofing items (and also protects the health of those living in the building).
- Protection against the entry of overheated air masses into the building during periods of extreme heat (heat) in the external environment (outside).
- Protection from moisture accumulation, and, as a result, protection from corrosive phenomena that can damage metal structures.
- Protection against the appearance of icicles under the eaves in winter (especially in severe frosts).
- Significant savings on electricity required for optimal heating of the attic during the winter and, sometimes, autumn periods (in general, during the cold season).
Hybrid type
On the attic floor it is possible to install hybrid ventilation. It provides natural suction. The system is maintained at low pressure. Cold air rises.
Scheme of natural ventilation in a private house and attic
The channels are installed in such a way as to ensure natural air draft. A special feature of hybrid ventilation is flow control. A mechanical regulator or a remote control unit is used.
According to environmental friendliness there is a division into classes:
- economy;
- standard;
- eco.
Hybrid ventilation uses filters to remove dust and allergens.
DIY attic roof ventilation in a private house
To make ventilation yourself, follow the plan:
- Roof markings.
- Openings through gables.
- Installation of valves.
- Fixing the pad.
If we describe the process in more detail, a drawing is initially drawn up. A standard three-channel circuit will do. You can mark them on the ceiling using a laser. When you have a tube in your hands, its diameter is taken into account. If the size is more than 50 mm, a standard drill is not enough.
Advice! To make a hole in the ceiling, a hammer drill is suitable.
Use the tool at high speeds, it is important that nothing interferes. When drilling, firmly fix the material. The attic can be made in layers:
- plastic;
- profile;
- insulation;
- roofing material.
When working with a hammer drill, it is better to know in advance about the presence of sheathing. The drill comes into contact with the metal and misalignment occurs. To install the purchased tubes, they are disassembled. Remove the umbrella and covers. A comrade from above fixes the workpiece, double-check the level. If the handset was not purchased from a cheap market, everything is already included in the kit.
The assistant’s task is to hold the workpiece; the lower part must be covered with sealant.
You shouldn’t skimp on the material; the excess can be cut off later. Standard ventilation comes with an overlay. Take the clamp and secure it to the tube. The option with a fan looks durable. It's better not to rely on natural cravings.
In a private house, the pipe is installed with a deflector. Otherwise it is called a cap, but in essence it is an aerodynamic device. Without a hood, all dirt and sewage from the street will enter the room.
Deflector types:
- open;
- closed;
- L-shaped;
- H-shaped.
An open round deflector is suitable for the attic.
Difference in layers
Proper ventilation of the room is carried out taking into account all the facts:
- environmental friendliness of the area;
- type of insulation;
- gusts of wind.
Manufacturers offer the following schemes:
- one layer;
- two layers.
The first option is standard; it includes only one layer of waterproofing film. Lay it on mineral wool. Membrane fabric can be used as insulation. At the exit, a person receives decent air permeability.
By the way, if you have a frame house, I recommend that you learn about how to do ventilation in it.
Double-layer ventilation involves placing a waterproofing film at several levels. The gap between the materials depends on the characteristics of the attic frame. The main mission is to provide a flow of fresh air. Start work after arranging the cornice. It is important to seal the cracks so that moisture does not accumulate anywhere. Grates are installed in the area of the tube.
Double-layer ventilation is primarily considered in houses with wooden floors. Mineral wool is used as insulation. If your budget allows, feel free to take membrane fabric.
Ventilation of the attic under-roof space
Ventilation of the attic under-roof space is arranged according to the principle of natural air circulation. It goes into special cavities between the waterproofing and thermal insulation in the eaves area. Removal is carried out on the upper part of the roof in the ridge area.
If the roof is made of metal tiles, it is convenient to use special ventilation valves. They are located in areas of inflow and exhaust. The valve design allows you to effectively solve several problems:
- let air through;
- provide protection from direct contact with precipitation, dust, dirt, insects, etc.
Another advantage of using valves for roof ventilation is ease of installation and reliability. The main thing is to make accurate calculations of the quantity and complete detailed drawings of the correct location.
In addition to the valve air exchange system for the under-roof space, an alternative option is used that does not require the use of special elements (valves):
- Holes (eaves vents) are made on the lower inner walls of the cornice with an outlet into the cavity between the insulation and the waterproofing layer. This is the supply part of the ventilation. Its location will provide protection from precipitation and wind.
- The exhaust part is equipped with a special ridge design, on the sides of which ventilation slots are left.
- Air enters through the cornice, rises to the top and exits in the ridge area, providing ventilation.
To remove air from the ridge area, a ridge aerator is installed. This part ensures high-quality air circulation while maintaining effective protection from precipitation. The ridge aerator is equipped with a grille that protects the interior of the roof from dust, dirt, leaves and insects.
A ridge aerator is necessary to remove air from the ridge area
- two-layer;
- single layer.
The single-layer view is described above. The double-layer design allows for better ventilation. This type of ventilation conventionally combines valve and cornice types of air exchange. Valves in the roofing material provide ventilation for the space between the roof and the waterproofing layer. The eaves (internal) type provides ventilation of the space between the waterproofing and vapor barrier.
The productivity of the ventilation system for the under-roof space depends not only on the structural elements, but also on compliance with quantitative and dimensional parameters. The number of valves and vents is determined by the design features and roof area.
There must be ventilation holes in each cavity between the rafters. The size and number of ventilation holes increases if the roof has a complex architecture with parapets, attics, and roof windows. All these structural elements significantly impair air circulation.
Mistakes of novice builders
Installing attic ventilation at random is not a tricky matter. The difficulty lies in the approach, since it is important to take into account a number of factors:
- site calculation;
- humidity level;
- material;
- tool;
- Preparation;
- plan.
At the stage of drawing up a diagram, it is clear how responsibly a person approaches the matter. Experts give advice regarding the location of the structure.
When selecting ventilation, the instructions from the manufacturer are considered separately. In some cases, it is not possible to securely fix the element. In fact, this is not a manufacturer's fault. During selection, many incidents also occur:
- selection of short tubes;
- small diameter;
- models without deflector.
The use of narrow ventilation in the attic is ineffective. The recommended parameter is 5 cm. Products up to 4 cm, first of all, do not allow the use of additional equipment. It is not possible to select a fan or filter for the system. The second point lies in the quality of exhaust air removal. In such houses, ventilation is used, but the room still looks damp.
Finishing is an important factor. The work is completed and a sufficient amount of sealant has been applied. Installing plumbs on the roof is a good solution. Aerators are selected from additional equipment. With their help, you can not only provide a flow of fresh air, but also repel insects so that they do not fly into the room.
Why do you need ventilation for the attic and roof?
In modern building architecture, the attic is understood as a floor in the attic space, the facade of which is completely or partially formed by the inclined or curved surface of the roof. This space can be residential or non-residential.
The features of the air exchange system depend on the nature of use and purpose. As in all other rooms, two types of ventilation are used:
- natural;
- forced.
In its natural form, air circulation occurs without the use of additional ventilated equipment. The movement of air flows is carried out due to the difference in temperature and pressure inside and outside the room. The disadvantage of natural ventilation is its dependence on weather conditions. In winter, the draft can be strong, and in summer, in hot weather, the functioning of air exchange may stop.
The forced ventilation system is based on the use of special ventilated equipment, which artificially organizes the circulation of air masses at the required speed. Forced air exchange is more effective than natural air exchange, but also has disadvantages - higher cost, constant energy consumption, dependence on the availability of electricity and the serviceability of the device.
The optimal option for air exchange equipment in the attic room is a mixed system. This design allows the use of natural and forced principles of air circulation depending on external factors.
The optimal type of ventilation for the attic is supply and exhaust. This system has two blocks:
- working on air flow;
- working to remove waste air masses.
It is worth distinguishing and separating attic ventilation and roof ventilation. These are two separate systems, each solving its own problems.
Ventilation of the attic roof is intended for:
- Ventilation of the under-roof space with insulation. Allows you to maintain an optimal level of humidity, protects against the development of fungi, bacteria, and mold.
- Maintaining a favorable microclimate and increasing the service life of the roof.
- Preventing the formation of condensation on the inner surface of the roofing material.
- Protecting roof elements from overheating.
- Ensuring uniform melting of snow, preventing the formation of ice and icicles on the eaves.
Attic ventilation is intended for:
- constant supply of fresh air;
- uninterrupted removal of waste air flows;
- maintaining favorable levels of humidity and temperature;
- reducing the overall cost of heating a home in winter and cooling it in summer.
The air exchange of the roof and the attic room is interconnected, but roof ventilation cannot perform the tasks of the attic system and vice versa.
Ventilation of the attic floor should not be combined with air exchange in residential premises.
Ventilation of the attic room should not be combined with the air exchange of other living rooms.
Exhaust from the toilet, bathroom, kitchen and other rooms is carried out using ventilation ducts that are led to the roof through the attic space.