If during the cold season the electric heater in the house does not turn off, and mold has grown on the walls due to dampness, it’s time to think about thermal insulation. The most popular method is to line the building with insulating material on the outside.
However, this option is difficult to implement in apartment buildings. Therefore, residents are wondering whether it is possible to insulate the interior with penoplex in order to retain heat in the apartment without disturbing the aesthetics of the building.
In an apartment, using penoplex you can insulate the walls, floor, and balcony.
General information
Previously, foam plastic and glass wool were used for such work. From the point of view of reliability, moisture resistance and heat-saving properties, there are no complaints about these materials. But glass wool contains harmful substances that, if inhaled, can cause an allergic reaction or poisoning. Extruded polystyrene foam developed in Russia is safe for health and easy to use.
There are products from different manufacturers on the market.
Preference should be given to brands whose names are associated with high-quality and reliable building materials.
The influence of production technology on harmful properties
During the creation process, expanded polystyrene is subjected to melting and chemical treatment. It acquires a dense, solid structure and loses its negative properties, i.e. stops releasing any harmful fumes into the air.
Unlike glass wool and low-grade foam, the material obtained as a result of extrusion is environmentally friendly and can be used in rooms where small children or allergy sufferers live.
Characteristics and properties of penoplex
Depending on the installation location, there are 4 types of penoplex: for roofing, for walls, for foundations and universal. The color is the same, orange, but the design is slightly different. For example, wall panels have ribs to improve adhesion to the surface.
The qualitative characteristics of penoplex make it a universal insulation material.
The main characteristics of the material include:
- low ability to absorb and retain moisture;
- no loss in thermal conductivity coefficient during the service life;
- resistance to water vapor;
- extended service life - up to 50 years;
- flammability class - G1-G4;
- Possibility of installation in rooms with temperatures -50…+75°C.
Features of extruded polystyrene foam
EPPS is a multifunctional insulation with a finely dispersed cellular structure, closed from most external influences. Its scope of application is very wide: from foundations to roofing systems, the maximum effect is achieved by thermal insulation of structures that are constantly in contact with soil and groundwater. These products are certified; the characteristics declared by the manufacturer are confirmed by numerous reviews and test results. But in comparison with conventional brands of polystyrene foam, extruded varieties are inferior in price; their use must be economically justified.
Properties and technical specifications
This insulation has a slab design, high geometric accuracy, stability of shapes and sizes, and a smooth surface (with rare exceptions for façade types). The internal structure is homogeneous, the diameter of closed gas-filled cells does not exceed 0.2 mm, almost all of its volume is occupied by air. This provides unique insulating abilities for both heat retention and sound absorption. Useful qualities remain unchanged for a long time - from 50 years and above.
The main operational and technical characteristics of extruded polystyrene foam include:
- Thermal conductivity coefficient varies from 0.03 to 0.035 W/m·K.
- Water absorption: within 24 hours within 0.4% of the volume, within 30 days – no more than 0.5. Moisture does not penetrate beyond the cells of the outer layer.
- Operating temperature range: -50 to +75 °C.
- Density, depending on the variety, ranges from 26 to 45 kg/m3; for some specialized brands of TechnoNikol it reaches 70.
- Compressive strength at 10% deformation - from 150 to 400 kPa for XPS for private, civil and industrial buildings (standard value - 250), 500-700 for varieties for transport and road construction. The limit of this bending characteristic is no less than 0.25-0.4 and 0.7 MPa, respectively.
- Frost resistance - up to 1000 cycles, compacted polystyrene foam can withstand repeated freezing and thawing and is best suited for insulating foundation structures.
- Vapor permeability coefficient – no more than 0.013 Mg/m·h·Pa. In practice, the value of this indicator tends to zero; reviews compare XPS with roofing felt in terms of air permeability.
- Flammability group: G4 and G3, the latter is recommended to be purchased if there are increased requirements for fire safety.
EPPS is resistant to biological threats and chemically inert to most reagents. The exception is a number of organic solvents: acetone, toluene, coal tars, which destroy the structure. Its UV resistance is weak; the material needs to be protected from rays in the same way as regular foam. The insulation meets sanitary standards and does not emit substances hazardous to health.
Key Benefits
Along with durability, soundproofing properties and ease of installation, extruded polystyrene foam has an impressive range of advantages.
Permeability
Foam plastic, like many other porous materials, allows moisture to pass through. There are voids inside it, which, when gradually filled with moisture or steam, worsen the thermal insulation properties. Penoplex is free from this drawback due to its integral structure. It absorbs moisture on average 10 times less than foam.
Mechanical strength and safety
The integrity of the structure affects the strength characteristics of penoplex.
With temperature changes and increased pressure during vertical installation, it does not crumble, deform or shrink like glass wool.
The flammability of the material is determined by the manufacturer. Depending on what processing was carried out during its creation, a class is assigned from low to high flammable. When purchasing, you should study the technical description of the goods and choose the safest one.
The undoubted advantage of penoplex is its non-toxicity.
The best option
A comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of various materials allows us to conclude that extruded polystyrene foam is the most suitable option for insulating rooms from the inside, loggias, floors, roofs, garages or verandas.
Medium thickness slabs (40 mm) are conveniently and securely installed on wood, concrete or brick surfaces.
Expanded polystyrene, extruded polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam - are they the same material?
Having looked at several Internet sources, one can assume that all three terms are synonymous and point to the same material. In fact, there are two materials in three titles. This is expanded polystyrene, which in everyday life is often called polystyrene foam.
And extruded polystyrene foam is foam that has undergone an additional processing step, extrusion.
These materials are similar in some characteristics, because they are made from the same raw material, polystyrene, but there are still differences. You can call them all foam plastic, but you need to clearly understand what kind of material we are talking about.
| Comparative characteristics of expanded polystyrene and extruded polystyrene foam | |||
| Indicators | Expanded polystyrene (foam plastic, PSB) | Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS) | Deviation (relative to EPS) |
| Thermal conductivity W/(m*K) | |||
| Hygroscopicity (% by mass) | |||
| Vapor permeability (Mg/(m*h*Pa)) | |||
| Density (kg/m3) | |||
| Flammability class (no dimension) | G2-G4 (depending on the manufacturer) | G1-G4 (depending on the manufacturer) | 1st class advantage |
Thermal conductivity is an indicator that reflects the ability of a material to transmit heat. The lower it is, the better. According to this indicator, PSB and EPPS do not have significant deviations.
Hygroscopicity is the ability to absorb moisture, it is lower in EPS, this is an advantage.
Vapor permeability is one of the controversial indicators. EPS has lower vapor permeability, which means that the material is less permeable to steam, that is, it does not remove residual moisture from the room well. Many people are afraid that the walls under extruded polystyrene foam do not “breathe” or “breathe” worse than under polystyrene foam. But in fact, a properly designed ventilation system, rather than the walls, is largely responsible for removing excess moisture. Only 0.5-3% of all moisture escapes through brick walls, for example. If they stop coming out through the insulated walls, this will not aggravate the problem with excess moisture.
We advise you to study - How to choose a high pressure washer - tips and tricks
The density of EPS is noticeably higher - this also speaks in favor of the insulation.
Flammability classes - the lower the number, the less combustible the material is. To insulate walls, polystyrene foam (extruded and non-extruded) is used only modified, containing fire retardants. Therefore, it cannot be said that any of the two materials burns better or worse: if compared by class, the ability to self-extinguish will be the same, or more precisely, equally useful for ensuring fire safety.
For reference: the marking of self-extinguishing foam is PSB-S.
Types of penoplex
Based on technical features and installation location, penoplex is divided into several types:
- “C” - used for thermal insulation of rooms on the ground floors, walls and room partitions;
- “F” - used for insulating foundations and basements;
- “K” - installed on roofing structures;
- “Comfort” - used when arranging loggias and free-standing small buildings;
- “45” (density 35 - 47 kg/m³) - suitable for thermal insulation of industrial structures, used at airfields and in civil engineering.
Main types of penoplex.
Material selection criteria
In order for the insulation to serve for a long time and justify the money invested in it, you should check whether it complies with GOST. Sometimes manufacturers offer products that are made in accordance with their internal requirements, but have passed state certification. In this case, the properties of the material may differ from generally accepted ones and require careful study.
It is recommended to touch the material before purchasing. It should be durable and not deform from light pressure. You should evaluate the storage location of the product, its protection from sunlight and possible exposure to solvents (acetone, petroleum products, etc.).
Before purchasing penoplex, you need to check the certificates of conformity.
The thickness of sheets of the same type must be the same. Pay attention to the fire safety mark. If, as a result of finishing, it is necessary to enhance sound insulation, the layer of material should be thicker.
Sequence of work
If you decide to carry out the insulation work yourself, it is better to study in advance and subsequently follow the procedure for performing the work.
Insulation calculation
First, determine the required thickness of the sheets. The final consumption of material depends on it. The thermal resistance indicator (in Russia it ranges between 3.5 to 4.6 m*K/W) is divided by the thermal conductivity coefficient of penoplex slabs. The second parameter is found in the characteristics of the material.
After taking measurements of the insulated room, the required amount of material is calculated. When purchasing, it is recommended to make a reserve of 10-15% to compensate for possible losses from defects or installation errors.
Required tools and materials
If work is carried out on the ceiling, scaffolding will be required to avoid the collapse of the structure. In all other situations, a basic set of tools is sufficient:
- drill with hammer;
- hacksaw;
- sandpaper or fine construction grater;
- laser level;
- hammer;
- spatulas of different sizes.
A set of tools for laying penoplex.
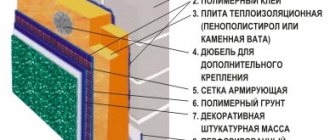
Auxiliary materials will also be required:
- dry adhesive mixture for installation of extruded polystyrene foam;
- polyurethane foam;
- reinforcing mesh;
- dowels;
- plaster mixture;
- finishing materials (lining, drywall, etc.).
Preparation
To ensure that the slabs are light, even and dense, before installation, you need to remove old finishing materials, dust and cement residues from the working surface. After this, using a building level, you should check the evenness of the structure and, if necessary, eliminate deviations with putty and plaster. Then the surface is primed.
When it stops being wet, you can start insulating it. There are 2 common installation methods: with glue and with the additional use of dowels. Whichever one is chosen, the slabs are first lightly rubbed with sandpaper to improve adhesion. The glue is applied with a spatula.
During installation, you can lay the finishing material directly on the insulation, or you can use a wooden frame and guides installed at the width of the slabs. The frame method will take more time, but is considered more reliable.
Walls
It is recommended to start insulation from the bottom corner of the wall, slightly moving the slabs at each next level. For reliable fixation, use bitumen mastic, cement-based glue, polyurethane glue or polyurethane foam.
The slabs are attached to the wall using special glue.
After applying glue to the slab, it should be pressed firmly against the wall and held for 1 minute, if necessary driving in dowels in the corners and in the center. The adhesive layer may be uneven, so it is necessary to check the evenness of the installation from time to time using a level. The gaps between the plates are filled with polyurethane foam. When it dries, the resulting mounds are cut off.
Ceiling
As in the case of walls, it can be mounted with or without a frame of guides. If a private house is being insulated, then penoplex is laid on the ceiling from the inside and outside, from the attic side.
In apartments there is no possibility to use the outside, so installation is carried out only from the room.
The ceiling should be cleaned, leveled and primed. Glue is applied to the material and pressed tightly to the installation site. For best fixation, dowels can be used. The seams are sealed with foam.
Finishing
Depending on what decorative material will be used to complete the finishing, the finishing of the insulation is carried out. Reinforcing plaster is applied under the tiles or wallpaper, then a reinforcing mesh is laid, plastered again (the second layer is at least 3 mm) and puttied.
It is permissible not to apply plaster under drywall. When the glue has dried, the decorative sheets are mounted to the insulating structure with self-tapping screws, and the joints between them are puttied. Before gluing wallpaper, the surface should be sanded.
Penoplex inside the walls
Frame houses
Penoplex as a wall insulation inside has found the most beneficial application. In a frame house, the main heat-protective function is assigned to it, and this material fully justifies itself. For internal wall insulation, the thickness of penoplex is calculated based on the climatic conditions of a particular region. For Moscow, for example, they recommend at least 100 mm for foam insulation inside the wall structure and 150 mm for the roof.
When building a frame house, to protect the insulation from external influences, it is usually necessary to have a vapor barrier film, a windproof membrane, and leave a ventilation gap for ventilation. Internal wall insulation with penoplex does not require their use during the construction of the frame. Almost zero moisture absorption, low vapor permeability combined with high density - these are the qualities of this insulation, thanks to which it itself protects from wind and moisture. However, despite the fact that there is penoplex inside the walls, it would not hurt to additionally insulate them from steam from the side of the room in order to definitely prevent the load-bearing wooden structures from getting wet. Penoplex insulation inside the wall, complemented by high-quality external finishing, ensures good heat retention in the house.
Well masonry
When constructing brick walls, well or layered masonry is often used. As the name suggests, it contains three layers. The first one is concrete, aerated concrete or brick, the middle one is penoplex as insulation and the outer one is brick. This entire structure is held together with embedded parts, and a straightening gap is left between the insulation and the external masonry, which is filled with dry sand. Well masonry is easy to use, durable and can significantly reduce the thickness of the brick structure.
Sandwich panels
It is worth mentioning separately about sandwich panels. Their use is a modern option for quick construction and at the same time internal insulation with penoplex, which is sewn between two profiled steel sheets. It can be other materials - OSB boards on one side and plastic “tile-like” on the other, etc. Panels with insulation are attached to the frame and can serve as both external walls of the building and interior partitions. In addition, sandwich panels with penoplex are used not only for internal insulation of walls, but also for external insulation and finishing of facades.
Insulation of walls with foam plastic from the inside begins with the construction of a wooden frame for the insulation. Wooden blocks are placed on the wall, at a distance of the width of the insulation slab minus 5 mm - the slabs must be mounted “by surprise”. The frame is constructed taking into account the location of windows, doors, heating registers, etc.
After fixing the frame, they begin to insulate the walls with polystyrene foam with their own hands: coat each slab with adhesive around the perimeter, retreating 1.5–2 cm from the edge and applying dot glue markers on the back side of the slab in an amount of at least 5 pieces on the back side of the slab.
The slab is placed into a cell of the frame and tapped with a mallet or the handle of a spatula. Work continues after the glue has completely dried, about 2–3 days.
The seams between the plates and the cracks must be carefully sealed with scraps of insulation, glue foam or polyurethane foam. It is impossible to use an adhesive composition for this purpose, as cold bridges will form.
The need to install vapor and waterproofing
If the outside of the wall is not insulated, experts recommend adding a vapor barrier.
Vapor barrier installation diagram.
This rule does not apply to wood and other “breathable” surfaces. The waterproofing layer is added when installing extruded polystyrene foam using a frame method, with lathing. At the same time, it is secured with a stapler, overlapping, after first checking that the layer is laid correctly. The joints are taped.
Common Mistakes
At first glance, insulation work looks simple. However, inexperienced installers may make mistakes that will not allow them to achieve the required thermal insulation properties or may lead to delamination of the material. Most often, beginners make the following mistakes:
- The number of slabs is calculated incorrectly or the design stage is completely neglected. There is not enough material or there is a large residue.
- During installation, moisture is allowed to enter the work surface or the temperature regime is not observed.
- The place and tools are poorly prepared. This increases the risk of damage to the insulation or contamination of surfaces.
- They do not follow a checkerboard pattern when laying them. Because of this, cracks form and heat escapes from the room.
- Glue is applied unevenly or in insufficient quantities.
- Neglect grinding the material. The grip becomes less strong.
- Do not fill the seams with foam.
To insulate the joints, fill them with polyurethane foam.
Myths and misconceptions
To finally decide to install extruded polystyrene foam, it is worth understanding the misconceptions and myths associated with it:
- Penoplex is harmful to health. It releases toxic substances into the environment. This is a myth, because during initial processing the material becomes denser and loses the ability to release any vapors.
- Walls must “breathe”, and insulation prevents this. This is a misconception, because if city houses were permeable to air or steam, they would be damp and cold in winter.
- Using insulation increases the risk of fire. This statement is partly true. To reduce the risk of fire, you should choose a material with a high class of fire protection and additionally treat them with protective substances.
Harm of extruded polystyrene foam to the body
The basis for the production of extruded polystyrene foam is the use of special installations - extruders.
This equipment operates on the basis of the extrusion principle, which consists in pressing the heated source material through narrow slots; during the production process, insulation is formed in the form of a plate.
The use of extruded polystyrene foam can cause significant harm to health. This material is especially harmful when exposed to high temperatures. This is due to the fact that toxic compounds such as:
- styrene vapor.
- Benzene fumes.
- Soot.
- Carbon dioxide.
- Carbon monoxide or carbon monoxide.
The combustion temperature of the main component of expanded polystyrene, styrene, is about 1100 degrees Celsius.
The use of this material in construction is also harmful to the environment; this is due to the long decomposition period of polystyrene, which is more than a hundred years. Over a period of intensive use of about 20-25 years, the material is subject to significant wear and tear, which leads to a significant increase in harmful effects on people.
During a period of intensive use, a polystyrene board releases up to 60% of decomposed styrene.
Styrene entering the surrounding atmosphere interacts with oxygen, which leads to the formation of highly toxic compounds such as formaldehyde and benzaldehyde.
The resulting toxins have a critical effect on the body of pregnant women.
The use of this material for insulating a house from the inside is unacceptable due to the high probability of toxic compounds being released from it.
Expanded polystyrene is recommended for external insulation of residential buildings and industrial premises.
Penoplex is best used for insulating the basement of a building, foundation and walls from the outside. It is permissible to use this material as insulation under roofing material on the roof if the attic space in the house is non-residential.
In residential premises it is allowed to use decorative elements made of polystyrene foam.
Reviews about penoplex insulation from the inside
Oleg, 36 years old, Moscow: “Our loggia runs along the room and kitchen. They installed double-glazed windows, but in the frosty winters we were still cold, and this also affected the temperature in the apartment. I read the reviews on the forum and chose penoplex for insulation. I did it myself by watching videos on the Internet. I liked that almost no debris was generated during operation. I installed all the slabs in a day, and another 2 were spent on clapboard cladding. The temperature on the loggia is now significantly higher than before insulation.”
Mikhail, 45 years old, Kaluga: “I bought an apartment on the ground floor with a rough finish. I decided to use thermal insulation when screeding the floor. The building materials store recommended penoplex. I was surprised by its weight - the slabs are light, but they are not so easy to break. I placed a reinforced mesh between the insulation and the cement. Installation went quickly and without any difficulties. And I didn’t have to spend money on electric heated floors.”
Advantages of foam insulation
At the same time, polystyrene foam has many advantages. It is resistant to moisture and practically does not absorb it, it has good thermal insulation properties. Mold and mildew will not appear on the surface of this material.
It is convenient to mount and cut. This is a lightweight material, which is very positive for any construction work. Another advantage of polystyrene foam is its low cost; it can be used for a long time and will not lose its properties.
It is able to withstand extreme heat and frost, and is not afraid of temperature fluctuations throughout the day. It has good soundproofing characteristics.
However, this material, like any other, has its drawbacks; its mechanical strength is limited. After installation, you need to provide additional protection against mechanical damage.
We advise you to study - Decorating a wooden house inside
This material practically does not allow air to pass through. It is easily destroyed when exposed to nitro paints and paint coatings that have this base.
Overall, this is a good choice of insulation for walls, especially for garages and outbuildings. It can also be used for residential premises, but it is advisable to do this in a climate that is not very cold. If you want to save on repairs and thermal insulation, then polystyrene foam is ideal.
In principle, you can do insulation yourself, but if you are not confident in your capabilities, then you can turn to professional specialists
In short, this is a good option for economical repairs, but it is not advisable to use it everywhere. Before starting work with it, study the maximum amount of information, consult with specialists; thermal insulation issues should be taken seriously, even if we are talking about non-residential premises.
More information about polystyrene foam and its use in construction can be found on the construction forum, where you will learn a lot of useful things.
The problem of insulating a private house or apartment has always had to be solved, and effective methods arose only after the advent of such building materials as polystyrene foam. Insulating the ceiling, floor and walls with its help allows you to retain heat in your home and at the same time save money.